J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Sep;52(3):254-256.
Treatment with Epidural Blood Patch for Iatrogenic Intracranial Hypotension after Spine Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. annn8432@gmail.com
Abstract
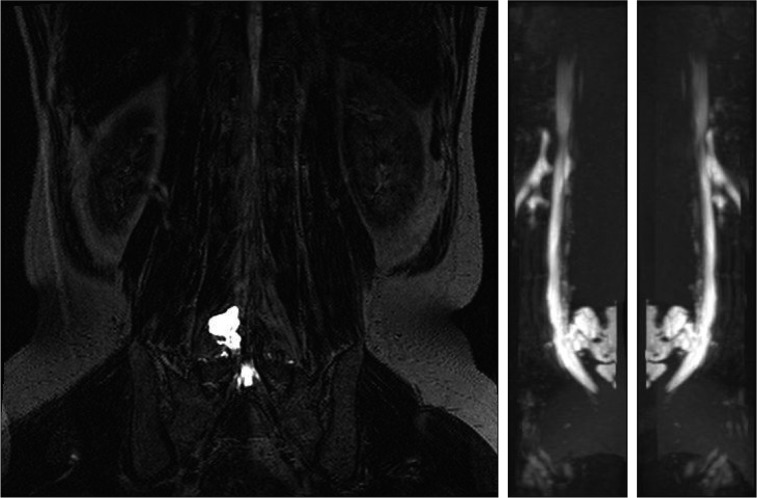
- Intracranial hypotension syndrome typically occurs spontaneously or iatrogenically. It can be associated with headache, drowsy mentality and intracranial heamorrhage. Iatrogenic intracranial hypotension can occur due to dural pucture, trauma and spine surgery. Treatment may include conservative therapy and operation. We report a case of a 54-year-old man who was successfully treated with epidural blood patches for intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage into the lumbosacral area after spine surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cammisa FP Jr, Girardi FP, Sangani PK, Parvataneni HK, Cadag S, Sandhu HS. Incidental durotomy in spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:2663–2667. PMID: 11034653.
Article2. Crawford JS. Experiences with epidural blood patch. Anesthesia. 1980; 35:513–515.
Article3. DiGiovanni AJ, Galbert MW, Wahle WM. Epidural injection of autologous blood for postlumbar-puncture headache. II. Additional clinical experiences and laboratory investigation. Anesth Analg. 1972; 51:226–232. PMID: 5062124.4. Goodkin R, Laska LL. Unintended "incidental" durotomy during surgery of the lumbar spine : medicolegal implications. Surg Neurol. 1995; 43:4–12. PMID: 7701421.5. Guerin P, El Fegoun AB, Obeid I, Gille O, Lelong L, Luc S, et al. Incidental durotomy during spine surgery : incidence, management and complications. A retrospective review. Injury. 2012; 43:397–401. PMID: 21251652.
Article6. Mokri B. Headaches caused by decreased intracranial pressure: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003; 16:319–326. PMID: 12858068.
Article7. Tafazal SI, Sell PJ. Incidental durotomy in lumbar spine surgery : incidence and management. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14:287–290. PMID: 15821921.
Article8. Usubiaga JE, Usubiaga LE, Brea LM, Goyena R. Effect of saline injections on epidural and subarachnoid space pressures and relation to postspinal anesthesia headache. Anesth Analg. 1967; 46:293–296. PMID: 6067279.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidural Blood Patch in Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A case report
- Intracranial Hypertension Following Epidural Blood Patch in a Patient With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Epidural Blood Patch to Treat Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Three Cases of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension ( SIH ) Treated with Epidural Blood Patch
- A Case of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension with Subdural Hematoma Mimicking Meningitis