J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2014 Jun;40(3):147-151.
Brain abscess due to odontogenic infection: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Sun Dental Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. omsdklee@gmail.com
Abstract
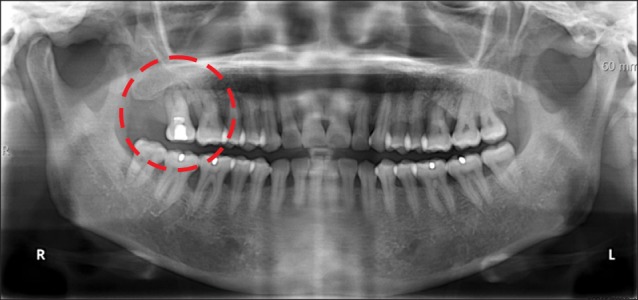
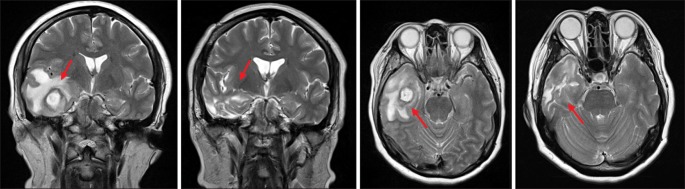
- In this report, we describe a case of brain abscess due to odontogenic infection. A 53-year-old female who had been suffering from headache and trismus for two weeks visited the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Sun Dental Hospital (Daejeon, Korea). Even after several routine tests, we still could not make a diagnosis. However, after the combined multidisciplinary efforts of oral surgeons and neurosurgeons, the patient was treated for odontogenic infection and made an uneventful recovery. Therefore, patients with infections in the head and neck region showing symptoms such as headache, changes in mental state, nausea, vomiting, seizures, hemiplegia, speech disturbance, and visual disturbance, a brain abscess should be included in the list of differential diagnoses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mamelak AN, Mampalam TJ, Obana WG, Rosenblum ML. Improved management of multiple brain abscesses: a combined surgical and medical approach. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:76–85. PMID: 7708172.
Article2. Mathisen GE, Johnson JP. Brain abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 1997; 25:763–779. PMID: 9356788.
Article3. Heilpern KL, Lorber B. Focal intracranial infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1996; 10:879–898. PMID: 8958173.
Article4. Xiao F, Tseng MY, Teng LJ, Tseng HM, Tsai JC. Brain abscess: clinical experience and analysis of prognostic factors. Surg Neurol. 2005; 63:442–449. PMID: 15883068.
Article5. Tseng JH, Tseng MY. Brain abscess in 142 patients: factors influencing outcome and mortality. Surg Neurol. 2006; 65:557–562. PMID: 16720170.
Article6. Tonon E, Scotton PG, Gallucci M, Vaglia A. Brain abscess: clinical aspects of 100 patients. Int J Infect Dis. 2006; 10:103–109. PMID: 16310393.
Article7. Carpenter J, Stapleton S, Holliman R. Retrospective analysis of 49 cases of brain abscess and review of the literature. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007; 26:1–11. PMID: 17180609.
Article8. Corson MA, Postlethwaite KP, Seymour RA. Are dental infections a cause of brain abscess? Case report and review of the literature. Oral Dis. 2001; 7:61–65. PMID: 11354924.
Article9. Petti CA, Simmon KE, Bender J, Blaschke A, Webster KA, Conneely MF, et al. Culture-Negative intracerebral abscesses in children and adolescents from Streptococcus anginosus group infection: a case series. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46:1578–1580. PMID: 18419492.10. Mamelak AN, Obana WG, Flaherty JF, Rosenblum ML. Nocardial brain abscess: treatment strategies and factors influencing outcome. Neurosurgery. 1994; 35:622–631. PMID: 7808604.11. Kao MC. Brain abscess. A clinical analysis of 26 cases with surgical treatment. Bull Tokyo Med Dent Univ. 1973; 20:35–50. PMID: 4515652.12. Lu CH, Chang WN, Lin YC, Tsai NW, Liliang PC, Su TM, et al. Bacterial brain abscess: microbiological features, epidemiological trends and therapeutic outcomes. QJM. 2002; 95:501–509. PMID: 12145389.
Article13. de Louvois J, Brown EM, Bayston R, Lees PD, Pople IK. The rational use of antibiotics in the treatment of brain abscess. Br J Neurosurg. 2000; 14:525–530. PMID: 11272029.14. Sjölin J, Lilja A, Eriksson N, Arneborn P, Cars O. Treatment of brain abscess with cefotaxime and metronidazole: prospective study on 15 consecutive patients. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 17:857–863. PMID: 8286626.15. Gorgan M, Neacsu A, Bucur N, Pruna V, Lipan C, Sandu AM, et al. Brain abscesses: management and outcome analysis in a series of 84 patients during 12 year period. Romanian Neurosurg. 2012; XIX 3:175–182.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Brain abscess following odontogenic infection
- Multiple brain abscesses treated by extraction of the maxillary molars with chronic apical lesion to remove the source of infection
- Deep Neck Space Infection Caused by Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor
- A Case Report of Fatal Mediastinal Abscess Secondary to Odontogenic Infection
- Retropharyngeal space abscess due to spread of odontogenic infection: two cases report