Gemigliptin: An Update of Its Clinical Use in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1LG Life Sciences Ltd., R&D Park, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cydoctor@chol.com
- KMID: 2354607
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.5.339
Abstract
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors are a new class of oral antidiabetic agent for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. They increase endogenous levels of incretin hormones, which stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, decrease glucagon secretion, and contribute to reducing postprandial hyperglycemia. Although DPP-4 inhibitors have similar benefits, they can be differentiated in terms of their chemical structure, pharmacology, efficacy and safety profiles, and clinical considerations. Gemigliptin (brand name: Zemiglo), developed by LG Life Sciences, is a potent, selective, competitive, and long acting DPP-4 inhibitor. Various studies have shown that gemigliptin is an optimized DPP-4 inhibitor in terms of efficacy, safety, and patient compliance for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this review, we summarize the characteristics of gemigliptin and discuss its potential benefits in clinical practice.
MeSH Terms
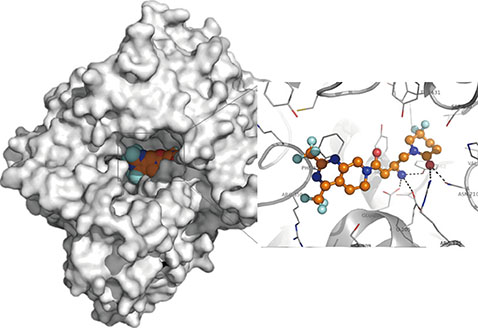
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Comparative Cardiovascular Risks of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Analyses of Real-world Data in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Bongseong Kim, Hae Sol Shin, Jinhee Lee, Hansol Choi, Hyeon Chang Kim, Dae Jung Kim
Korean Circ J. 2018;48(5):395-405. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2017.0324.Effect of gemigliptin on cardiac ischemia/reperfusion and spontaneous hypertensive rat models
Dae-Hwan Nam, Jinsook Park, Sun-Hyun Park, Ki-Suk Kim, Eun Bok Baek
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;23(5):329-334. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.5.329.Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors versus Other Antidiabetic Drugs Added to Metformin Monotherapy in Diabetic Retinopathy Progression: A Real World-Based Cohort Study
Yoo-Ri Chung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Hyeon Chang Kim, Sang Jun Park, Kihwang Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):640-648. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0137.Increasing Age Associated with Higher Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition Rate Is a Predictive Factor for Efficacy of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
Sangmo Hong, Chang Hee Jung, Song Han, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):63-70. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0253.Efficacy and Safety of the Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Gemigliptin in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Deep Dutta, Anshita Agarwal, Indira Maisnam, Rajiv Singla, Deepak Khandelwal, Meha Sharma
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):374-387. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.818.
Reference
-
1. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2014. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:Suppl 1. S14–S80.2. Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, Dagogo-Jack S, DeFronzo RA, Einhorn D, Fonseca VA, Garber JR, Garvey WT, Grunberger G, Handelsman Y, Henry RR, Hirsch IB, Jellinger PS, McGill JB, Mechanick JI, Rosenblit PD, Umpierrez GE. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm: 2016 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2016; 22:84–113.3. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. American Diabetes Association (ADA). European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1364–1379.4. Deacon CF. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a comparative review. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011; 13:7–18.5. Kim SH, Lee SH, Yim HJ. Gemigliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor: first new anti-diabetic drug in the history of Korean pharmaceutical industry. Arch Pharm Res. 2013; 36:1185–1188.6. Kim SH, Jung E, Yoon MK, Kwon OH, Hwang DM, Kim DW, Kim J, Lee SM, Yim HJ. Pharmacological profiles of gemigliptin (LC15-0444), a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016; 788:54–64.7. Lim KS, Cho JY, Kim BH, Kim JR, Kim HS, Kim DK, Kim SH, Yim HJ, Lee SH, Shin SG, Jang IJ, Yu KS. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LC15-0444, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor, after multiple dosing in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009; 68:883–890.8. Lim KS, Kim JR, Choi YJ, Shin KH, Kim KP, Hong JH, Cho JY, Shin HS, Yu KS, Shin SG, Kwon OH, Hwang DM, Kim JA, Jang IJ. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor LC15-0444 in healthy Korean men: a dose-block-randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending single-dose, phase I study. Clin Ther. 2008; 30:1817–1830.9. Kim N, Patrick L, Mair S, Stevens L, Ford G, Birks V, Lee SH. Absorption, metabolism and excretion of [14C]gemigliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, in humans. Xenobiotica. 2014; 44:522–530.10. Filippatos TD, Athyros VG, Elisaf MS. The pharmacokinetic considerations and adverse effects of DPP-4 inhibitors [corrected]. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014; 10:787–812.11. Deacon CF, Lebovitz HE. Comparative review of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and sulphonylureas. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:333–347.12. Baetta R, Corsini A. Pharmacology of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: similarities and differences. Drugs. 2011; 71:1441–1467.13. Nabeno M, Akahoshi F, Kishida H, Miyaguchi I, Tanaka Y, Ishii S, Kadowaki T. A comparative study of the binding modes of recently launched dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in the active site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 434:191–196.14. Morishita R, Nakagami H. Teneligliptin: expectations for its pleiotropic action. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015; 16:417–426.15. Omar B, Ahren B. Pleiotropic mechanisms for the glucose-lowering action of DPP-4 inhibitors. Diabetes. 2014; 63:2196–2202.16. Aroor AR, Sowers JR, Jia G, DeMarco VG. Pleiotropic effects of the dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors on the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014; 307:H477–H492.17. Jung E, Kim J, Ho Kim S, Kim S, Cho MH. Gemigliptin improves renal function and attenuates podocyte injury in mice with diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015; 761:116–124.18. Jung GS, Jeon JH, Choe MS, Kim SW, Lee IK, Kim MK, Park KG. Renoprotective effect of gemigliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic mice. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:211–221.19. Min HS, Kim JE, Lee MH, Song HK, Kang YS, Lee MJ, Lee JE, Kim HW, Cha JJ, Chung YY, Hyun YY, Han JY, Cha DR. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor protects against renal interstitial fibrosis in a mouse model of ureteral obstruction. Lab Invest. 2014; 94:598–607.20. Jung E, Kim J, Kim CS, Kim SH, Cho MH. Gemigliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, inhibits retinal pericyte injury in db/db mice and retinal neovascularization in mice with ischemic retinopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015; 1852:2618–2629.21. Jung E, Kim J, Kim SH, Kim S, Cho MH. Gemigliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, exhibits potent anti-glycation properties in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014; 744:98–102.22. Moon JY, Woo JS, Seo JW, Lee A, Kim DJ, Kim YG, Kim SY, Lee KH, Lim SJ, Cheng XW, Lee SH, Kim W. The dose-dependent organ-specific effects of a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor on cardiovascular complications in a model of type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0150745.23. Choi SH, Park S, Oh CJ, Leem J, Park KG, Lee IK. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition by gemigliptin prevents abnormal vascular remodeling via NF-E2-related factor 2 activation. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015; 73:11–19.24. Hwang HJ, Chung HS, Jung TW, Ryu JY, Hong HC, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Choi KM, Choi DS, Baik SH, Yoo HJ. The dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor inhibits the expression of vascular adhesion molecules and inflammatory cytokines in HUVECs via Akt- and AMPK-dependent mechanisms. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015; 405:25–34.25. Hwang HJ, Jung TW, Ryu JY, Hong HC, Choi HY, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Choi KM, Choi DS, Baik SH, Yoo HJ. Dipeptidyl petidase-IV inhibitor (gemigliptin) inhibits tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis and inflammation in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014; 392:1–7.26. Choi HY, Noh YH, Kim YH, Kim MJ, Lee SH, Kim JA, Kim B, Lim HS, Bae KS. Effects of food on the pharmacokinetics of gemigliptin/metformin sustained-release 50/1,000 mg (25/500 mg x 2 tablets) fixeddose combination tablet in healthy male volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 52:381–391.27. Kim Y, Kim U, Kim IS, Lee SH, Lee J, Kim DH, Yoo HH. Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of gemigliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor, in rats. Xenobiotica. 2014; 44:627–634.28. Shon JH, Kim N, Park SJ, Oh MK, Kim EY, Lee SH, Kim YH, Shin JG. Effect of renal impairment and haemodialysis on the pharmacokinetics of gemigliptin (LC15-0444). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:1028–1031.29. Zemiglo: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) Package insert. cited 2016 Aug 3. Available from: https://ezdrug.mfds.go.kr.30. Choi HY, Lim HS, Kim YH, Jeon HS, Kim MJ, Lee SH, Jung JH, Lee YK, Kim HJ, Bae KS. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of the DPP-4 inhibitor gemigliptin when coadministered with rosuvastatin or irbesartan to healthy subjects. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015; 31:229–241.31. Choi HY, Kim YH, Kim MJ, Lee SH, Bang K, Han S, Lim HS, Bae KS. Evaluation of pharmacokinetic drug interactions between gemigliptin (dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitor) and glimepiride (sulfonylurea) in healthy volunteers. Drugs R D. 2014; 14:165–176.32. Shin D, Cho YM, Lee S, Lim KS, Kim JA, Ahn JY, Cho JY, Lee H, Jang IJ, Yu KS. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interaction between gemigliptin and metformin in healthy subjects. Clin Drug Investig. 2014; 34:383–393.33. Kim SE, Yi S, Shin KH, Kim TE, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Yoon SH, Cho JY, Shin SG, Jang IJ, Yu KS. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetic interaction between the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor LC15-0444 and pioglitazone in healthy volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 50:17–23.34. Noh YH, Lim HS, Jin SJ, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Sung HR, Choi HY, Bae KS. Effects of ketoconazole and rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of gemigliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor: a crossover drug-drug interaction study in healthy male Korean volunteers. Clin Ther. 2012; 34:1182–1194.35. Rhee EJ, Lee WY, Yoon KH, Yoo SJ, Lee IK, Baik SH, Kim YK, Lee MK, Park KS, Park JY, Cha BS, Lee HW, Min KW, Bae HY, Kim MJ, Kim JA, Kim DK, Kim SW. A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase II trial evaluating the optimal dose, efficacy and safety of LC 15-0444 in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010; 12:1113–1119.36. Yang SJ, Min KW, Gupta SK, Park JY, Shivane VK, Pitale SU, Agarwal PK, Sosale A, Gandhi P, Dharmalingam M, Mohan V, Mahesh U, Kim DM, Kim YS, Kim JA, Kim PK, Baik SH. A multicentre, multinational, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gemigliptin (LC15-0444) in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:410–416.37. Lim S, Min K, Yu JM, Chamnan P, Kim ES, Yoon KH, Kwon S, Moon MK, Lee KW, Kim DJ, Kim M, Wongtanate M, Kim EY, Kim SH, Lee MK. No. 109: Efficacy and safety of gemigliptin/metformin initial combination therapy versus either as monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes. In : Oral presentation of 51st Annual Meeting of European Association for the Study of Diabetes; 2015 Sep 14-18; Stockholm, SZ.38. Rhee EJ, Min KW, Jang HC, Nam-Goong IS, Chung CH, Park JY, Bae HY, Kim DM, Baik SH, Lee MK, Kim BJ, Chang SA, Ahn CW, Kim YS, Yoon KH, Park KS, Kim HJ, Shivane VK, Sosale AR, Dharmalingam M, Gandhi P, Gupta SK, Pitale SU, Agarwal PK, Rais N, Mohan V, Mahesh U, Kim JA, Kim PK, Kim SW. No. 1128: Efficacy and safety of gemigliptin compared with sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone. In : Poster presentation of American Diabetes Association 72nd Scientific sessions; 2012 Jun 8-12; Philadelphia, PA.39. Kim SH, Yu J, Jang H, Song Y, Ahn K, Oh T, Lee H, Lee D, Kim J, Park TS, Jeong CH, Kim BJ, Han K, Park K. No. 1169: Efficacy and safety of gemigliptin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin and glimepiride. In : Poster presentation of American Diabetes Association 76th Scientific sessions; 2016 Jun 10-14; New Orleans, LA.40. Yoon S, Han B, Kim S, Han S, Jo YI, Jeong K, Oh KH, Park H, Park SH, Kang SW, Na KR, Jang Y, Kim SH, Cha D. GUARD Study. No. 804: Efficacy and safety of gemigliptin in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment. In : Poster presentation of 51st Annual Meeting of European Association for the Study of Diabetes; 2015 Sep 14-18; Stockholm, SZ.41. Raz I, Hanefeld M, Xu L, Caria C, Williams-Herman D, Khatami H. Sitagliptin Study 023 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2006; 49:2564–2571.42. Dejager S, Razac S, Foley JE, Schweizer A. Vildagliptin in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose study. Horm Metab Res. 2007; 39:218–223.43. Rosenstock J, Sankoh S, List JF. Glucose-lowering activity of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor saxagliptin in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008; 10:376–386.44. Barnett AH, Patel S, Harper R, Toorawa R, Thiemann S, von Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Linagliptin monotherapy in type 2 diabetes patients for whom metformin is inappropriate: an 18-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial with a 34-week active-controlled extension. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012; 14:1145–1154.45. Kadowaki T, Kondo K. Efficacy, safety and dose-response relationship of teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:810–818.46. Aschner P, Kipnes MS, Lunceford JK, Sanchez M, Mickel C, Williams-Herman DE. Sitagliptin Study 021 Group. Effect of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:2632–2637.47. Pi-Sunyer FX, Schweizer A, Mills D, Dejager S. Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007; 76:132–138.48. Rosenstock J, Aguilar-Salinas C, Klein E, Nepal S, List J, Chen R. CV181-011 Study Investigators. Effect of saxagliptin monotherapy in treatment-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009; 25:2401–2411.49. Del Prato S, Barnett AH, Huisman H, Neubacher D, Woerle HJ, Dugi KA. Effect of linagliptin monotherapy on glycaemic control and markers of β-cell function in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011; 13:258–267.50. DeFronzo RA, Fleck PR, Wilson CA, Mekki Q. Alogliptin Study 010 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and inadequate glycemic control: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:2315–2317.51. Hong S, Park CY, Han KA, Chung CH, Ku BJ, Jang HC, Ahn CW, Lee MK, Moon MK, Son HS, Lee CB, Cho YW, Park SW. Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 24-week multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:528–532.52. Goldstein BJ, Feinglos MN, Lunceford JK, Johnson J, Williams-Herman DE. Sitagliptin 036 Study Group. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and metformin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:1979–1987.53. Bosi E, Dotta F, Jia Y, Goodman M. Vildagliptin plus metformin combination therapy provides superior glycaemic control to individual monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009; 11:506–515.54. Jadzinsky M, Pfutzner A, Paz-Pacheco E, Xu Z, Allen E, Chen R. CV181-039 Investigators. Saxagliptin given in combination with metformin as initial therapy improves glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with either monotherapy: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009; 11:611–622.55. Haak T, Meinicke T, Jones R, Weber S, von Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Initial combination of linagliptin and metformin improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012; 14:565–574.56. Pratley RE, Fleck P, Wilson C. Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with alogliptin plus metformin versus either as monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, 6-month study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:613–621.57. Charbonnel B, Karasik A, Liu J, Wu M, Meininger G. Sitagliptin Study 020 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:2638–2643.58. Bosi E, Camisasca RP, Collober C, Rochotte E, Garber AJ. Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control over 24 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:890–895.59. DeFronzo RA, Hissa MN, Garber AJ, Luiz Gross J, Yuyan Duan R, Ravichandran S, Chen RS. Saxagliptin 014 Study Group. The efficacy and safety of saxagliptin when added to metformin therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes with metformin alone. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1649–1655.60. Taskinen MR, Rosenstock J, Tamminen I, Kubiak R, Patel S, Dugi KA, Woerle HJ. Safety and efficacy of linagliptin as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011; 13:65–74.61. Nauck MA, Ellis GC, Fleck PR, Wilson CA, Mekki Q. Alogliptin Study 008 Group. Efficacy and safety of adding the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin to metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Clin Pract. 2009; 63:46–55.62. Kim MK, Rhee EJ, Han KA, Woo AC, Lee MK, Ku BJ, Chung CH, Kim KA, Lee HW, Park IB, Park JY, Chul Jang HC, Park KS, Jang WI, Cha BY. Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, combined with metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 16-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015; 17:309–312.63. Hermansen K, Kipnes M, Luo E, Fanurik D, Khatami H, Stein P. Sitagliptin Study 035 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on glimepiride alone or on glimepiride and metformin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007; 9:733–745.64. Lukashevich V, Del Prato S, Araga M, Kothny W. Efficacy and safety of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with dual combination of metformin and sulphonylurea. