J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Dec;55(12):1734-1738. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1734.
Surgical Outcomes of Levator Resection in Ptosis Patients with Deep Superior Sulcus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. hbahn@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2338953
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1734
Abstract
- PURPOSE
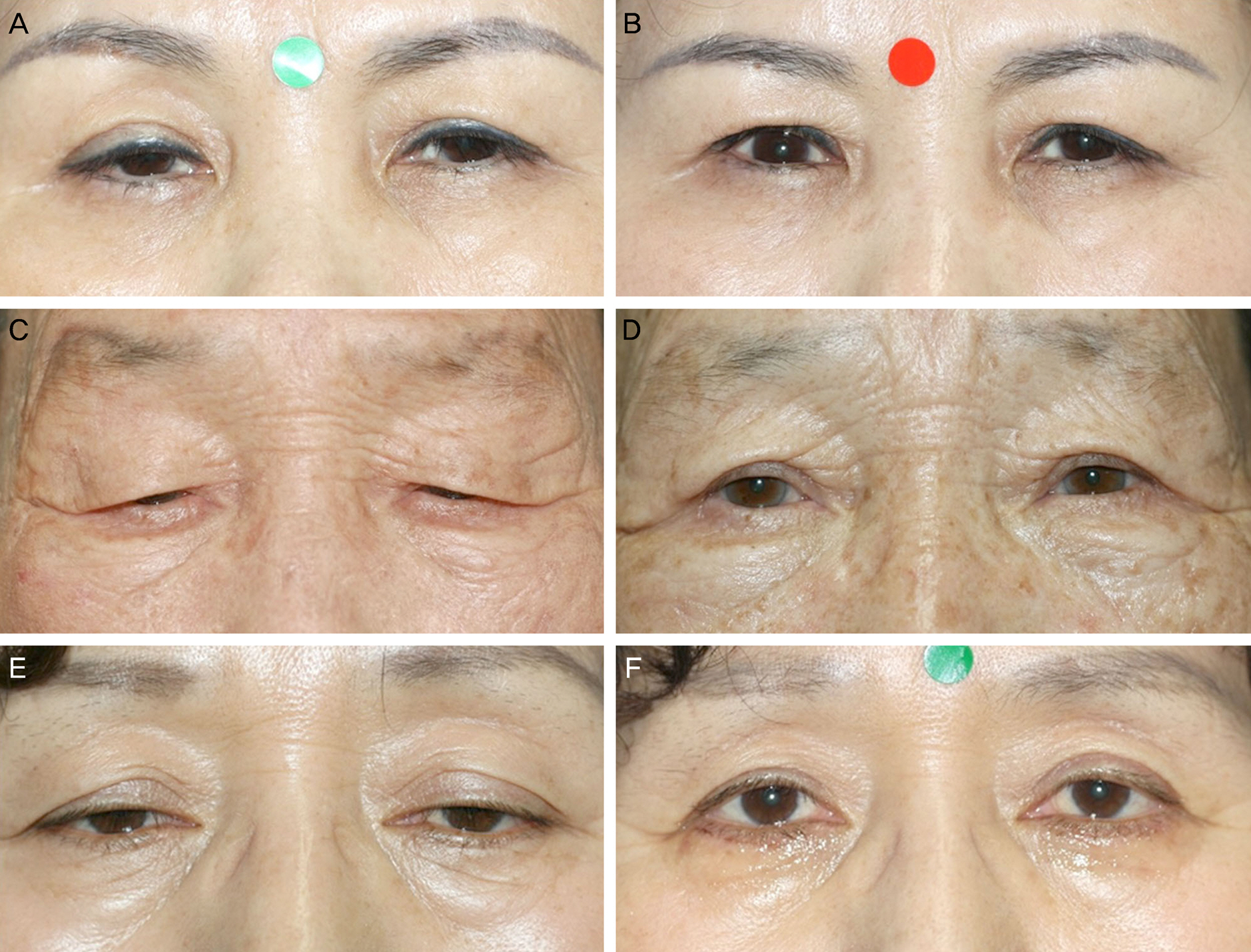
To investigate the characteristics and postoperative complications of ptosis patients with deep superior sulcus following levator resection surgery.
METHODS
Records of 33 ptosis patients (59 lids) with deep superior sulcus who underwent levator resection surgery from March 2008 to May 2013 were reviewed retrospectively. Operation success rate, reoperation rate, preoperative and postoperative marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1), and levator function were compared and postoperative complications were evaluated.
RESULTS
The patient's mean age was 65.8 years. The MRD1 was -1.0 +/- 1.4 mm preoperatively, 2.5 +/- 1.2 mm at 1 month after surgery, and 2.3 +/- 1.1 mm at 3 months after surgery. Operation success rate was 84.8%. At 1 month after surgery, 52.5% of lids had lagophthalmos as a surgery complication but later all recovered. Additionally, 44.1% of the patients had worn therapeutic contact lenses postoperatively for 7.0 +/- 12.1 days.
CONCLUSIONS
Occurrence rate of postoperative lagophthalmos was higher than in other previous studies suggesting a tendency for overcorrection in levator resection surgery for ptosis patients with deep superior sulcus. Additionally, levator resection surgery is cosmetically as well as functionally very effective for deep superior sulcus.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Exploring Brow Position Changes with Age in Koreans
Noh Seung Yoon, Hee Bae Ahn
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2019;33(1):91-94. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2018.0013.
Reference
-
References
1. Sutula FC, Thomas O. Repair of the superior sulcus deformity using autogenous costal cartilage. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:424–7.
Article2. Camirand A, Doucet J, Harris J. Eyelid aging: the historical evolution of its management. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005; 29:65–73.
Article3. Choi BH, Lee SH, Chung WS. Correction of superior sulcus deformity and enophthalmos with porous high-density polyethylene sheet in anophthalmic patients. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:168–73.
Article4. Matsuo K, Kondoh S, Kitazawa T, et al. Pathogenesis and surgical correction of dynamic lower scleral show as a sign of disinsertion of the levator aponeurosis from the tarsus. Br J Plast Surg. 2005; 58:668–75.
Article5. Sultana R, Matsuo K, Yuzuriha S, Kushima H. Disinsertion of the levator aponeurosis from the tarsus in growing children. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 106:563–70.
Article6. Lee JY. A statistical study on the corneal diameters in Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1983; 24:53–8.7. Linberg JV, Vasquez RJ, Chao GM. Aponeurotic ptosis repair under local anesthesia. Prediction of results from operative lid height. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:1046–52.8. Kim JY, Kim YD. Changes in eyelid height with time after levator resection under local anesthesia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:1303–11.
Article9. Park CY, Jeon SL, Woo KI, Chang HR. The frequency and aspects of ptosis in Korean old age. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:205–10.10. Lee IJ, Park MC, Lim H, et al. Blepharoptosis correction: repositioning the levator aponeurosis. J Craniofac Surg. 2011; 22:2284–7.11. Abrishami A, Bagheri A, Salour H, et al. Outcomes of levator resection at tertiary eye care center in Iran: a 10-year experience. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2012; 26:1–5.
Article12. Yip CC, Gonzalez-Candial M, Jain A, et al. Lagophthalmos in enophthalmic eyes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89:676–8.
Article13. Liang L, Sheha H, Fu Y, et al. Ocular surface morbidity in eyes with senile sunken upper eyelids. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:2487–92.
Article14. Leyngold IM, Berbos ZJ, McCann JD, et al. Use of hyaluronic acid gel in the treatment of lagophthalmos in sunken superior sulcus syndrome. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014; 30:175–9.
Article15. Sutula FC, Thomas O. Repair of the superior sulcus deformity using autogenous costal cartilage. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:424–7.
Article16. Hobar PC, Burt JD, Masson JA, et al. Pericranial flap correction of superior sulcus depression in the anophthalmic orbit. J Craniofac Surg. 1999; 10:487–90.
Article17. Sihota R, Sujatha Y, Betharia SM. The fat pad in dermis fat grafts. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:231–4.
Article18. Laiseca A, Laiseca D, Laiseca J, Laiseca J Jr. Correcting superior sulcus deformities. Adv Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 8:229–42.19. Kim KH, Lee TS, Hwang SJ. The effect of autologous dermis-fixation to orbital periosteum in superior sulcus deformity. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:878–85.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Outcomes of Anterior Levator Resection and Frontalis Sling in Congenital Ptosis with Poor Levator Function
- Clinical Study of Simple Levator Resection in Ptosis Patients
- Clinical Observation of Congenital Blepharoptosis
- Outcomes of Levator Resection at Tertiary Eye Care Center in Iran: A 10-Year Experience
- External Levator Resection in Mild to Moderate Unilateral Ptosis