J Nutr Health.
2013 Aug;46(4):369-381.
Perception of environment-friendly foods and satisfaction with school meals among students, their parents, and nutrition teachers at elementary schools in the Jindo area, Jeonnam
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Foods & Nutrition, Kookmin University, Seoul 136-702, Korea. shkim@kookmin.ac.kr
Abstract
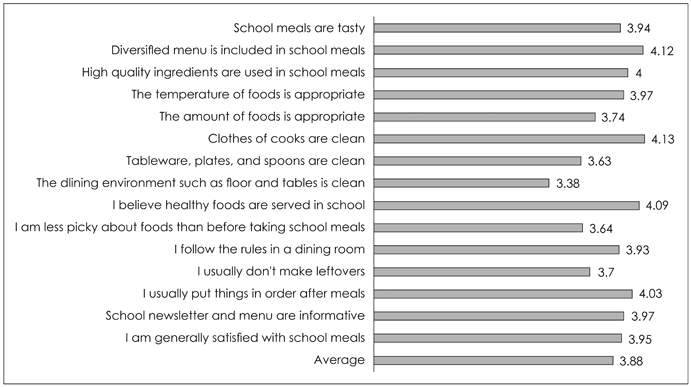
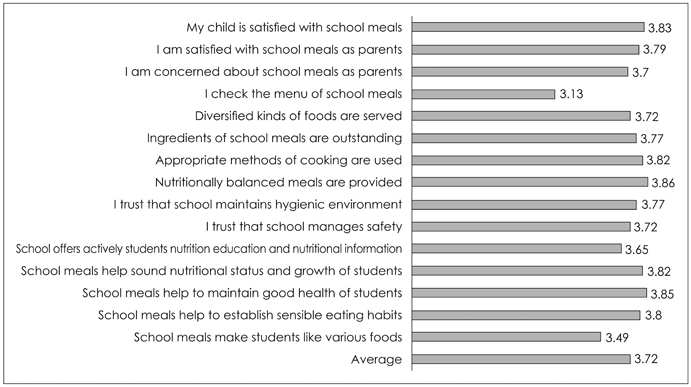
- The aim of this study was to investigate the perception of students, their parents, and nutrition teachers regarding environment-friendly foods (EFF) and the satisfaction with school meals at elementary schools. Questionnaires were sent to nutrition teachers at five elementary schools located in the Jindo area, Jeonnam province, and were distributed to students and their parents. A total of 351 questionnaires from students and 334 from parents were collected from March to April, 2013. In addition, 43 nutrition teachers/dietitians working at elementary schools in the Jindo area responded to questionnaires. Nutrition teachers primarily recognized the classification and certification standards of EFF, and verified the certification mark of EFF when they purchased foods. However, 13.4% of students and 38.6% of parents replied as 'know well' regarding the classification and certification standards of EFF and they verified the mark of EFF less often than the nutrition teachers (p < 0.001). Most of the nutrition teachers and parents indicated 'safety' as the main advantage of EFF. The students and parents were satisfied with EFF at home and school meals because of the safety and favorable effect on health. The results showed that EFF compromised 20~40% of monthly food costs for 51.1% of nutrition teachers. The overall score for satisfaction with school meals for students was 3.88 based on a 5-point Likert scale; however, that of the parents was 3.72. The nutrition teachers realized that the parents were more interested in EFF and satisfied with EFF than the students. The major barriers to using EFF in school meals were 'lack of information about EFF' and 'unstable supply.' Therefore, the above results suggested that there should be improvement in the supply of EFF to include more EFF in school meals and efforts should be made to provide students and parents with more information for understanding EFF.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stoch MB, Smythe PM. Undernutrition during infancy, and subsequent brain growth and intellectual development. In : Scrimshaw NS, Gordon JE, editors. Malnutrition, Learning, and Behavior. Cambridge, MA: M.I.T. Press;1968. p. 279–287.2. Ministry of Education. A status of school foodservice in 2012. Seoul: Ministry of Education;2013. cited 2013 June 05. Available from: http://www.moe.go.kr/web/100066/ko/board/view.do?bbsId=318&boardSeq=44455&mode=view.3. Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. Student Health Service Division. A guidebook for sanitation management of school foodservice. 3rd edition. Seoul: Sun-Myung Pub;2010.4. NamKung S, Lee JY, Kim KD. A study on the recognition of organic food of housewives in Seoul area. Korean J Food Preserv. 2007; 14(6):676–680.5. Oh SE, Lee SH. An analysis on countermove of its farmer and consumption in environment-friendly agricultural products. J Digit Policy Manag. 2012; 10(5):105–116.6. Huh E, Kim JW. Consumer knowledge and attitude to spending on environment-friendly agricultural products. Korean J Hum Ecol. 2010; 19(5):883–896.
Article7. Kasim A, Ismail A. Environmentally friendly practices among restaurants: drivers and barriers to change. J Sustain Tour. 2012; 20(4):551–570.
Article8. National Agricultural Products Quality Management Service. Certification system of environmentally-friendly agricultural products. Anyang: National Agricultural Products Quality Management Service;2013. cited 2013 Feb 27. Available from: http://www.naqs.go.kr/serviceInfo/service_01_01.jsp.9. Dahm MJ, Samonte AV, Shows AR. Organic foods: do eco-friendly attitudes predict eco-friendly behaviors? J Am Coll Health. 2009; 58(3):195–202.
Article10. Aschemann-Witzel J, Maroscheck N, Hamm U. Are organic consumers preferring or avoiding foods with nutrition and health claims? Food Qual Prefer. 2013; 30(1):68–76.
Article11. Hallmann E, Lipowski J, Marszałek K, Rembiałkowska E. The seasonal variation in bioactive compounds content in juice from organic and non-organic tomatoes. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2013; 68(2):171–176.
Article12. Jeollanamdo Office of Education. The basic plan for school meals. Muan: Jeollanamdo Office of Education;2013. p. 53–54.13. He C, Breiting S, Perez-Cueto FJ. Effect of organic school meals to promote healthy diet in 11-13 year old children. A mixed methods study in four Danish public schools. Appetite. 2012; 59(3):866–876.
Article14. Jeong JH, Kim EJ, Kim MH, Choi MK. Perception of eco-friendly agricultural products and food service satisfaction of elementary and middle school students according to eco-friendly food service day in Chungnam. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2013; 42(1):114–119.
Article15. Kim NR, Cho YS, Kim SA. Satisfaction and recognition level of environment-friendly agricultural products in Cheongju area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16(1):75–85.
Article16. Jang JA, Ahn SW, Choi MK. Actual status of school dietitians' recognition and use of superior agricultural products in Daegu. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17(3):312–320.
Article17. Lee YS, Lee NO, Ko SH. A survey on use of environment-friendly agricultural products for school food service by dietitians in Chungnam province. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(5):556–564.18. Rho JO, Kim MO. A study on the utilization, recognition, and satisfaction of environment-friendly agricultural products in school food services according to the type of food service in Jeonbuk area. Korean J Hum Ecol. 2011; 20(2):427–437.
Article19. Lee YS, Park MJ. Parental perception and satisfaction with environment-friendly agricultural products used for school foodservice in elementary schools in Daejeon. Korean J Food Cult. 2008; 23(6):737–747.20. Choi MK, Seo HC, Baek SH. The influence of environment-friendly agricultural products (EAPs) perception of parents in Chung-buk area on EAPs consumption behavior. Korean J Food Nutr. 2010; 23(2):269–275.21. Jo JU, Yoo DK. Analysis of customer loyalty and purchasing behaviors towards environment-friendly agricultural products. Korean J Org Agric. 2009; 17(3):273–289.22. Kim DK, Kim SJ, Lee KH. The effect of food choice motive on attitude and intention of purchasing organic food. Korean J Food Cult. 2011; 26(5):506–512.23. Kim HK, Kim JH. Comparison of awareness and practice on well-being life and related behaviors according to generations. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12(4):426–439.24. Nam YS, Kim HA. Parents' perception on middle school foodservice using environment friendly agricultural products (EFAP) in Masan area. Korean J Nutr. 2012; 45(2):181–191.
Article25. Kwak MJ, Kim KN. Perception and consumption of environment-friendly farm products (EP) among the parents of children in the schools where EP had been used or never been used in their foodservice. J Hum Ecol. 2012; 16(1):85–94.26. Chang HS, Lee MJ. The perception for management of school foodservice using of environmentally friendly agricultural products of elementary school children's mothers in Gunsan. Korean J Community Nutr. 2008; 13(6):867–878.27. Ryu MJ, Suh JS, Lyu ES. A perception of dietitians for using imported foods and pro-environment farm products for elementary school foodservice operations in Busan. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2004; 10(4):452–466.28. Choi HY. A study on the current use and satisfaction in environmentally-friendly farm products in school feeding for secondary and high schools in Gwangju [MS thesis]. Gwangju: Chosun University;2008.29. Lee JH. A research on recognition and actual use of eco-friendly agricultural products by dieticians in charge of school lunch in south Gyeongsang province [MS thesis]. Busan: Silla University;2009.30. Yang IS, Lee BS, Lee SJ, Lee HY, Jung HY. Using status of Korean agricultural products in school food service and dieticians' perception. Korean J Food Cult. 2006; 21(2):142–153.31. Kim YH, Lee YK. A survey of purchasing management for school foodservice foods in Daegu and Gyeongbuk province. Korean J Food Preserv. 2012; 19(3):376–384.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perception of Nutritional Education among School Administrators, Parents, and School Nutrition Teachers at an Elementary School
- Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
- Perception on food allergy labelling and management of nutritional education among higher grade elementary school students in Jeju area
- Perception of Elementary School Teachers about Nutrition Education in the Kyungnam Area
- The use Frequency and Amount of Food Sources of Sodium and Knowledge Requirement, and Job Satisfaction of Dietitians and Nutrition Teachers according to the School Types in Busan