Prevalence of Anti-Ganglioside Antibodies and Their Clinical Correlates with Guillain-Barre Syndrome in Korea: A Nationwide Multicenter Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea. jsb_res@hotmail.co.kr
- 3Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Kinki University, Osaka, Japan.
- 5Department of Industrial and Occupational Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 8Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 9Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea.
- 10Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
- 11Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 14Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- 15Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 16Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 17Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 18Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan, Korea.
- 19Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea.
- 20Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 21Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 22Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2287526
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.2.94
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
No previous studies have investigated the relationship between various anti-ganglioside antibodies and the clinical characteristics of Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) in Korea. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence and types of anti-ganglioside antibodies in Korean GBS patients, and to identify their clinical significance.
METHODS
Serum was collected from patients during the acute phase of GBS at 20 university-based hospitals in Korea. The clinical and laboratory findings were reviewed and compared with the detected types of anti-ganglioside antibody.
RESULTS
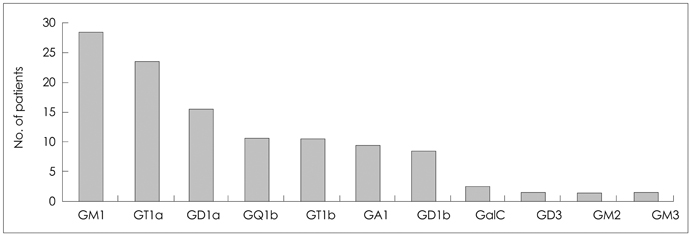
Among 119 patients, 60 were positive for immunoglobulin G (IgG) or immunoglobulin M antibodies against any type of ganglioside (50%). The most frequent type was IgG anti-GM1 antibody (47%), followed by IgG anti-GT1a (38%), IgG anti-GD1a (25%), and IgG anti-GQ1b (8%) antibodies. Anti-GM1-antibody positivity was strongly correlated with the presence of preceding gastrointestinal infection, absence of sensory symptoms or signs, and absence of cranial nerve involvement. Patients with anti-GD1a antibody were younger, predominantly male, and had more facial nerve involvement than the antibody-negative group. Anti-GT1a-antibody positivity was more frequently associated with bulbar weakness and was highly associated with ophthalmoplegia when coupled with the coexisting anti-GQ1b antibody. Despite the presence of clinical features of acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN), 68% of anti-GM1- or anti-GD1a-antibody-positive cases of GBS were diagnosed with acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP) by a single electrophysiological study.
CONCLUSIONS
Anti-ganglioside antibodies were frequently found in the serum of Korean GBS patients, and each antibody was correlated strongly with the various clinical manifestations. Nevertheless, without an anti-ganglioside antibody assay, in Korea AMAN is frequently misdiagnosed as AIDP by single electrophysiological studies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 10 articles
-
Early Electrodiagnostic Features of Upper Extremity Sensory Nerves Can Differentiate Axonal Guillain-Barré Syndrome from Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
Yong Seo Koo, Ha Young Shin, Jong Kuk Kim, Tai-Seung Nam, Kyong Jin Shin, Jong-Seok Bae, Bum Chun Suh, Jeeyoung Oh, Byeol-A Yoon, Byung-Jo Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(4):495-501. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.4.495.Guillain-Barré and Miller Fisher Overlap Syndrome Mimicking Alimentary Botulism
Gabriela Moreno Legast, Agustina M. Lascano, Markus Gschwind, Armin Schnider, Nicolas Nicastro
J Clin Neurol. 2017;13(4):442-443. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.442.Clinical Heterogeneity of Anti-GM2-Ganglioside-Antibody Syndrome
Jong Kuk Kim, Yoo Hwan Kim, Byeol-A Yoon, Joong-Yang Cho, Sun-Young Oh, Ha Young Shin, Ji Soo Kim, Kee Hong Park, Sun Young Kim, Bum Chun Suh, Hung Youl Seok, Jin Hyuk Yoo, Jong Seok Bae
J Clin Neurol. 2018;14(3):401-406. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2018.14.3.401.Pattern of Extraocular Muscle Involvements in Miller Fisher Syndrome
