Nat Prod Sci.
2016 Jun;22(2):82-86. 10.20307/nps.2016.22.2.82.
Compounds from a jellyfish-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigates
- Affiliations
-
- 1Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 510301 Guangzhou, China. yonghongliu@scsio.ac.cn
- 2School of Life Science, South China Normal University, 510361 Guangzhou, China.
- 3College of Pharmacy, Pusan National University, Busan 609-735, Korea.
- 4School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, 510515 Guangzhou, China.
- 5South China Sea Bio-Resource Exploitation and Utilization Collaborative Innovation Center, China.
- KMID: 2328871
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2016.22.2.82
Abstract
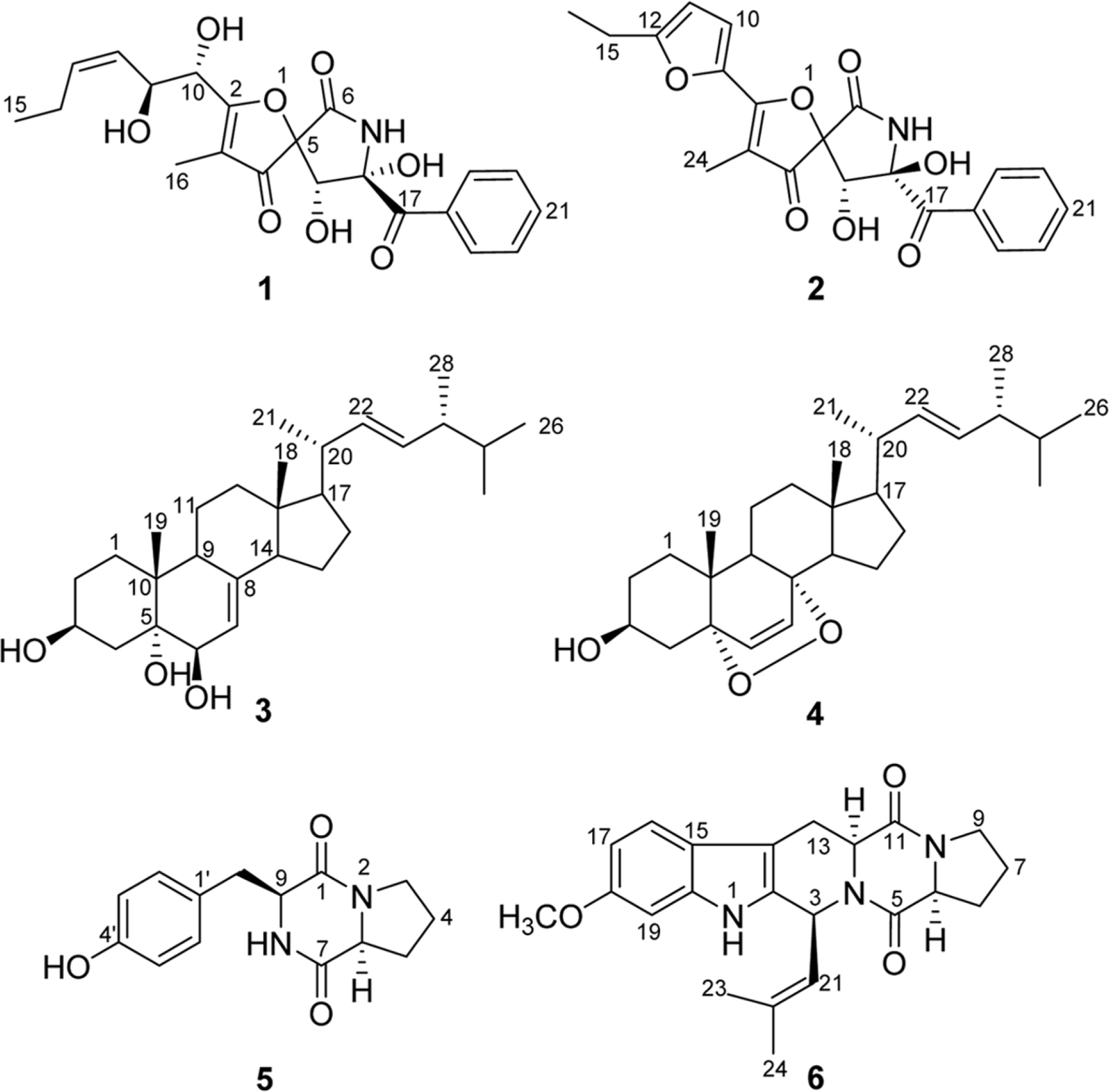
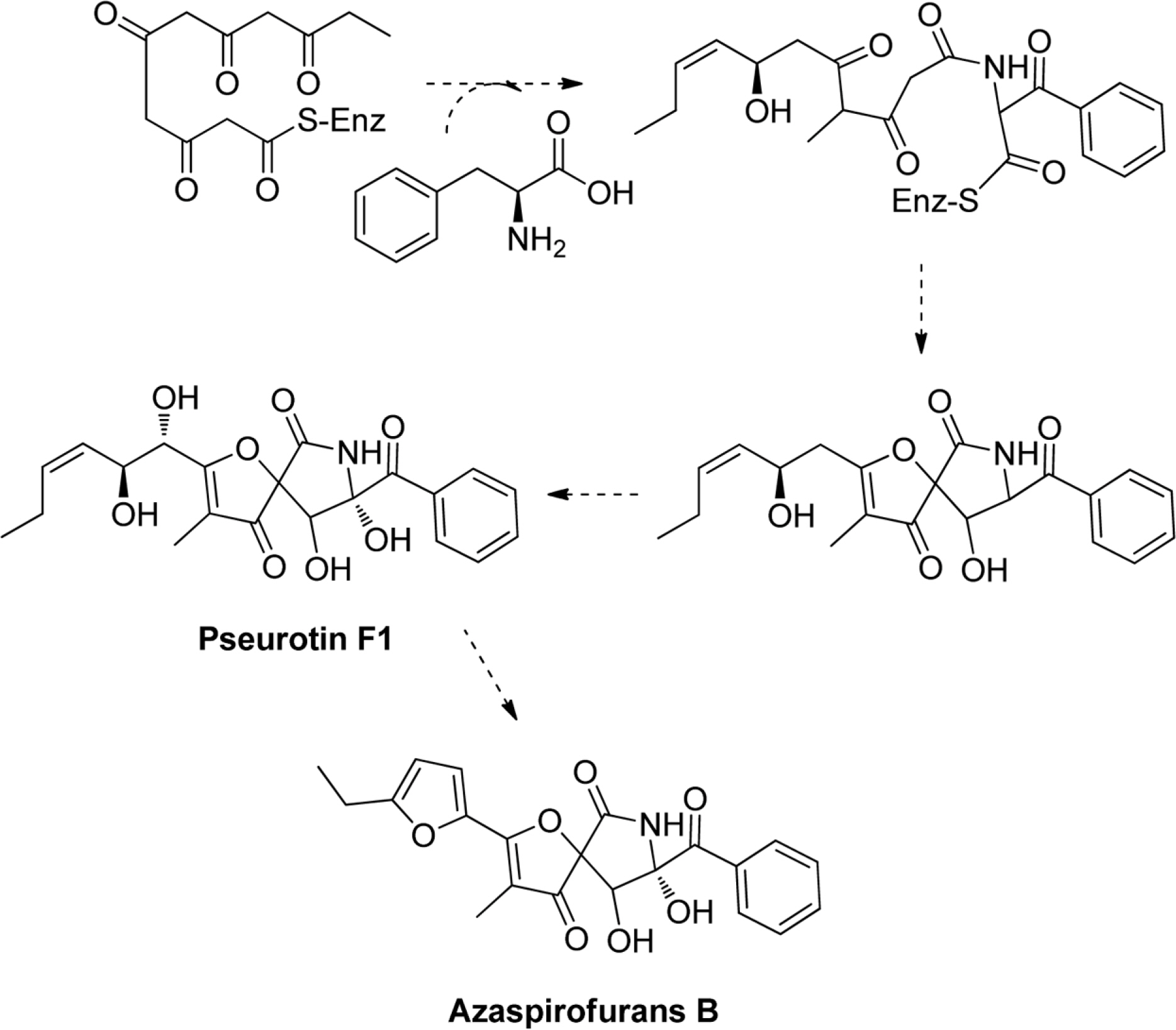
- Six compounds were isolated from the secondary metabolites of the jellyfish-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigates, whose structures were identified by chemical methods and spectroscopic analysis as pseurotin F1 (1), azaspirofurans B (2), (22E, 24R)-24-methyl-5α-cholesta-7,22-diene-3β,5,6β-triol (3), 5α,8α-epidioxyergosta-6,22-dien-3β-o1 (4), cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Tyr) (5), fumitremorgin C (6). The compounds 1 - 5 were isolated from the fungus Aspergillus fumigates for the first time. The isolated compounds (1 - 6) were evaluated for antibiotic activity and cytotoxicity against six bacterial strains and ten human tumor cell lines, respectively.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
(1). Mille-Lindblom C., Fischer H., Tranvik L. J.OIKOS. 2006; 113:233–242.(2). Zhang H. W., Song Y. C., Tan R. X.Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006; 23:753–771.(3). Blunt J. W., Copp B. R., Keyzers, R. A. Munro M. H., Prinsep M. R.Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014; 31:160–258.(4). Uye S.Plankton Benthos Res. 2008; 3:125–131.(5). Wink J., Grabley S., Gareis M., Thiericke R., Kirsch R.European Patent Application. 1993; EP0546474A1.(6). Frisvad J. C., Rank C., Nielsen K. F.Med. Mycol. 2009; 47:S53–S71.(7). Wenke J., Anke H., Sterner O.Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1993; 57:961–964.(8). Ren H., Liu R., Chen, L. Zhu T., Zhu W. M., Gu Q. Q.Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010; 33:499–502.(9). Mohr P., Tamm C.Tetrahedron. 1981; 37:201–212.(9). Mohr P., Tamm C.Tetrahedron Lett. 1987; 28:391–394.(10). Tsunematsu Y., Fukutomi M., Saruwatari, T. Noguchi H., Hotta K., Tang Y., Watanabe K.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014; 53:8475–8479.(11). Vincenzo P., Donato S. J.Nat. Prod. 1987; 50:915–920.