J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2011 Jul;49(3):206-213.
Success rate and marginal bone loss of Osstem USII plus implants; Short term clinical study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. donghoohan@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Periodontology, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
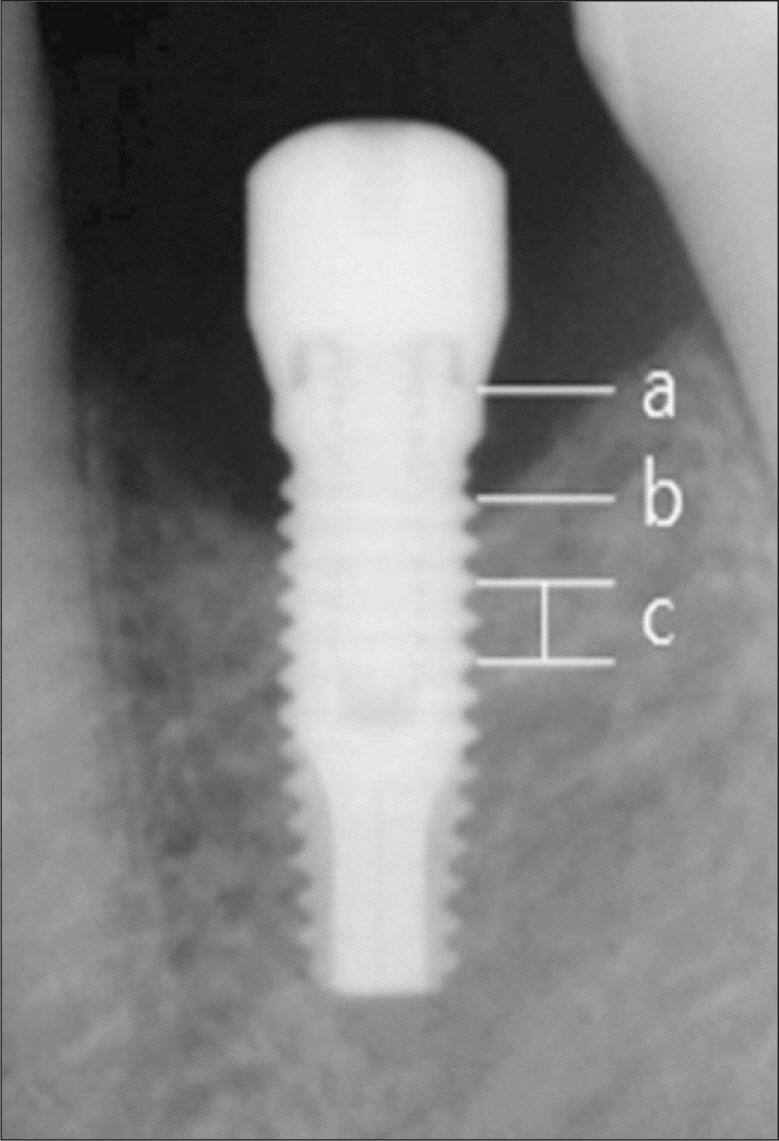
The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical value of Osstem(R) USII plus system implants. Clinical and radiographic data were analyzed for 88 implants placed and functionally loaded for a 12 month period at the Yonsei University Dental Hospital. MATERIALS AND METHOD: Based on the patient's medical records, clinical factors and their effects on implant marginal bone resorption, distribution and survival rate were analyzed. The marginal bone loss was evaluated at implant placement and during a 6 to 12 months functional loading period. The independent sample t-test was used to evaluate the interrelationship between the factors (alpha=0.05), and one way repeated measures ANOVA was used to compare the amount of marginal bone resorption.
RESULTS
The cumulative survival rate for 88 implants was 100%. The marginal bone resorption from implant placement to prosthetic delivery was 0.24 mm and the average marginal bone resorption from prosthetic delivery to 12 months of functional loading was 0.19 mm. The total average bone resorption from implant placement to 12 months of functional loading was 0.43 mm. There were no statistically differences in the amount of marginal bone resorption when implants were placed in the maxilla or the mandible (P>.05), however, implants placed in the posterior areas showed significantly more marginal bone loss than those placed in the anterior areas (P<.05).
CONCLUSION
Based on these results, the short term clinical success rate of RBM surface treated external connection domestic implants showed satisfactory results and the marginal bone loss was in accord with the success criteria of dental implants.
Figure
Reference
-
1.Adell R., Lekholm U., Rockler B., Branemark PI. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981. 10:387–416.
Article2.Buser D., Mericske-Stern R., Bernard JP., Behneke A., Behneke N., Hirt HP., Belser UC., Lang NP. Long-term evaluation of non-submerged ITI implants. Part 1: 8-year life table analysis of a prospective multicenter study with 2359 implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997. 8:161–72.
Article3.Albrektsson T., Dahl E., Enbom L., Engevall S., Engquist B., Eriksson AR., Feldmann G., Freiberg N., Glantz PO., Kjellman O, et al. Osseointegrated oral implants. A Swedish multicenter study of 8139 consecutively inserted Nobelpharma implants. J Periodontol. 1988. 59:287–96.4.Becker W., Becker BE., Alsuwyed A., Al-Mubarak S. Long-term evaluation of 282 implants in maxillary and mandibular molar positions: a prospective study. J Periodontol. 1999. 70:896–901.
Article5.Bahat O. Branemark system implants in the posterior maxilla: clinical study of 660 implants followed for 5 to 12 years. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000. 15:646–53.6.Kim SG., Oh MS., Kim YK., Oh HK., Choi GL., Oh YH. Multicenter retrospective clinical study of Osstem USII implant system in complete edentulous patients. Implantology. 2007. 11:12–21.7.Kim YK., Yun PY., Kwon MJ. Short-term retrospective clinical Study of Osstem. GS II, US III, SS III Implants. Implantology. 2008. 12:12–22.8.Krennmair G., Schmidinger S., Waldenberger O. Single-tooth replacement with the Frialit-2 system: a retrospective clinical analysis of 146 implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:78–85.9.Romeo E., Lops D., Margutti E., Ghisolfi M., Chiapasco M., Vogel G. Long-term survival and success of oral implants in the treatment of full and partial arches: a 7-year prospective study with the ITI dental implant system. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:247–59.10.Wennstro ¨m JL., Ekestubbe A., Gro ¨ndahl K., Karlsson S., Lindhe J. Implant-supported single-tooth restorations: a 5-year prospective study. J Clin Periodontol. 2005. 32:567–74.
Article11.Kim JH., Jung MK., Moon HS., Han DH. The influence of Collar design on peri-implant marginal bone tissue. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2008. 46:53–64.12.Albrektsson T., Isidor F. Consensus report of session IV. In: Lang NP, Karring T. Proceedings of the 1st European Workshop on Periodontology. London: Quintessence;1993. p. 365–9.13.Kim SH., Kim SJ., Lee KW., Han DH. The effects of local factors on the survival of dental implants: A 19-year retrospective study. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2010. 48:28–40.14.Cochran DL., Buser D., ten Bruggenkate CM., Weingart D., Taylor TM., Bernard JP., Peters F., Simpson JP. The use of reduced healing times on ITI implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched (SLA) surface: early results from clinical trials on ITI SLA implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:144–53.15.Kim YK., Yun PY., Son DI., Kim BS., Hwang JW. Analysis of clinical application of Osstem(R) (Korea) implant system for 6 years. Implantology. 2006. 10:56–65.16.Oh TJ., Yoon J., Misch CE., Wang HL. The causes of early implant bone loss: myth or science? J Periodontol. 2002. 73:322–33.
Article17.strand P., Engquist B., Dahlgren S., Gro ¨ndahl K., Engquist E., Feldmann H. Astra Tech and Branemark system implants: a 5-year prospective study of marginal bone reactions. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004. 15:413–20.
Article18.Peñarrocha M., Palomar M., Sanchis JM., Guarinos J., Balaguer J. Radiologic study of marginal bone loss around 108 dental implants and its relationship to smoking, implant location, and morphology. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:861–7.19.Hwang JW., Kim YK. Retrospective study of Implantium(R) dental implants: clinical and radiographic results of 22 months. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005. 9:30–40.20.Cho JY., Kim YJ., Yu MG., Kook MS., Oh HK., Park HJ. The effect of surface treatment of the cervical area of implant on bone regeneration in mini-pig. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008. 34:285–92.21.Davies JE. Mechanisms of endosseous integration. Int J Prosthodont. 1998. 11:391–401.22.Won MK., Park CJ., Chang KS., Kim CW., Kim YS., Isa ZM., Ariffin YT. An experimental study of newly designed implant with RBM surface in the rabbit tibia: resonance frequency analysis and removal torque study. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2003. 41:720–31.23.Wyatt CC., Zarb GA. Bone level changes proximal to oral implants supporting fixed partial prostheses. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:162–8.
Article24.Moy PK., Medina D., Shetty V., Aghaloo TL. Dental implant failure rates and associated risk factors. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005. 20:569–77.25.Naert I., Koutsikakis G., Duyck J., Quirynen M., Jacobs R., van Steenberghe D. Biologic outcome of implant-supported restorations in the treatment of partial edentulism. Part I: a longitudinal clinical evaluation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:381–9.26.Wyatt CC., Zarb GA. Treatment outcomes of patients with implant-supported fixed partial prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998. 13:204–11.27.Lindquist LW., Carlsson GE., Jemt T. A prospective 15-year followup study of mandibular fixed prostheses supported by osseointegrated implants. Clinical results and marginal bone loss. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996. 7:329–36.
Article28.Weber HP., Crohin CC., Fiorellini JP. A 5-year prospective clinical and radiographic study of non-submerged dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000. 11:144–53.
Article29.Tolstunov L. Implant zones of the jaws: implant location and related success rate. J Oral Implantol. 2007. 33:211–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term Retrospective Clinical Study Comparing Submerged Type with External Hex Connection and Non-submerged Type with Internal Morse Taper Connection Implants
- Short-Term Retrospective Clinical Study of Resorbable Blasting Media Surface Tapered Implants
- Long-term evaluation of the prognosis of straight and tapered implant with resorbable blast media surface: Retrospective clinical study
- Long-term observation of immediately-installed implants after extraction: Retrospective clinical study
- A retrospective clinical study of single short implants (less than 8 mm) in posterior edentulous areas