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:403–409.65. Moses RG, Kalra S, Brook D, Sockler J, Monyak J, Visvanathan J, Montanaro M, Fisher SA. A randomized controlled trial of the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes and inadequate glycaemic control on metformin plus a sulphonylurea. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:443–450.66. Owens DR, Swallow R, Dugi KA, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and safety of linagliptin in persons with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by a combination of metformin and sulphonylurea: a 24-week randomized study. Diabet Med. 2011; 28:1352–1361.67. Vilsboll T, Rosenstock J, Yki-Jarvinen H, Cefalu WT, Chen Y, Luo E, Musser B, Andryuk PJ, Ling Y, Kaufman KD, Amatruda JM, Engel SS, Katz L. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010; 12:167–177.68. Kothny W, Foley J, Kozlovski P, Shao Q, Gallwitz B, Lukashevich V. Improved glycaemic control with vildagliptin added to insulin, with or without metformin, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:252–257.69. Barnett AH, Charbonnel B, Donovan M, Fleming D, Chen R. Effect of saxagliptin as add-on therapy in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes on insulin alone or insulin combined with metformin. Curr Med Res Opin. 2012; 28:513–523.70. Duran-Garcia S, Lee J, Yki-Jarvinen H, Rosenstock J, Hehnke U, Thiemann S, Patel S, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and safety of linagliptin as add-on therapy to basal insulin and metformin in people with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2016; 33:926–933.71. Rosenstock J, Rendell MS, Gross JL, Fleck PR, Wilson CA, Mekki Q. Alogliptin added to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes reduces HbA(1C) without causing weight gain or increased hypoglycaemia. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009; 11:1145–1152.72. Cho YM. New clinical experience of gemigliptin, the new DPPIV inhibitor. In : Proceedings of 9th International Diabetes Federation Western Pacific Region Congress & 4th Scientific Meeting of the Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes; 2012 Nov 25; Kyoto, JP.73. Rhee EJ, Lee WY, Min KW, Shivane VK, Sosale AR, Jang HC, Chung CH, Nam-Goong IS, Kim JA, Kim SW. Gemigliptin Study 006 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor gemigliptin compared with sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:523–530.74. Rhee EJ, Min KW, Jang HC, Chung CH, Nam-Goong IS, Bae HY, Baik SH, Shivane VK, Sosale AR, Dharmalingam M, Gandhi P, Gupta SK, Ahn JY, Bang KS, Lee MK. No. 111: Gemigliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy provides sustained glycemic control over 52 weeks and was well tolerated in patients with type 2 diabetes. In : Oral presentation of 49th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes; 2013 Sep 23-27; Barcelona, ES.75. Lee BW, Kim J, Park S, Jung C, Lee SH, Suh S, Lee W, Cho JH, Jang Y, Kim SH, Park CY. STABLE Study. No. 803: Effects of gemigliptin versus sitagliptin or glimepiride on glycaemic variability as initial combination therapy with metformin in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes. In : Poster presentation of 51st Annual Meeting of European Association for the Study of Diabetes; 2015 Sep 14-18; Stockholm, SZ.76. Yoon S, Han B, Kim S, Han S, Jo YI, Jeong K, Oh KH, Park H, Park SH, Kang SW, Na KR, Jang Y, Kim SH, Cha D. No. 1199: Efficacy and safety of gemigliptin in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment. In : Poster presentation of American Diabetes Association 76th Scientific sessions; 2016 Jun 10-14; New Orleans, LA.77. Marfella R, Barbieri M, Grella R, Rizzo MR, Nicoletti GF, Paolisso G. Effects of vildagliptin twice daily vs. sitagliptin once daily on 24-hour acute glucose fluctuations. J Diabetes Complications. 2010; 24:79–83.78. Rizzo MR, Barbieri M, Marfella R, Paolisso G. Reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation by blunting daily acute glucose fluctuations in patients with type 2 diabetes: role of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibition. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:2076–2082.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Multicentre, Multinational, Open-Label, 52-Week Extension Study of Gemigliptin (LC15-0444) Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Comprehensive Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Genetics in Diabetes Mellitus - Contribution to the Classification and Management
- Pharmacokinetic Equivalence of the High Dose Strength Fixed-Dose Combination Tablet of Gemigliptin/Metformin Sustained Release (SR) and Individual Component Gemigliptin and Metformin XR Tablets in Healthy Subjects
- Successful Management of Tardive Dyskinesia with Quetiapine and Clonazepam in a Patient of Schizophrenia with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus