Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Mar;60(3):314-320.
The Relationship between Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression and Response to Cisplatin Containing Chemotherapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. chshon@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 5Medical Research, Center for Cancer Molecular Therapy, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: The overall response (20-30%) to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is quite poor. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is the rate-limiting enzyme in heme degradation. There is increasing evidence suggesting that the induction of HO-1 might have an important protective effect against oxidative stress including cisplatin containing chemotherapy. This study retrospectively investigated the relationship between HO-1 expression and the response to chemotherapy containing cisplatinin advanced NSCLC patients.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: The medical records including the responses to chemotherapy of fifty nine cases were evaluated retrospectively, and the tissue samples of these patients were immunohistochemically stained for HO-1.
RESULTS
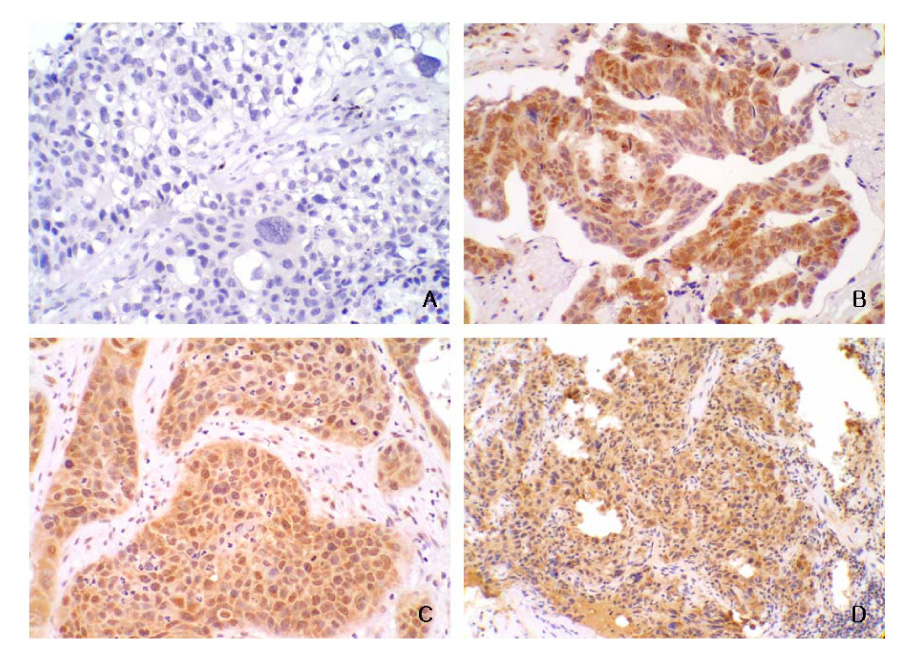
Forty three of the fifty nine patients(72.8%) showed positive staining for HO-1 in their cancer tissues. There was no significant difference according to the cell type, stage and tumor size. In addition, there was no correlation between HO-1 expression and the responses to chemotherapy.
CONCLUSION
HO-1 expression in tumor tissue dose not predict the response to cisplatin containing chemotherapy in advanced NSCLC. Further prospective studies with a larger number of patients will be needed to confirm these results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korea National Statistical Office. Deaths and death rate by cause. 2004.2. Minna JD. Neoplasms of the lung. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2005. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;506–515.3. Scientific Committee of Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. The national survey of lung cancer in Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1999. 46:455–465.4. Graziano SL. Non-small cell lung cancer: clinical value of new biological predictors. Lung cancer. 1997. 17:S37–S58.5. Fang J, Akaike T, Maeda H. Antiapoptotic role of heme oxygenase(HO) and the potential of HO as a target in anticancer treatment. Apoptosis. 2004. 9:27–35.6. Liu ZM, Chen GG, Ng EK, Leung WK, Sung JJ, Chung SS. Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 and p21 confers resistance to apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004. 23:503–513.7. Agarwal A, Balla J, Alam J, Croatt AJ, Nath KA. Induction of heme oxygenase in toxic renal injury: a protective role in cisplatin nephrotoxicity in the rat. Kidney Int. 1995. 48:1298–1307.8. Fang J, Sawa T, Akaike T, Greish K, Maeda H. Enhancement of chemotherapeutic response of tumor cells by a heme oxygenase inhibitor, pegylated zinc protoporphyrin. Int J Cancer. 2004. 109:1–8.9. Mountain CF. Revisions in the international system for staging lung cancer. Chest. 1997. 111:1710–1717.10. Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer. 1981. 47:207–214.11. Tenhunen R, Marver HS, Schmid R. The enzymatic conversion of heme to bilirubin by microsomal heme oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968. 61:748–755.12. Alam J. Heme oxygenase-1: past, present, and future. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. 4:559–562.13. Stocker R, MacDonagh AF, Glazer AN, Ames BN. Antioxidant activities of bile pigments: biliverdin and bilirubin. Methods Enzymol. 1990. 186:301–309.14. Verma A, Hirsch DJ, Glatt CE, Ronnett GV, Snyder SH. Carbon monoxide: a putative neural messenger. Science. 1993. 259:381–384.15. Applegate LA, Luscher P, Tyrrell RM. Induction of heme oxygenase: a general response to oxidant stress in cultured mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1991. 51:974–978.16. Nath KA, Balla G, Vercellotii GM, Balla J, Jacob HS, Levitt MD, et al. Induction of heme oxygenase is a rapid, protective response in rhabdomyolysis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1992. 90:267–270.17. Tanaka S, Akaike T, Fang J, Beppu T, Ogawa M, Tamura F, et al. Antiapoptotic effect of haem oxygenase-1 induced by nitric oxide in experimental solid tumour. Br J Cancer. 2003. 88:902–909.18. Doi K, Akaike T, Fujii S, Tanaka S, Ikebe N, Beppu T, et al. Induction of heam oxygenase-1 by nitric oxide and ischaemia in experimental solid tumors and implications for tumour growth. Br J Cancer. 1999. 80:1945–1954.19. Agarwal A, Balla J, Alam J, Croatt AJ, Nath KA. Induction of heme oxygenase in toxic renal injury: a protective role in cisplatin nephrotoxicity in the rat. Kidney Int. 1995. 48:1298–1307.20. Yokoyama S, Mita S, Okabe A, Abe M, Ogawa M. Prediction of radiosensitivity in human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas with heme oxygenase-1: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study. Oncol Rep. 2001. 8:355–358.21. Yanagawa T, Omura K, Harada H, Nakaso K, Iwasa S, Koyama Y, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 expression predicts cervical lymph node metastasis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2004. 40:21–27.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Inhibition of Heme Oxygenase-1 on Chemosensitivity of Cisplatin in Lung Cancer Cells
- Efficacy of Combination Chemotherapy with Paclitaxel and Cisplatin in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Effects of Combination Chemotherapy Depending on The Expression of Neuron Specific Enolase (NSE), P-Glycoprotein (PgP) and Glutathione S-Transferase (GST)-pai in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Chemotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer