J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Sep;54(9):1435-1439.
Confocal Microscopic Findings of Corneal Tissue in Fuchs' Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jongsool@pusan.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the morphology and density of corneal tissue in patients with early stage Fuchs' corneal endothelial dystrophy (FCED) by in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM).
CASE SUMMARY
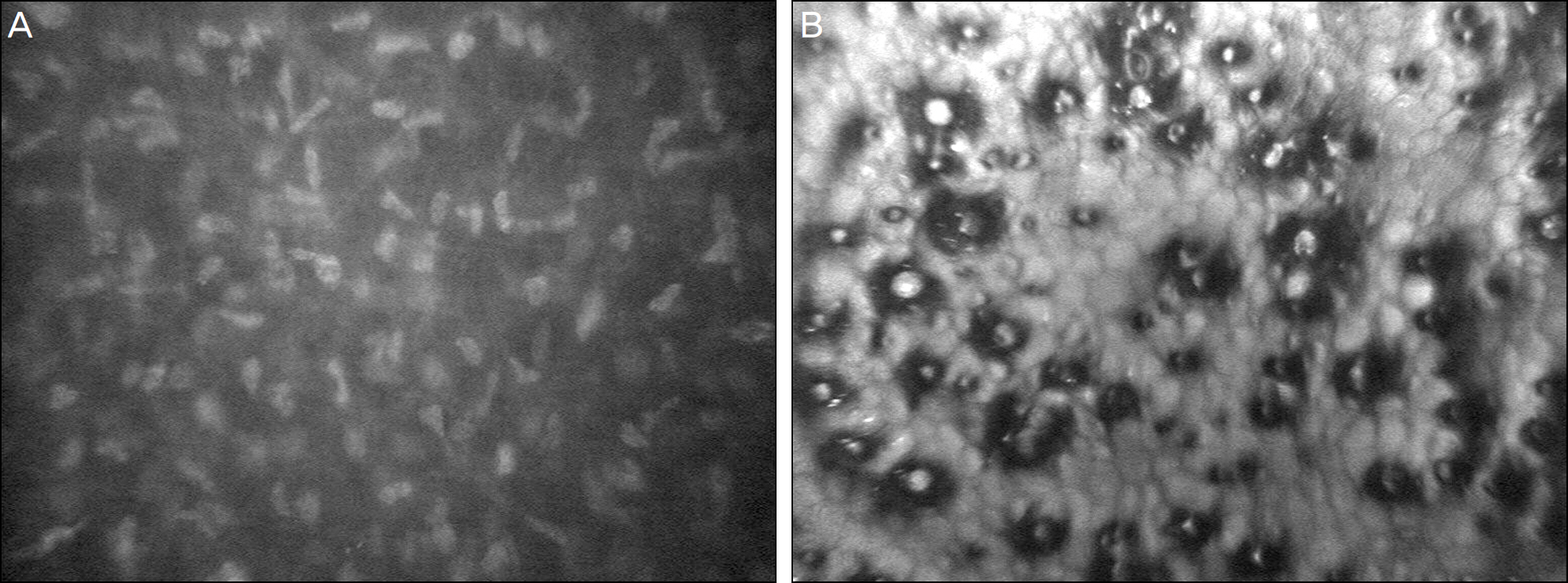
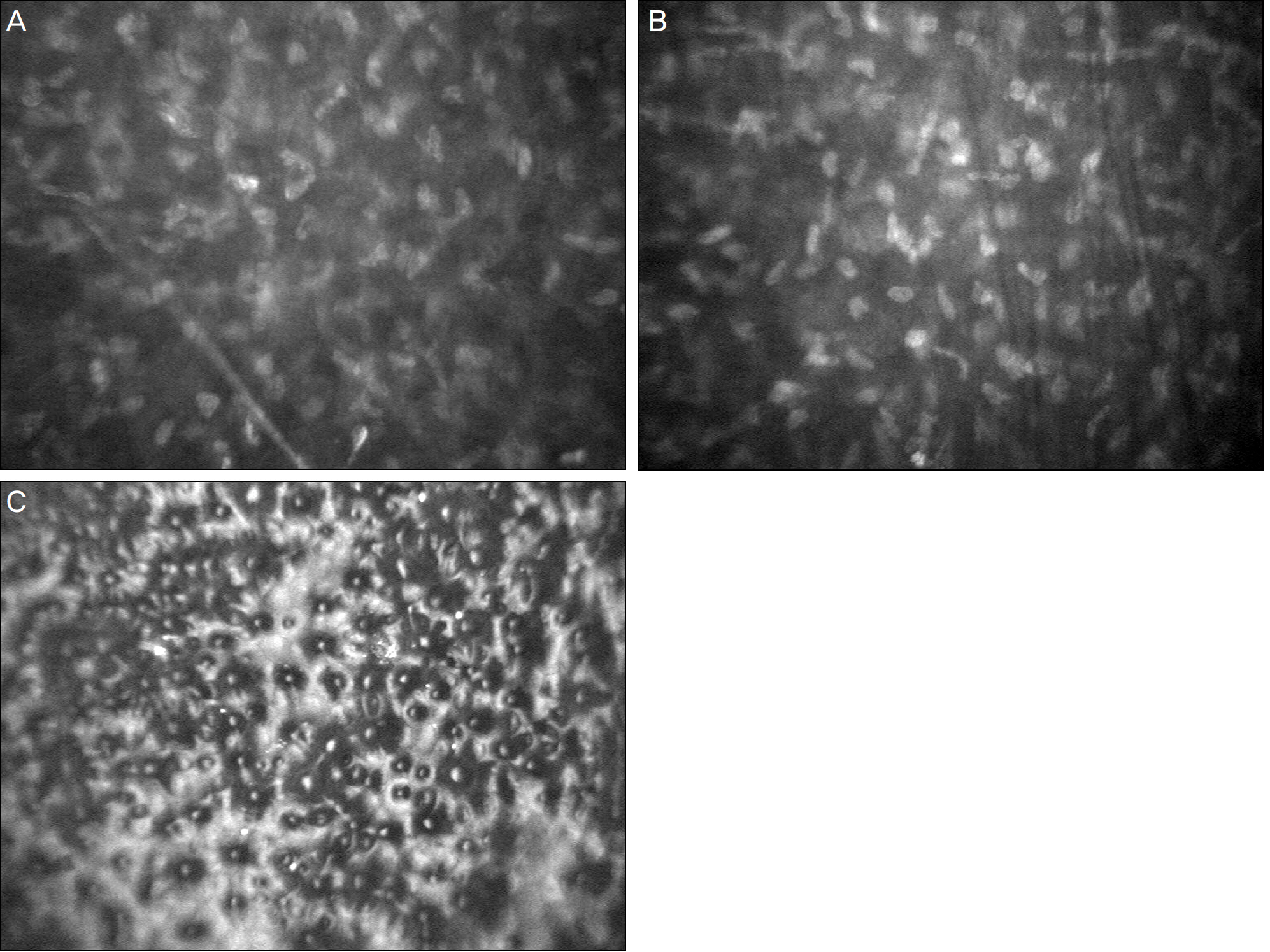
Each layer of the cornea in 2 patients with early-stage FCED was examined with IVCM (ConfoScan 4.0, NIDEK, Co. Ltd., albignasego, Italy). Cross-sectioned corneal images of the corneal epithelium, Bowman's layer, stromal layer, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium were evaluated. Corneal epithelium, Bowman's layer, and anterior stroma of both patients showed no abnormalities. Case 1 was diagnosed as Stage 1 FCED, demonstrating typical changes including pleomorphism, polymegathism, and the presence of guttae in the corneal endothelial layer. Case 2 was diagnosed as Stage 2 FCED, showing several hyper-reflective whitish dots in the posterior stroma, hypo-reflective vertical strands in the stroma adjacent to Descemet's membrane, and pleomorphism, polymegathism, and guttae in the corneal endothelial layer.
CONCLUSIONS
IVCM is a non-invasive and effective tool to diagnose early-stage FCED.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Repp DJ, Hodge DO, Baratz KH. . Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy: subjective grading versus objective grading based on the central-to-peripheral thickness ratio. Ophthalmology. 2013; 120:687–94.2. Schrems-Hoesl LM, Schrems WA, Cruzat A. . Cellular and subbasal nerve alterations in early stage Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy: an in vivo confocal microscopy study. Eye (Lond). 2013; 27:42–9.
Article3. Li QJ, Ashraf MF, Shen DF. . The role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of fuchs endothelial dystrophy of the cornea. Arch opthalmol. 2001; 119:1597–604.
Article4. Lee YK, Kim MS. Long-term outcomes of penetrating kerato-plasty in treating macular corneal dystrophy, TGFBI dystrophy, and Fuchs’ dystrophy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1397–402.
Article5. Hara M, Morishige N, Chikama T, Nishida T. Comparison of con-focal biomicroscopy and noncontact specular microscopy for eval-uation of the corneal endothelium. Cornea. 2003; 22:512–5.
Article6. Mustonen RK, McDonald MB, Srivannaboon S. . In vivo con-focal microscopy of Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy. Cornea. 1998; 17:493–503.
Article7. Waring GO 3rd, Rodrigues MM, Laibson PR. Corneal dystrophies. II. Endothelial dystrophies. Surv Ophthalmol. 1978; 23:147–68.
Article8. Efron N, Mutalib HA, Perez-Gomez I, Koh HH. Confocal micro-scopic observations of the human cornea following overnight con-tact lens wear. Clin Exp Optom. 2002; 85:149–55.
Article9. Chiou AG, Kaufman SC, Beuerman RW. . Confocal micro-scopy in cornea guttata and Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999; 83:185–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Confocal Microscopic Findings in Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy
- Long-Term Outcomes of Penetrating Keratoplasty in Treating Macular Corneal Dystrophy, TGFBI Dystrophy, and Fuchs' Dystrophy
- Epidemiology of Corneal Dystrophy in Korea
- In Vivo Confocal Microscopic Findings of Corneal Tissue in Amiodarone-Induced Vortex Keratopathy
- Confocal Microscopic Findings of Avellino Corneal Dystrophy According to Disease Severity