Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2015 Jun;18(2):134-137. 10.5223/pghn.2015.18.2.134.
A Case of Intussusception with Acute Appendicitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. meltemp2@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2315561
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.2.134
Abstract
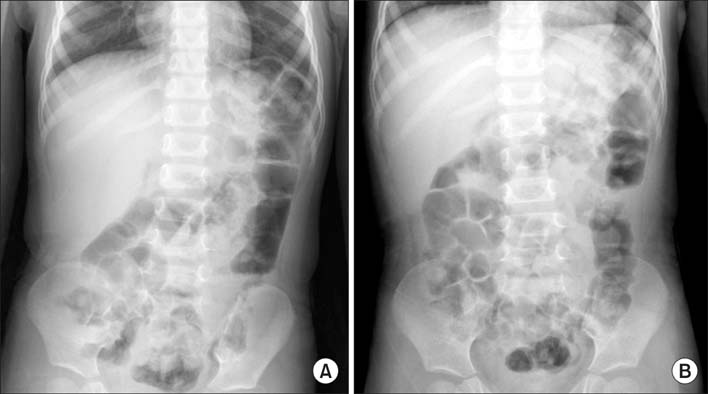
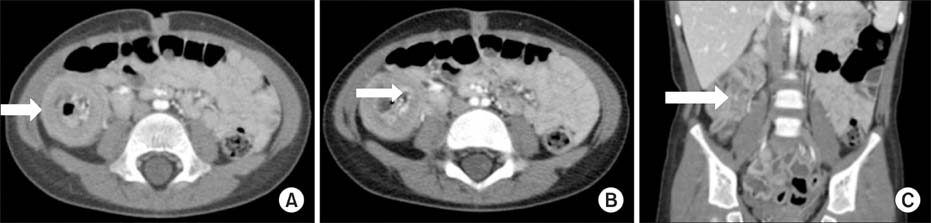
- In children presenting to hospital with gastrointestinal symptoms, diseases such as intussusception and acute appendicitis require particular attention and careful examination. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are important because of possible severe complications such as peritonitis and death. Intussusception and appendicitis share similar clinical manifestations. More importantly, the presence of acute appendicitis together with intussusception in children is very rare. We describe an interesting case of a 38-month-old boy who presented with abdominal pain in the right lower quadrant. His vital signs were stable and laboratory test findings showed no specific alterations. We detected tenderness in the right lower quadrant. A computed tomography scan showed an ileocolic intussusception with no strangulation and diffuse wall thickening of the appendix trapped within the intussusception. The patient underwent an appendectomy and manual reduction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McCollough M, Sharieff GQ. Abdominal surgical emergencies in infants and young children. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2003; 21:909–935.
Article2. Kim JS. Acute abdominal pain in children. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2013; 16:219–224.
Article3. Jiang J, Jiang B, Parashar U, Nguyen T, Bines J, Patel MM. Childhood intussusception: a literature review. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e68482.
Article4. Hardin DM Jr. Acute appendicitis: review and update. Am Fam Physician. 1999; 60:2027–2034.5. Peyvasteh M, Askarpour S, Javaherizadeh H, Beigom Al-Taha B. Intussuception at atypical ages in children and adults--11 years experiences. Pol Przegl Chir. 2011; 83:304–309.6. Cochran AA, Higgins GL 3rd, Strout TD. Intussusception in traditional pediatric, nontraditional pediatric, and adult patients. Am J Emerg Med. 2011; 29:523–527.
Article7. Ksia A, Mosbahi S, Brahim MB, Sahnoun L, Haggui B, Youssef SB, et al. Recurrent intussusception in children and infants. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2013; 10:299–301.
Article8. Mills RW, McCrudden K, Gupta VK, Britton A, Al Qahtani M, Hasan RA. Intussusception caused by heterotopic pancreatic tissue in a child. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2011; 30:106–110.
Article9. Sonmez K, Turkyilmaz Z, Demirogullari B, Karabulut R, Kale N, Basaklar AC. Intussusception in children: experience with 105 patients in a department of paediatric surgery, Turkey. S Afr J Surg. 2012; 50:37–39.10. Soccorso G, Puls F, Richards C, Pringle H, Nour S. A ganglioneuroma of the sigmoid colon presenting as leading point of intussusception in a child: a case report. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:e17–e20.
Article11. Gal R, Kolkow Z, Nobel M. Adenomyomatous hamartoma of the small intestine: a rare cause of intussusception in an adult. Am J Gastroenterol. 1986; 81:1209–1211.12. Gurbulak B, Kabul E, Dural C, Citlak G, Yanar H, Gulluoglu M, et al. Heterotopic pancreas as a leading point for small-bowel intussusception in a pregnant woman. JOP. 2007; 8:584–587.13. Bevan PG. Intussusception and acute appendicitis. Br Med J. 1957; 1:931–932.
Article14. Kang J, Lee KY, Sohn SK. Cecocolic intussusception in adult caused by acute appendicitis. Case Rep Surg. 2014; 2014:108327.
Article15. Lee CT, Lien WC, Wang HP, Lin BR, Huang PH, Lin JT. Primary appendiceal adenocarcinoma with cecocolic intussusception. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 21:1079–1081.
Article16. Pepper VK, Stanfill AB, Pearl RH. Diagnosis and management of pediatric appendicitis, intussusception, and Meckel diverticulum. Surg Clin North Am. 2012; 92:505–526. vii
Article17. Mc Cabe K, Babl FE, Dalton S. Paediatric Research in Emergency Departments International Collaborative (PREDICT). Management of children with possible appendicitis: a survey of emergency physicians in Australia and New Zealand. Emerg Med Australas. 2014; 26:481–486.
Article18. Cheong LH, Emil S. Outcomes of pediatric appendicitis: an international comparison of the United States and Canada. JAMA Surg. 2014; 149:50–55.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ileocecocolic Intussusception Induced by Acute Appendicitis: A Case Report
- Imaging Findings of Gastrointestinal Emergency in Infants and Young Children
- Appendiceal Intussusception Showing Various Shapes During a Colonoscopy
- Ileocolic Intussusception Accompanied with Inflamed Appendix: 2 Case Reports
- Adult Intussusception Caused by an Appendiceal Mucocele and Reduced by Colonoscopy