Restor Dent Endod.
2014 Aug;39(3):226-229.
An esthetic appliance for the management of crown-root fracture: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Advanced General Dentistry, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. jby1004@yuhs.ac
Abstract
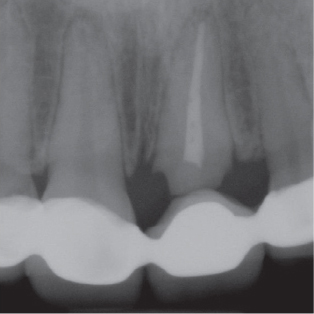
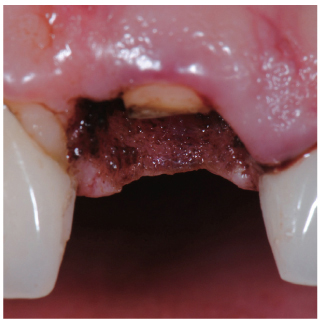
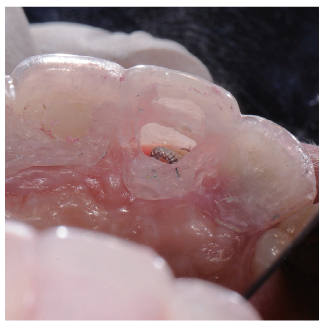
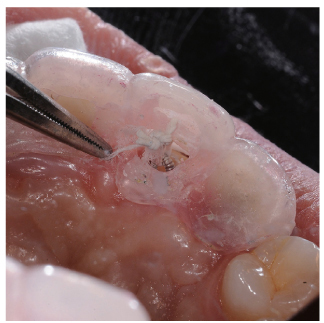
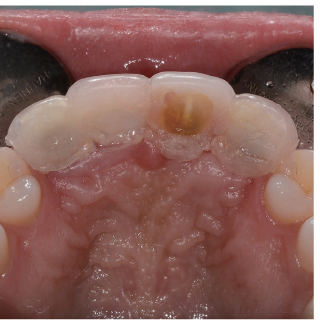
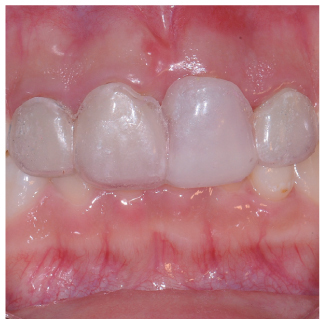
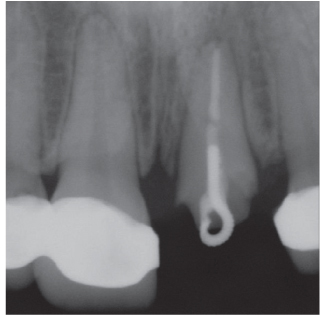
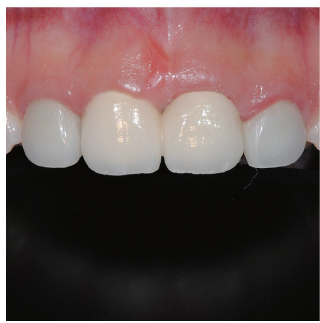
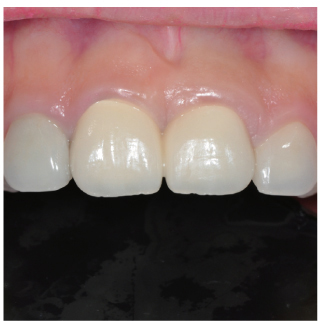
- Orthodontic extrusion is usually performed by means of a fixed orthodontic appliance that utilizes arch wire attached to adjacent teeth and transfers the desired force by elastic from the wire to the root. However, clinicians often encounter cases where the bonding required for tooth traction is not possible because the adjacent teeth have been restored with ceramic or veneer. The purpose of this case report is to describe a modified orthodontic extrusion appliance that is useful when conventional orthodontic treatment is not possible. The modified appliance was fabricated using an artificial tooth, clear plastic sheeting, and a braided fiber-reinforced composite strip that covered adjacent teeth without bonding. It satisfied the esthetic and functional needs of the patient and established the optimal biologic width.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aggarwal V, Logani A, Shah N. Complicated crown fractures - management and treatment options. Int Endod J. 2009; 42:740–753.
Article2. Garrett GB. Forced eruption in the treatment of transverse root fractures. J Am Dent Assoc. 1985; 111:270–272.
Article3. Simon JH. Root extrusion. Rationale and techniques. Dent Clin North Am. 1984; 28:909–921.4. Ingber JS. Forced eruption. I. A method of treating isolated one and two wall infrabony osseous defects-rationale and case report. J Periodontol. 1974; 45:199–206.
Article5. Heithersay GS. Combined endodontic-orthodontic treatment of transverse root fractures in the region of the alveolar crest. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973; 36:404–415.
Article6. Ribeiro JG, Segalla JC, Perez F, Ribeiro JC, Moyses MR. Effect of ceramic surface treatment on the shear bond strength of a resin cement to different ceramic systems. Gen Dent. 2012; 60:e315–e320.7. Ziskind D, Schmidt A, Hirschfeld Z. Forced eruption technique: rationale and clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 1998; 79:246–248.
Article8. Emerich-Poplatek K, Sawicki L, Bodal M, Adamowicz-Klepalska B. Forced eruption after crown/root fracture with a simple and aesthetic method using the fractured crown. Dent Traumatol. 2005; 21:165–169.
Article9. Veis R, Salzer A, Christian J. Manual of appliance therapy for adults and children. Los Angeles, CA: Space Maintainers Laboratory;1994.10. Felippe LA, Monteiro Junior S, Vieira LC, Araujo E. Reestablishing biologic width with forced eruption. Quintessence Int. 2003; 34:733–738.11. Uddin M, Mosheshvili N, Segelnick SL. A new appliance for forced eruption. N Y State Dent J. 2006; 72:46–50.12. Oshagh M, Sadeghi AR, Sharafeddin F, Alavi AA, Amid R, Derafshi R. Forced eruption by fiber-reinforced composite. Dent Today. 2009; 28:666870–71.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Esthetic restoration of subgingival crown-root fractured maxillary anterior tooth using surgical extrusion
- Esthetic enhancement of a traumatized anterior tooth with a combination of forced eruption and tooth alignment: a case report
- Report on a case treated with lingual multibracket appliance
- Treatment of crown-root fracture with a modified crown fragment reattachment technique
- A multidisciplinary approach to restore crown-root fractured maxillary central incisors: orthodontic extrusion and surgical extrusion