Korean J Hematol.
2007 Sep;42(3):292-295. 10.5045/kjh.2007.42.3.292.
A Case of High Dose Cytosine Arabinoside Induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Patient with Malignant Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Catholic University Medical College, Seoul, Korea. y331@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2305206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2007.42.3.292
Abstract
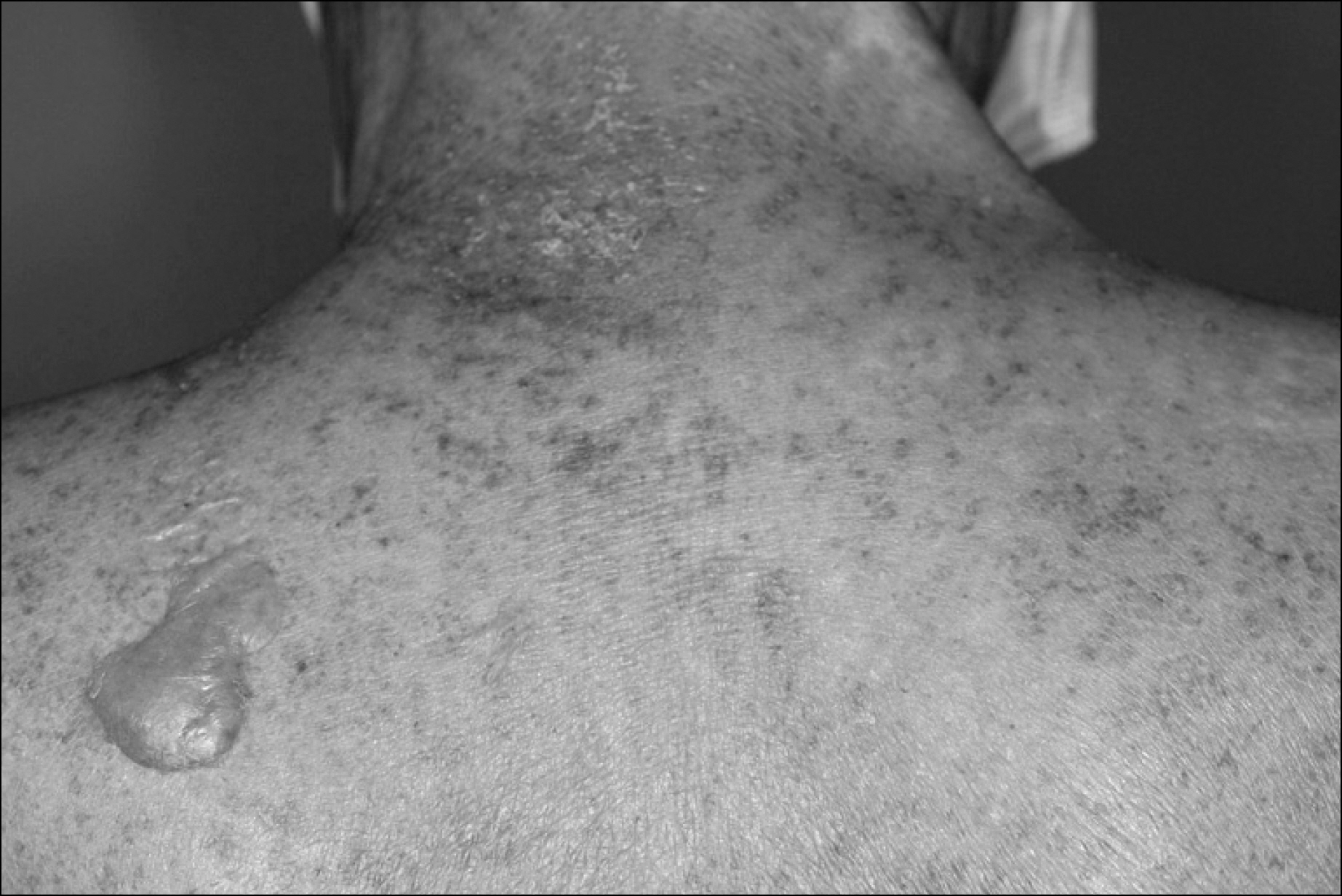
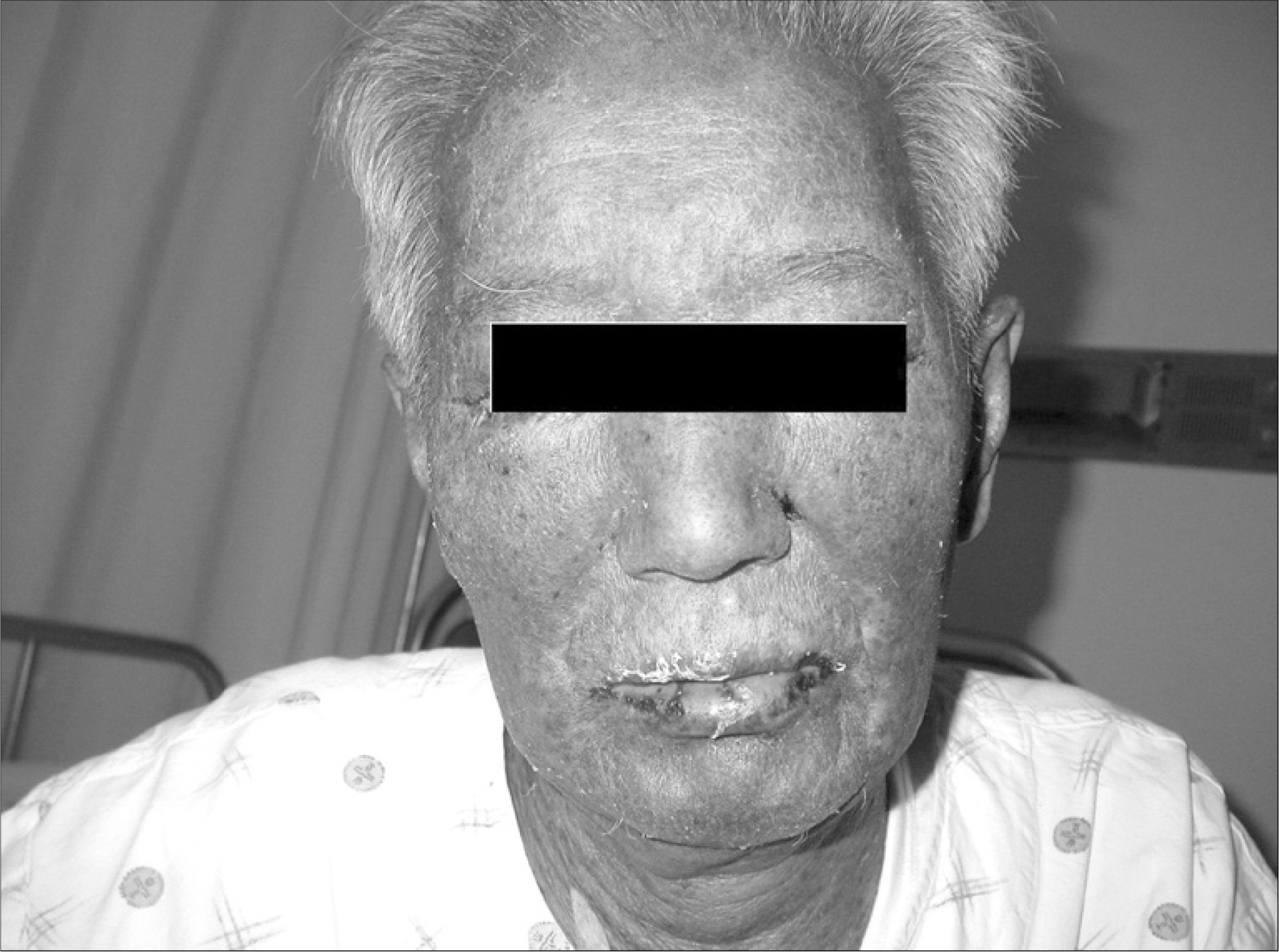
- Many chemotherapeutic agents induce variable cutaneous adverse reactions. Among the side effects, Stevens-Johnson syndrome is rare, but a fatal complication. There are two prior reports of cytosine arabinoside (ARA-C) induced toxic epidermal necrolysis, which is considered in the continuum of Stevens- Johnson syndrome. The prior cases were female patients under 16 years old with acute lymphocytic leukemia. We treated a 77-year-old man with recurrent mantle cell lymphoma who developed Stevens- Johnson syndrome after high dose ARA-C therapy. This is the first case of ARA-C induced Stevens- Johnson syndrome in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Abeloff MD., Armitage JO., Niederhuber JE., Kastan MB., McKenna WG. Clinical oncology. 3rd ed.Pennsylvania, USA: Elsevier;2004. p. 793–816.2). Roujeau JC., Stern RS. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994. 331:1272–85.
Article3). Ozkan A., Apak H., Celkan T., Yuksel L., Yildiz I. Toxic epidermal necrolysis after the use of high-dose cytosine arabinoside. Pediatr Dermatol. 2001. 18:38–40.4). Figueiredo MS., Yamamoto M., Kerbauy J. Toxic epidermal necrolysis after the use of intermediate dose of cytosine arabinoside. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 1998. 44:53–5.5). Graves T., Hooks MA. Drug-induced toxicities associated with high-dose cytosine arabinoside infusions. Pharmacotherapy. 1989. 9:23–8.
Article6). Cetkovsk P., Pizinger K., Cetkovsk P. High-dose cytosine arabinoside-induced cutaneous reactions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2002. 16:481–5.7). Khalili B., Bahna SL. Pathogenesis and recent therapeutic trends in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006. 97:272–80.
Article8). Hynes AY., Kafkala C., Daoud YJ., Foster CS. Controversy in the use of high-dose systemic steroids in the acute care of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2005. 45:25–48.
Article9). Severino G., Chillotti C., De Lisa R., Del Zompo M., Ardau R. Adverse reactions during imatinib and lansoprazole treatment in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Ann Pharmacother. 2005. 39:162–4.
Article10). Hsiao LT., Chung HM., Lin JT, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome after treatment with STI571: a case report. Br J Haematol. 2002. 117:620–2.
Article11). Hiraki A., Aoe K., Murakami T., Maeda T., Eda R., Takeyama H. Stevens-Johnson syndrome induced by paclitaxel in a patient with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: a case report. Anticancer Res. 2004. 24:1135–7.12). Moisidus C., Mobus V. Erythema multiforme major following docetaxel. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2005. 271:267–9.
Article13). Sommers KR., Kong KM., Bui DT., Fruehauf JP., Holcombe RF. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient receiving concurrent radiation and gemcitabine. Anticancer Drugs. 2003. 14:659–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cerebral Syndrome Associated with High-Dose Cytosine Arabinoside Chemotherapy
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Hypoxic Brain Injury Patient Treated with Carbamazepine
- A Case of Methotrexate-induced Bullous Acral Erythema
- Five Cases of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome May Be Associated with Methazolamide Treatment
- Clinical Study of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome