Korean J Leg Med.
2014 Feb;38(1):8-12. 10.7580/kjlm.2014.38.1.8.
A Classification of Asphyxia Autopsy Cases of the Korea in 2012 according to New Classification of Asphyxia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Forensic Medicine Division, Gwangju Institute of Scientific Investigation, Jangseong-gun, Jeollanam, Korea. pdrdream@gmail.com
- 2Forensic Medical Center, National Forensic Service, Wonju-si, Gangwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Forensic Medicine Investigation, Seoul Institute of Scientific Investigation, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2305458
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2014.38.1.8
Abstract
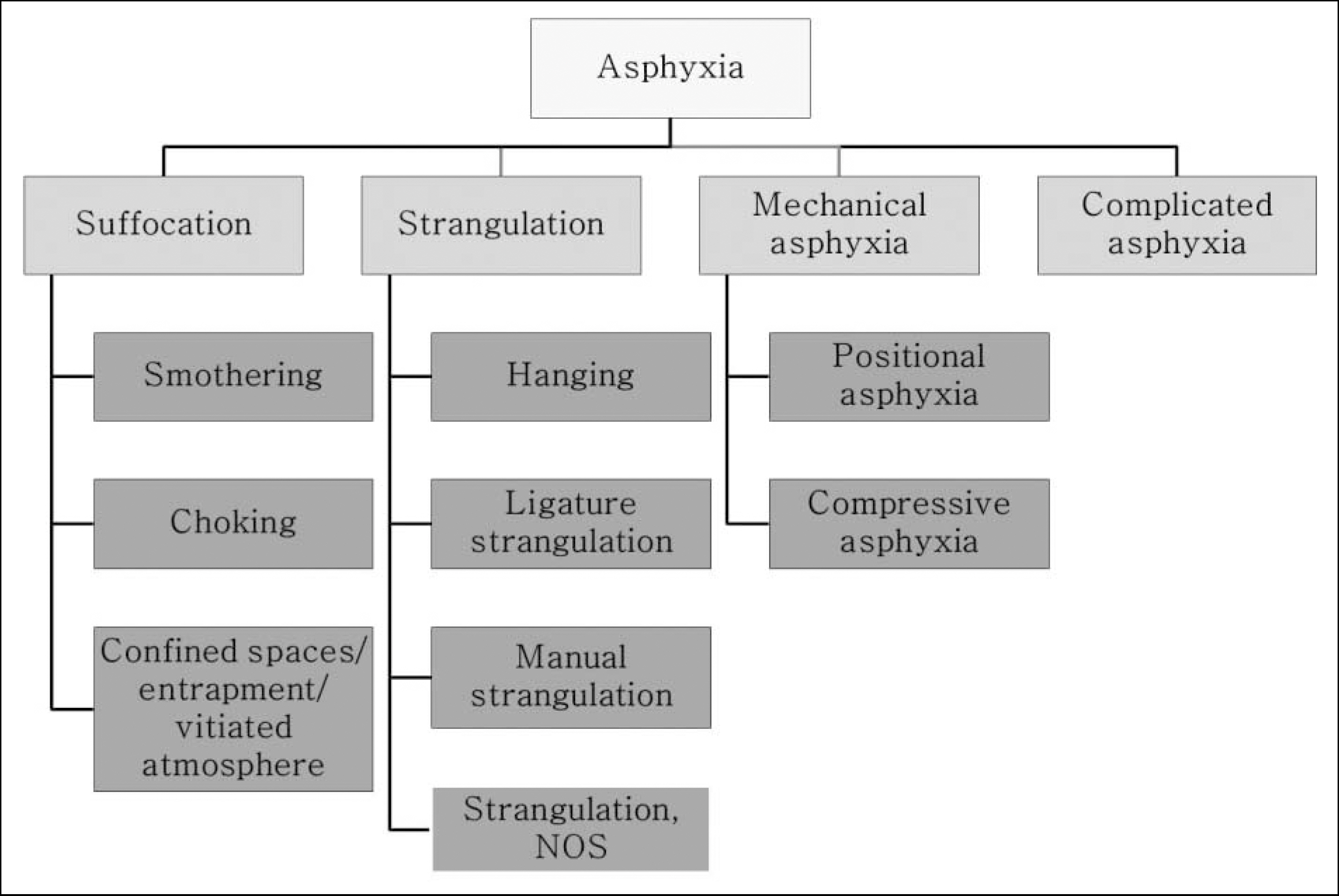
- No accepted standard currently exists to classify asphyxia and define its subtypes. Sauvageau and Boghossian proposed an asphyxia classification system in 2010 that divided asphyxia into suffocation, strangulation, mechanical asphyxia, and drowning. Here, we present a modification of this classification system. We propose to classify asphyxia into four main categories: suffocation, strangulation, mechanical asphyxia, and complicated asphyxia. Suffocation includes smothering and choking as well as confined spaces, entrapment, and vitiated atmosphere. Strangulation is subdivided into hanging, ligature strangulation, manual strangulation, and other unspecified strangulation. Mechanical asphyxia includes positional and traumatic asphyxia. Finally, complicated asphyxia is defined as cases with two or more identifiable mechanisms of asphyxia. In this study, we review autopsy cases from 2012 diagnosed as asphyxia and classify them according to our proposed asphyxia classification system. In 24.7% of cases, the age range was 40-49 years, and 51.9% were men. The most common method of asphyxia was hanging (245 cases, 55.1%), followed by ligature or manual strangulation (53 cases, 11.9%). Most hangings were suicides; smothering, ligature, and manual strangulation were usually homicides. Eighteen cases were complicated asphyxia. This classification provides a simplified, unified, and useful tool to classify and understand deaths due to asphyxia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
A Statistical Analysis on Forensic Autopsies Performed in Korea in 2017
Ji Hye Park, Joo-Young Na, Bong Woo Lee, Kyung-moo Yang, Young Shik Choi
Korean J Leg Med. 2018;42(4):111-125. doi: 10.7580/kjlm.2018.42.4.111.A Statistical Analysis on Forensic Autopsies Performed in Korea in 2016
Ji Hye Park, Joo-Young Na, Bong Woo Lee, Young Shik Choi
Korean J Leg Med. 2018;42(1):8-21. doi: 10.7580/kjlm.2018.42.1.8.A Statistical Analysis on Forensic Autopsies Performed in Korea in 2015
Ji Hye Park, Joo-Young Na, Bong Woo Lee, Nak Eun Chung, Young Shik Choi
Korean J Leg Med. 2016;40(4):104-118. doi: 10.7580/kjlm.2016.40.4.104.
Reference
-
1. Yun JJ. Forensic medicine. Seoul: Korea Medical Publisher;1993. p. 126–63.2. Kang HW, Lee SD. Asphyxia. Kang DY, Kang HW, Kwak JS, editors. ed.A textbook of legal medicine. Seoul: Jungmunkag;2007. p. 215–42.3. Sauvageau A, Boghossian E. Classification of asphyxia: the need for standardization. J Forensic Sci. 2010; 55:1259–67.
Article4. Na JY, Park JP, Park HJ, et al. The statistical analysis on legal autopsy performed in Korea during 2012 year. Korean J Leg Med. 2013; 37:198–207.
Article5. Byard RW. Commentary on: Sauvageau A, Boghossian E. Classification of asphyxia: the need for standardization. J Foresnic Sci. 2012; 55(5):): 1259-67. J Forensic Sci 2011;56:. 264.6. Azmak D. Asphyxial deaths: a retrospective study and review of the literature. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2006; 27:134–44.7. Wyatt JP, Wyatt PW, Squires TJ, et al. Hanging deaths in children. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1998; 19:343–46.
Article8. Rodge S, Hougen HP, Poulsen K. Asphyxial homicide in two Scandinavian capitals. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2001; 22:128–33.9. Lupascu C, Lupascu C, Beldiman D. Mechanical asphyxia by three different mechanisms. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2003; 5:110–1.
Article10. Abder-Rahman HA, Abu-Alrageb SY. Killing tools in mechanical asphyxia. Legal Med. 1999; 1:2–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unusual Asphyxia: Two Autopsy Cases Report
- An Unusual Case of Asphyxia by Ligature about the Thorax
- Positional Asphyxia of the Paralyzed: Implicated on the View of Death Scene
- Asphyxia Due to Oxygen Deficiency: The Report of Two Autopsy Cases
- Analysis of Cases of Infants and Children Asphyxia at Day Care Center: Cases of Asphyxia in the Process of Teachers Putting the Infants and Children to Sleep