Tuberc Respir Dis.
2014 Jul;77(1):18-23.
Annual Change in Pulmonary Function and Clinical Characteristics of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Over a 3-Year Follow-up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. jsw@gilhospital.com
- 2Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) have different pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and outcomes than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The intention of this study was to identify unknown differences between CPFE and IPF by a retrospective comparison of clinical data including baseline and annual changes in pulmonary function, comorbidities, laboratory findings, clinical characteristics and cause of hospitalization.
METHODS
This study retrospectively enrolled patients with CPFE and IPF who had undergone PFTs once or several times per year during a follow-up period of three years. Baseline clinical characteristics and the annual changes in the pulmonary function during the follow-up period were compared between 26 with CPFE and 42 patients with IPF.
RESULTS
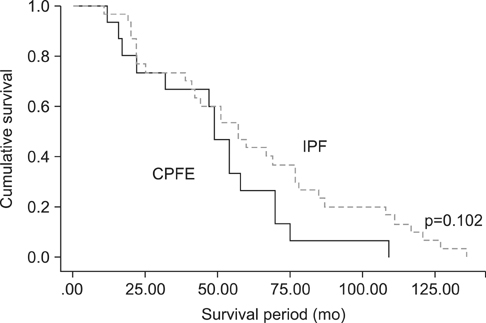
The baseline ratio of forced expiratory volume in one second to forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC%) in patients with CPFE was lower than that in patients with IPF (78.6+/-1.7 vs. 82.9+/-1.1, p=0.041). The annual decrease in FEV1/FVC in the CPFE was significantly higher than in the IPF. The annual decreases in diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide and FVC showed no significant differences between the two groups. The symptom durations of cough and sputum were in the CPFE significantly lower than in the IPF. The serum erythrocyte sedimentation rate level at the acute stage was significantly higher than in the IPF. There were no significant differences in the hospitalization rate and pneumonia was the most common cause of hospitalization in both study groups.
CONCLUSION
The annual decrease of FEV1/FVC was in patients with CPFE significantly higher than in the patients with IPF.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Blood Sedimentation
Carbon Monoxide
Comorbidity
Cough
Diffusion
Emphysema*
Follow-Up Studies*
Forced Expiratory Volume
Hospitalization
Humans
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis*
Intention
Pneumonia
Pulmonary Emphysema
Pulmonary Fibrosis*
Respiratory Function Tests
Retrospective Studies
Sputum
Vital Capacity
Carbon Monoxide
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 165:277–304.2. Cottin V, Nunes H, Brillet PY, Delaval P, Devouassoux G, Tillie-Leblond I, et al. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: a distinct underrecognised entity. Eur Respir J. 2005; 26:586–593.3. Mura M, Zompatori M, Pacilli AM, Fasano L, Schiavina M, Fabbri M. The presence of emphysema further impairs physiologic function in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Care. 2006; 51:257–265.4. Jankowich MD, Rounds SI. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema syndrome: a review. Chest. 2012; 141:222–231.5. Grubstein A, Bendayan D, Schactman I, Cohen M, Shitrit D, Kramer MR. Concomitant upper-lobe bullous emphysema, lower-lobe interstitial fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension in heavy smokers: report of eight cases and review of the literature. Respir Med. 2005; 99:948–954.6. Kurashima K, Takayanagi N, Tsuchiya N, Kanauchi T, Ueda M, Hoshi T, et al. The effect of emphysema on lung function and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology. 2010; 15:843–848.7. Collard HR, King TE Jr, Bartelson BB, Vourlekis JS, Schwarz MI, Brown KK. Changes in clinical and physiologic variables predict survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 168:538–542.8. Jankowich MD, Rounds S. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema alters physiology but has similar mortality to pulmonary fibrosis without emphysema. Lung. 2010; 188:365–373.9. Kitaguchi Y, Fujimoto K, Hanaoka M, Kawakami S, Honda T, Kubo K. Clinical characteristics of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Respirology. 2010; 15:265–271.10. Schmidt SL, Nambiar AM, Tayob N, Sundaram B, Han MK, Gross BH, et al. Pulmonary function measures predict mortality differently in IPF versus combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Eur Respir J. 2011; 38:176–183.11. Akagi T, Matsumoto T, Harada T, Tanaka M, Kuraki T, Fujita M, et al. Coexistent emphysema delays the decrease of vital capacity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med. 2009; 103:1209–1215.12. Mejia M, Carrillo G, Rojas-Serrano J, Estrada A, Suarez T, Alonso D, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: decreased survival associated with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest. 2009; 136:10–15.13. Usui K, Tanai C, Tanaka Y, Noda H, Ishihara T. The prevalence of pulmonary fibrosis combined with emphysema in patients with lung cancer. Respirology. 2011; 16:326–331.14. Lim TK. Respiratory failure from combined emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis. Singapore Med J. 1993; 34:169–171.15. Kitaguchi Y, Fujimoto K, Hayashi R, Hanaoka M, Honda T, Kubo K. Annual changes in pulmonary function in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: over a 5-year follow-up. Respir Med. 2013; 107:1986–1992.16. Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 183:788–824.17. Ryerson CJ, Hartman T, Elicker BM, Ley B, Lee JS, Abbritti M, et al. Clinical features and outcomes in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2013; 144:234–240.18. Corsonello A, Pedone C, Battaglia S, Paglino G, Bellia V, Incalzi RA. C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) as inflammation markers in elderly patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011; 53:190–195.19. Tkacova R, Kluchova Z, Joppa P, Petrasova D, Molcanyiova A. Systemic inflammation and systemic oxidative stress in patients with acute exacerbations of COPD. Respir Med. 2007; 101:1670–1676.20. Mura M, Belmonte G, Fanti S, Contini P, Pacilli AM, Fasano L, et al. Inflammatory activity is still present in the advanced stages of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology. 2005; 10:609–614.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two cases of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- One-year Follow-up of Three Cases of Smoking-related Interstitial Fibrosis
- A Case of Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum and Pneumopericardium in a Patient with Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Pulmonary Comorbidities of Lung Emphysema
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia