Korean J Sports Med.
2012 Jun;30(1):1-8. 10.5763/kjsm.2012.30.1.1.
The Management of Knee Dislocation and Multiple Ligament Injuries
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Chodang University, Muan, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. cch@wonkwang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2288642
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2012.30.1.1
Abstract
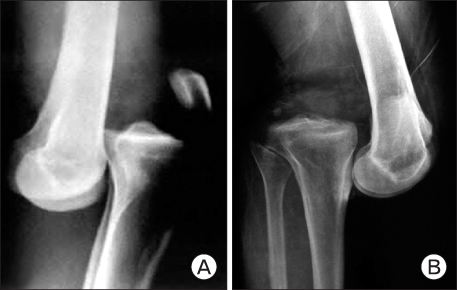
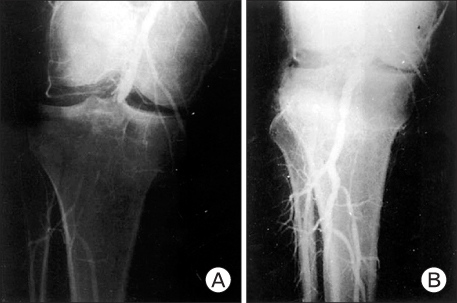
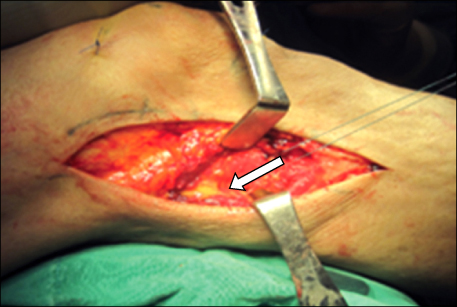
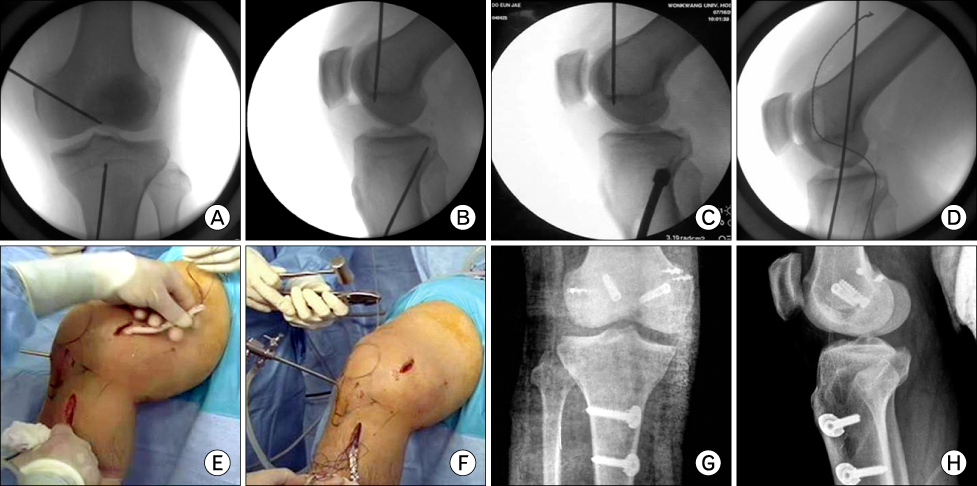
- Multiple ligament injuries of the knee means more than two ligament injuries, using as an analogue of the knee dislocation. The first priority in the early diagnosis and treatment of the knee dislocation is a vascular evaluation of extremity and careful neurovascular examination should be done firstly. It is common opinion in the treatment of multiple ligament injuries that surgical treatment is superior to conservative treatment. Especially, early ligament repair or reconstruction and aggressive rehabilitation are recommended in young active patients.
Keyword
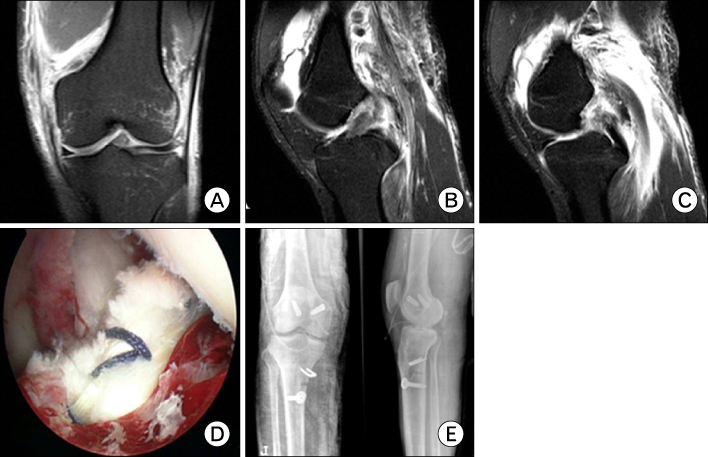
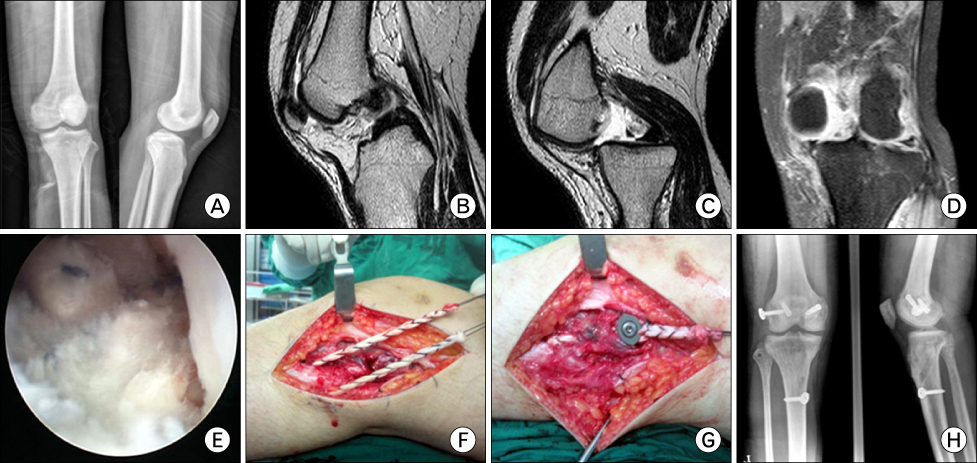
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wascher DC, Dvirnak PC, DeCoster TA. Knee dislocation: initial assessment and implications for treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 1997. 11:525–529.2. Good L, Johnson RJ. The Dislocated Knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1995. 3:284–292.3. Kennedy JC. Complete Dislocation of the Knee Joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1963. 45:889–904.4. McCoy GF, Hannon DG, Barr RJ, Templeton J. Vascular injury associated with low-velocity dislocations of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987. 69:285–287.5. Wascher DC. High-velocity knee dislocation with vascular injury. Treatment principles. Clin Sports Med. 2000. 19:457–477.6. Green NE, Allen BL. Vascular injuries associated with dislocation of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:236–239.7. Noyes FR, Grood ES. The strength of the anterior cruciate ligament in humans and Rhesus monkeys. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976. 58:1074–1082.8. Hill JA, Rana NA. Complications of posterolateral dislocation of the knee: case report and literature review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981. 154:212–215.9. Shelbourne KD, Haro MS, Gray T. Knee dislocation with lateral side injury: results of an en masse surgical repair technique of the lateral side. Am J Sports Med. 2007. 35:1105–1116.10. Shelbourne KD, Porter DA, Clingman JA, McCarroll JR, Rettig AC. Low-velocity knee dislocation. Orthop Rev. 1991. 20:995–1004.11. Hughston JC, Andrews JR, Cross MJ, Moschi A. Classification of knee ligament instabilities. Part II. The lateral compartment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976. 58:173–179.12. Mills WJ, Barei DP, McNair P. The value of the ankle-brachial index for diagnosing arterial injury after knee dislocation: a prospective study. J Trauma. 2004. 56:1261–1265.13. Levy BA, Zlowodzki MP, Graves M, Cole PA. Screening for extermity arterial injury with the arterial pressure index. Am J Emerg Med. 2005. 23:689–695.14. Redmond JM, Levy BA, Dajani KA, Cass JR, Cole PA. Detecting vascular injury in lower-extremity orthopedic trauma: the role of CT angiography. Orthopedics. 2008. 31:761–767.15. Rihn JA, Groff YJ, Harner CD, Cha PS. The acutely dislocated knee: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004. 12:334–346.16. Urguden M, Bilbasar H, Ozenci AM, Akyildiz FF, Gur S. Irreducible posterolateral knee dislocation resulting from a low-energy trauma. Arthroscopy. 2004. 20:Suppl 2. 50–53.17. Levy BA, Dajani KA, Whelan DB, et al. Decision making in the multiligament-injured knee: an evidence-based systematic review. Arthroscopy. 2009. 25:430–438.18. Schenck RC Jr, Hunter RE, Ostrum RF, Perry CR. Knee dislocations. Instr Course Lect. 1999. 48:515–522.19. Shelbourne KD, Wilckens JH, Mollabashy A, DeCarlo M. Arthrofibrosis in acute anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. The effect of timing of reconstruction and rehabilitation. Am J Sports Med. 1991. 19:332–336.20. Tzurbakis M, Diamantopoulos A, Xenakis T, Georgoulis A. Surgical treatment of multiple knee ligament injuries in 44 patients: 2-8 years follow-up results. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006. 14:739–749.21. Noyes FR, Barber-Westin SD. Reconstruction of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments after knee dislocation. Use of early protected postoperative motion to decrease arthrofibrosis. Am J Sports Med. 1997. 25:769–778.22. Chun CH, Han JK. Arthroscopic assisted simultaneously ACL and PCL reconstruction in knee dislocation. Korean J Sports Med. 2006. 24:89–96.23. Chun CH. Multiple ligament injury of Knee. Instr Course Lect. 2011. Seoul: Korean Orthop Assoc;23–29.24. Liow RY, McNicholas MJ, Keating JF, Nutton RW. Ligament repair and reconstruction in traumatic dislocation of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003. 85:845–851.25. Harner CD, Waltrip RL, Bennett CH, Francis KA, Cole B, Irrgang JJ. Surgical management of knee dislocations. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86-A:262–273.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Multiple Ligaments Injuries
- Reconstuction of the Anterior and Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Associated with Traumatic Knee Joint Dislocation: Six Cases of Reconstruction Using Autogenous Achilles Tendon
- Ipsilateral Tibial Shaft Fractures and Knee Ligament Injuries
- Operative Treatment of Traumatic Dislocation of the Knee Joint: Result of Staged Reconstruction of Cruciate Ligament
- Dislocation of Tibial Insert after Fixed Bearing TKA using Minimal Invasive Surgery: A Case Report