Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Mar;74(3):111-119.
Risk Factors Influencing Rebleeding after Bronchial Artery Embolization on the Management of Hemoptysis Associated with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Respiratory Devision, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Gumi Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Gumi, Korea.
- 2Respiratory Division, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. juokna@schmc.ac.kr
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Hemoptysis due to pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) frequently develops in Korea where the prevalence of TB is intermediate. The effect of bronchial artery embolization (BAE) on the control of massive hemoptysis has been well known. This study is designed to identify the risk factors contributing to rebleeding after BAE in patients with TB.
METHODS
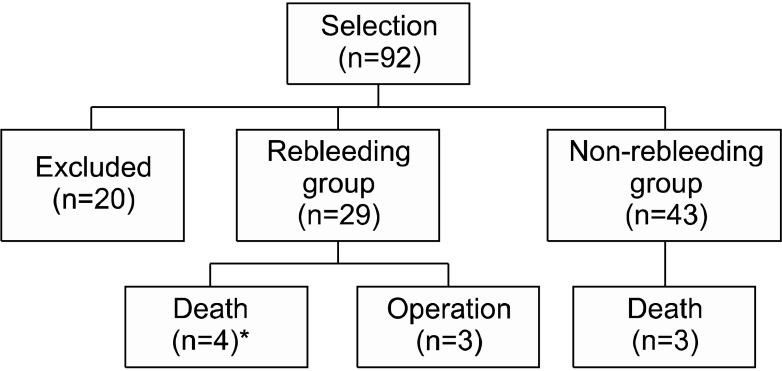
We retrospectively evaluated risk factors and the time for rebleeding after BAE in 72 patients presenting with hemoptysis.
RESULTS
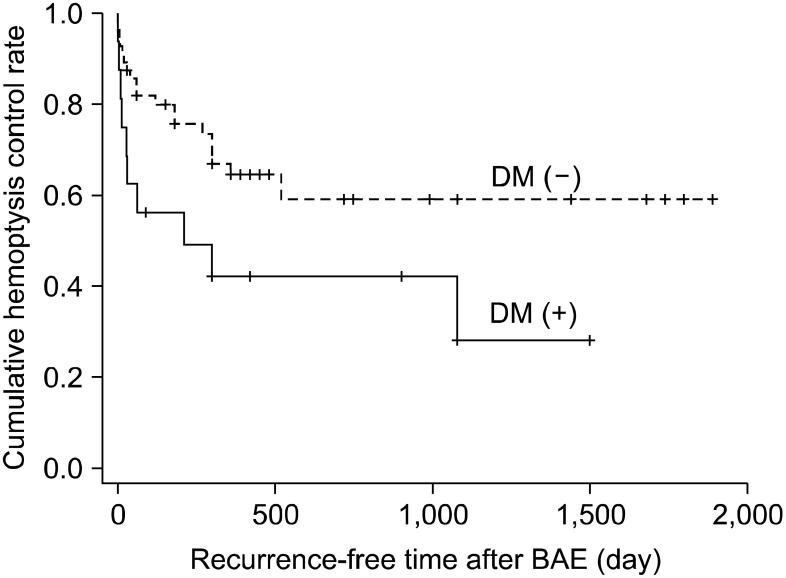
The overall immediate success rate of BAE was 93.1% (67 of 72 patients). Of the 29 patients (40.3%) who showed rebleeding after BAE, 13 patients experienced rebleeding within 1 month, and 14 patients between 1 month to 1 year. The existence of a shunt in angiographic finding, aspergilloma, and diabetes mellitus were risk factors of rebleeding after BAE in multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSION
BAE was very effective for obtaining immediate bleeding control in hemoptysis associated with active TB or post-TB sequelae. It is important to observe whether or not rebleeding occurs up to 1 year of BAE especially in TB patients with aspergilloma, DM, or a shunt. Even rebleeding can be managed well by second BAE.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garzon AA, Gourin A. Surgical management of massive hemoptysis: a ten-year experience. Ann Surg. 1978; 187:267–271. PMID: 637582.2. Hayakawa K, Tanaka F, Torizuka T, Mitsumori M, Okuno Y, Matsui A, et al. Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis: immediate and long-term results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1992; 15:154–158. PMID: 1628281.
Article3. Rabkin JE, Astafjev VI, Gothman LN, Grigorjev YG. Transcatheter embolization in the management of pulmonary hemorrhage. Radiology. 1987; 163:361–365. PMID: 3562815.
Article4. Kim BC, Kim JM, Kim YS, Kim SM, Choi WY, Lee KS, et al. Effect of bronchial artery embolization in the management of massive hemoptysis: factors influencing rebleeding. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1996; 43:590–599.5. World Health Organization. TB country profile for Rep. Korea [Internet]. 2011. cited 2013 Jan 1. Geneva: World Health Organization;Available from: http://www.whoint/countries/kor/en.2011.6. Ramakantan R, Bandekar VG, Gandhi MS, Aulakh BG, Deshmukh HL. Massive hemoptysis due to pulmonary tuberculosis: control with bronchial artery embolization. Radiology. 1996; 200:691–694. PMID: 8756916.
Article7. Kim YG, Yoon HK, Ko GY, Lim CM, Kim WD, Koh Y. Long-term effect of bronchial artery embolization in Korean patients with haemoptysis. Respirology. 2006; 11:776–781. PMID: 17052307.
Article8. van den Heuvel MM, Els Z, Koegelenberg CF, Naidu KM, Bolliger CT, Diacon AH. Risk factors for recurrence of haemoptysis following bronchial artery embolisation for life-threatening haemoptysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007; 11:909–914. PMID: 17705959.9. Gross AM, Diacon AH, van den Heuvel MM, Janse van Rensburg J, Harris D, Bolliger CT. Management of life-threatening haemoptysis in an area of high tuberculosis incidence. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009; 13:875–880. PMID: 19555538.10. Im JG, Itoh H, Shim YS, Lee JH, Ahn J, Han MC, et al. Pulmonary tuberculosis: CT findings. Early active disease and sequential change with antituberculous therapy. Radiology. 1993; 186:653–660. PMID: 8430169.11. Bobrowitz ID, Rodescu D, Marcus H, Abeles H. The destroyed tuberculous lung. Scand J Respir Dis. 1974; 55:82–88. PMID: 4854707.12. Cremaschi P, Nascimbene C, Vitulo P, Catanese C, Rota L, Barazzoni GC, et al. Therapeutic embolization of bronchial artery: a successful treatment in 209 cases of relapse hemoptysis. Angiology. 1993; 44:295–299. PMID: 8457080.
Article13. Corey R, Hla KM. Major and massive hemoptysis: reassessment of conservative management. Am J Med Sci. 1987; 294:301–309. PMID: 3425580.
Article14. Yoon W, Kim JK, Kim YH, Chung TW, Kang HK. Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: a comprehensive review. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1395–1409. PMID: 12432111.
Article15. Uflacker R, Kaemmerer A, Neves C, Picon PD. Management of massive hemoptysis by bronchial artery embolization. Radiology. 1983; 146:627–634. PMID: 6828674.
Article16. Rémy J, Voisin C, Dupuis C, Beguery P, Tonnel AB, Denies JL, et al. [Treatment of hemoptysis by embolization of the systemic circulation]. Ann Radiol (Paris). 1974; 17:5–16. PMID: 4820232.17. Haponik EF, Fein A, Chin R. Managing life-threatening hemoptysis: has anything really changed? Chest. 2000; 118:1431–1435. PMID: 11083697.18. Fartoukh M, Khalil A, Louis L, Carette MF, Bazelly B, Cadranel J, et al. An integrated approach to diagnosis and management of severe haemoptysis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit: a case series from a referral centre. Respir Res. 2007; 8:11. PMID: 17302979.
Article19. Swanson KL, Johnson CM, Prakash UB, McKusick MA, Andrews JC, Stanson AW. Bronchial artery embolization : experience with 54 patients. Chest. 2002; 121:789–795. PMID: 11888961.20. Uflacker R, Kaemmerer A, Picon PD, Rizzon CF, Neves CM, Oliveira ES, et al. Bronchial artery embolization in the management of hemoptysis: technical aspects and long-term results. Radiology. 1985; 157:637–644. PMID: 4059552.
Article21. Mal H, Rullon I, Mellot F, Brugiere O, Sleiman C, Menu Y, et al. Immediate and long-term results of bronchial artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest. 1999; 115:996–1001. PMID: 10208199.
Article22. Remy J, Arnaud A, Fardou H, Giraud R, Voisin C. Treatment of hemoptysis by embolization of bronchial arteries. Radiology. 1977; 122:33–37. PMID: 830351.
Article23. Lee S, Chan JW, Chan SC, Chan YH, Kwan TL, Chan MK, et al. Bronchial artery embolisation can be equally safe and effective in the management of chronic recurrent haemoptysis. Hong Kong Med J. 2008; 14:14–20. PMID: 18239238.24. Mossi F, Maroldi R, Battaglia G, Pinotti G, Tassi G. Indicators predictive of success of embolisation: analysis of 88 patients with haemoptysis. Radiol Med. 2003; 105:48–55. PMID: 12700545.25. Chun JY, Belli AM. Immediate and long-term outcomes of bronchial and non-bronchial systemic artery embolisation for the management of haemoptysis. Eur Radiol. 2010; 20:558–565. PMID: 19727742.
Article26. Kato A, Kudo S, Matsumoto K, Fukahori T, Shimizu T, Uchino A, et al. Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis due to benign diseases: immediate and longterm results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2000; 23:351–357. PMID: 11060364.
Article27. Stoll JF, Bettmann MA. Bronchial artery embolization to control hemoptysis: a review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1988; 11:263–269. PMID: 3145138.
Article28. Osaki S, Nakanishi Y, Wataya H, Takayama K, Inoue K, Takaki Y, et al. Prognosis of bronchial artery embolization in the management of hemoptysis. Respiration. 2000; 67:412–416. PMID: 10940796.
Article29. Wang CS, Yang CJ, Chen HC, Chuang SH, Chong IW, Hwang JJ, et al. Impact of type 2 diabetes on manifestations and treatment outcome of pulmonary tuberculosis. Epidemiol Infect. 2009; 137:203–210. PMID: 18559125.
Article30. Hendy M, Stableforth D. The effect of established diabetes mellitus on the presentation of infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis in the immigrant Asian community of an inner city area of the United Kingdom. Br J Dis Chest. 1983; 77:87–90. PMID: 6860557.
Article31. Koziel H, Koziel MJ. Pulmonary complications of diabetes mellitus: pneumonia. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1995; 9:65–96. PMID: 7769221.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bronchial artery embolization: clinical analysis of 129 cases
- Effect of bronchial artery embolization in the management of massive hemoptysis : factors influencing rebleeding
- Coronary to Bronchial Artery Fistula Causing Massive Hemoptysis in Patients with Longstanding Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Arterial Embolization for Management of Hemoptysis in Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Factors of Rebleeding
- Bronchial artery embolization in the management of hemoptysis