Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2015 Mar;18(1):48-54. 10.5223/pghn.2015.18.1.48.
Liver Transplantation for Metabolic Liver Disease: Experience at a Living Donor Dominant Liver Transplantation Center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Korea. kmkim@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Division of Hepato-Biliary Surgery and Liver Transplantation, Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2315535
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.1.48
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Metabolic liver disease (MLD) often progresses to life-threatening conditions. This study intends to describe the outcomes of liver transplantation (LTx) for MLD at a living donor-dominant transplantation center where potentially heterozygous carrier grafts are employed.
METHODS
We retrospectively evaluated the medical records of 54 patients with MLD who underwent LTx between November 1995 and February 2012 at Asan Medical Center in Seoul, Korea. The cumulative graft and patient survival rates were analyzed according to patient age, and living or deceased donor LTx. Recurrence of the original disease was also investigated.
RESULTS
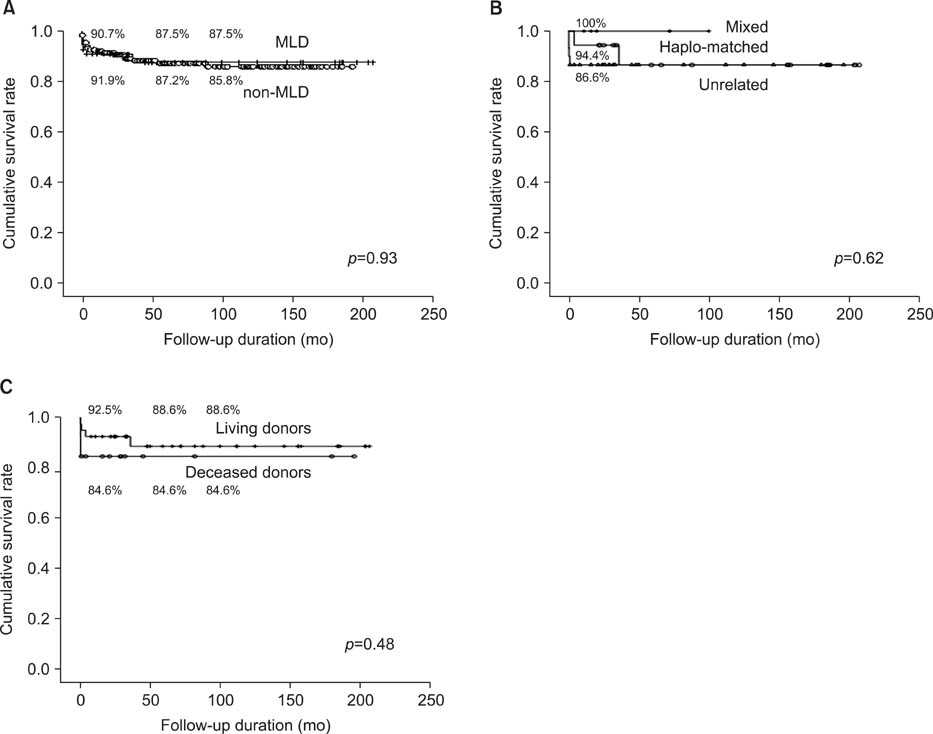
The post-transplant cumulative patient survival rates at one, five, and 10 years were 90.7%, 87.5% and 87.5%, and the graft survival rates were 88.8%, 85.5%, and 85.5%, respectively. There were no differences in the patient survival rates according to the recipient age, human leukocyte antigen matching, and living or deceased donor LTx. There were also no differences in the patient survival rates between the MLD and the non-MLD groups for children. Recurrence of the original metabolic disease was not observed in any patient during the follow-up period.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that the living donor-dominant transplantation program is well-tolerated in MLD without recurrence of the original MLD using all types of transplantation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Changes in the indications for living donor liver transplantation: single-institution experience of 3,145 cases over 10 years
Sang-Hyun Kang, Shin Hwang, Chul-Soo Ahn, Ki-Hun Kim, Deok-Bog Moon, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gil-Chun Park, Jung-Man Namgoong, Young-In Yoon, Hui-Dong Cho, Jae-Hyun Kwon, Yong-Kyu Chung, Jin-Uk Choi, Sung-Gyu Lee
Korean J Transplant. 2020;34(1):47-54. doi: 10.4285/kjt.2020.34.1.47.Complete Recovery of Oxysterol 7α-Hydroxylase Deficiency by Living Donor Transplantation in a 4-Month-Old Infant: the First Korean Case Report and Literature Review
Jeana Hong, Seak Hee Oh, Han-Wook Yoo, Hiroshi Nittono, Akihiko Kimura, Kyung Mo Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(51):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e324.
Reference
-
1. Shneider BL. Pediatric liver transplantation in metabolic di'sease: clinical decision making. Pediatr Transplant. 2002; 6:25–29.
Article2. Oh SH, Kim KM, Kim DY, Lee YJ, Rhee KW, Jang JY, et al. Long-term outcomes of pediatric living donor liver transplantation at a single institution. Pediatr Transplant. 2010; 14:870–878.
Article3. Oh SH, Kim KM, Kim DY, Song SM, Kim T, Hwang S, et al. Clinical experience of more than 200 cases of pediatric liver transplantation at a single center: improved patient survival. Transplant Proc. 2012; 44:484–486.
Article4. Arnon R, Kerkar N, Davis MK, Anand R, Yin W, González-Peralta RP. SPLIT Research Group. Liver transplantation in children with metabolic diseases: the studies of pediatric liver transplantation experience. Pediatr Transplant. 2010; 14:796–805.
Article5. Bellary S, Hassanein T, Van Thiel DH. Liver transplantation for Wilson's disease. J Hepatol. 1995; 23:373–381.
Article6. Sternlieb I, Scheinberg IH. The role of radiocopper in the diagnosis of Wilson's disease. Gastroenterology. 1979; 77:138–142.
Article7. Asonuma K, Inomata Y, Kasahara M, Uemoto S, Egawa H, Fujita S, et al. Living related liver transplantation from heterozygote genetic carriers to children with Wilson's disease. Pediatr Transplant. 1999; 3:201–205.
Article8. Kim JT, Chang SH, Choi BH, Kim KM, Yoo HW, Lee YJ, et al. Living-related liver transplantation with heterozygote carrier graft in children with wilson disease. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003; 6:161–166.
Article9. Roche-Sicot J, Benhamou JP. Acute intravascular hemolysis and acute liver failure associated as a first manifestation of Wilson's disease. Ann Intern Med. 1977; 86:301–303.
Article10. Hwang S, Lee SG, Lee YJ, Sung KB, Park KM, Kim KH, et al. Lessons learned from 1,000 living donor liver transplantations in a single center: how to make living donations safe. Liver Transpl. 2006; 12:920–927.
Article11. Kim BS, Kim KM, Yoo HW, Lee SG. A case of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency successfully treated with protein restriction and living related liver transplantation. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1999; 42:868–873.12. Kayler LK, Rasmussen CS, Dykstra DM, Punch JD, Rudich SM, Magee JC, et al. Liver transplantation in children with metabolic disorders in the United States. Am J Transplant. 2003; 3:334–339.
Article13. Sze YK, Dhawan A, Taylor RM, Bansal S, Mieli-Vergani G, Rela M, et al. Pediatric liver transplantation for metabolic liver disease: experience at King's College Hospital. Transplantation. 2009; 87:87–93.
Article14. Morioka D, Kasahara M, Takada Y, Corrales JP, Yoshizawa A, Sakamoto S, et al. Living donor liver transplantation for pediatric patients with inheritable metabolic disorders. Am J Transplant. 2005; 5:2754–2763.
Article15. Lee BH, Kim JH, Lee SY, Jin HY, Kim KJ, Lee JJ, et al. Distinct clinical courses according to presenting phenotypes and their correlations to ATP7B mutations in a large Wilson's disease cohort. Liver Int. 2011; 31:831–839.
Article16. Stracciari A, Tempestini A, Borghi A, Guarino M. Effect of liver transplantation on neurological manifestations in Wilson disease. Arch Neurol. 2000; 57:384–386.
Article17. Marin C, Robles R, Parrilla G, Ramírez P, Bueno FS, Parrilla P. Liver transplantation in Wilson's disease: are its indications established? Transplant Proc. 2007; 39:2300–2301.
Article18. Medici V, Mirante VG, Fassati LR, Pompili M, Forti D, Del Gaudio M, et al. Monotematica AISF 2000 OLT Study Group. Liver transplantation for Wilson's disease: The burden of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:1056–1063.
Article19. Kassam N, Witt N, Kneteman N, Bain VG. Liver transplantation for neuropsychiatric Wilson disease. Can J Gastroenterol. 1998; 12:65–68.
Article20. Yoshitoshi EY, Takada Y, Oike F, Sakamoto S, Ogawa K, Kanazawa H, et al. Long-term outcomes for 32 cases of Wilson's disease after living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2009; 87:261–267.
Article21. Franco LM, Krishnamurthy V, Bali D, Weinstein DA, Arn P, Clary B, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in glycogen storage disease type Ia: a case series. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005; 28:153–162.
Article22. Mazariegos G, Shneider B, Burton B, Fox IJ, Hadzic N, Kishnani P, et al. Liver transplantation for pediatric metabolic disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2014; 111:418–427.
Article23. Häberle J, Boddaert N, Burlina A, Chakrapani A, Dixon M, Huemer M, et al. Suggested guidelines for the diagnosis and management of urea cycle disorders. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012; 7:32.
Article24. Angelis M, Pegelow CH, Khan FA, Verzaro R, Tzakis AG. En bloc heterotopic auxiliary liver and bilateral renal transplant in a patient with homozygous protein C deficiency. J Pediatr. 2001; 138:120–122.
Article25. Ryu J, Shin YH, Ko JS, Gwak MS, Kim GS. Intractable metabolic acidosis in a child with propionic acidemia undergoing liver transplantation -a case report-. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013; 65:257–261.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pediatric liver transplantation in Korea: long-term outcomes and allocations
- Endoscopic management of anastomotic stricture after living-donor liver transplantation
- Left at right heterotopic implantation of left liver graft in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: the technical concern for decision-making
- Liver retransplantation for adult recipients
- Clinical implication of hepatic volumetry for living donor liver transplantation