(12). Wang X., Wang H., Liu T., Xin Z.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014; 98:4875–4885.(13). Ioannou E., Abdel-Razik A. F., Zervou M., Christofidis D., Alexi X., Vagias C., Alexis M. N., Roussis V.Steroids. 2009; 74:73–80.(14). Gauvin A., Smadja J., Aknin M. Can. J.Chem. 2000; 78:986–992.(15). Bu M., Yang B. B., Hu L.Med. Chem. 2014; 4:709–716.(16). Jayatilake G. S., Thornton M. P., Leonard A. C. J.Nat. Prod. 1996; 59:293–296.(17). Cimmino A., Puopolo G., Perazzolli M., Andolfi A., Melck D., Pertot I., Evidente A.Chem. Heterocycl. Compds. 2014; 50:290–295.(18). Borthwick A. D.Chem. Rev. 2012; 112:3641–3716.(19). Zhang D., Noviendri D., Nursid M., Yang X., Son B. W.Nat. Prod. Sci. 2007; 13:251–254.(20). Puopolo G., Cimmino A., Palmieri, M. C. Giovannini O., Evidente A., Pertot I. J.Appl. Microbiol. 2014; 117:1168–1180.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Jellyfish Dermatitis
- Antifungal Activity of an Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus versicolor DYSJ3 from Aphanamixis grandifolia Blume against Colletotrichum musae
- Gliotoxin is Antibacterial to Drug-resistant Piscine Pathogens
- Antifungal Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Kimchi Against Aspergillus fumigatus
- A Case of Jellyfish Stings Contracted in Korean Coastline