Won Yeol Ryu, Yoo Hwan Kim, Byeol-A Yoon, Hwan Tae Park, Jong Seok Bae, Jong Kuk Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(3):308-312. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.308.Recurrent Guillain-Barré Syndrome with Anti-GT1a and Anti-GQ1b Ganglioside Antibodies
Jihyeon Hwang, Ye-Ji Kwon, Jong Kuk Kim, Nam Jun Kim, Seol-Hee Baek
J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(3):404-406. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.404.A case of acute motor sensory axonal neuropathy presenting reversible conduction block
Dongah Lee, Hyung Chan Kim, Kang Min Park, Jinse Park, Sam Yeol Ha, Sung Eun Kim, Byung In Lee, Jong Kuk Kim, Byeola Yoon, Kyong Jin Shin
Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;20(1):49-52. doi: 10.14253/acn.2018.20.1.49.Miller Fisher syndrome mimicking Wer-nicke encephalopathy during pregnancy
Jung Hwa Seo, Mi-Ri Kang, Byeol-A Yoon, Ki-Hwan Ji, Seong-il Oh
Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;21(1):53-56. doi: 10.14253/acn.2019.21.1.53.A Variant Guillain-Barré Syndrome with Anti-Ganglioside Complex Antibody
So-Young Huh, So-Young Lee, Jin-Hyung Lee, Won Gu Lee, Jong Kuk Kim, Byeol-A Yoon, Nam Jun Kim
J Neurocrit Care. 2018;11(2):134-136. doi: 10.18700/jnc.180073.Isolated facial diplegia variant of Guillain–Barré syndrome with anti-GM1 IgG antibody
Jin Ho Jung, Sukyoon Lee, Jung Hwa Seo, Jong Seok Bae, Kyong Jin Shin, Jong Kuk Kim, Byeol-A Yoon, Seong-il Oh
Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;24(1):17-20. doi: 10.14253/acn.2022.24.1.17.A Case of Postoperative Guillain-Barré Syndrome After Nasal Surgery
Chan Ho Yoon, Young Bin Yun, Sangjun Kim, Woo Yong Bae
J Rhinol. 2023;30(1):53-56. doi: 10.18787/jr.2023.00011.
Reference
-
1. Asbury AK, Cornblath DR. Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990; 27:Suppl. S21–S24.
Article2. Hughes RA, Cornblath DR. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet. 2005; 366:1653–1666.
Article3. Kusunoki S, Shimizu J, Chiba A, Ugawa Y, Hitoshi S, Kanazawa I. Experimental sensory neuropathy induced by sensitization with ganglioside GD1b. Ann Neurol. 1996; 39:424–431.
Article4. Yuki N, Yamada M, Koga M, Odaka M, Susuki K, Tagawa Y, et al. Animal model of axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome induced by sensitization with GM1 ganglioside. Ann Neurol. 2001; 49:712–720.
Article5. Yuki N. Ganglioside mimicry and peripheral nerve disease. Muscle Nerve. 2007; 35:691–711.
Article6. Sekiguchi Y, Uncini A, Yuki N, Misawa S, Notturno F, Nasu S, et al. Antiganglioside antibodies are associated with axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome: a Japanese-Italian collaborative study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2012; 83:23–28.
Article7. Uncini A, Manzoli C, Notturno F, Capasso M. Pitfalls in electrodiagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome subtypes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010; 81:1157–1163.8. Lee SH, Lim GH, Kim JS, Oh SY, Kim JK, Cha JK, et al. Acute ophthalmoplegia (without ataxia) associated with anti-GQ1b antibody. Neurology. 2008; 71:426–429.
Article9. Nagashima T, Koga M, Odaka M, Hirata K, Yuki N. Clinical correlates of serum anti-GT1a IgG antibodies. J Neurol Sci. 2004; 219:139–145.
Article10. Miyazaki T, Kusunoki S, Kaida K, Shiina M, Kanazawa I. Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with IgG monospecific to ganglioside GD1b. Neurology. 2001; 56:1227–1229.
Article11. Kusunoki S, Chiba A, Kon K, Ando S, Arisawa K, Tate A, et al. N-acetylgalactosaminyl GD1a is a target molecule for serum antibody in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1994; 35:570–576.
Article12. Nagashima T, Koga M, Odaka M, Hirata K, Yuki N. Continuous spectrum of pharyngeal-cervical-brachial variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2007; 64:1519–1523.
Article13. Koga M, Yuki N, Hirata K. Antiganglioside antibody in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome who show bulbar palsy as an initial symptom. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999; 66:513–516.
Article14. Paparounas K. Anti-GQ1b ganglioside antibody in peripheral nervous system disorders: pathophysiologic role and clinical relevance. Arch Neurol. 2004; 61:1013–1016.15. Odaka M, Yuki N, Hirata K. Anti-GQ1b IgG antibody syndrome: clinical and immunological range. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001; 70:50–55.
Article16. Chiba A, Kusunoki S, Shimizu T, Kanazawa I. Serum IgG antibody to ganglioside GQ1b is a possible marker of Miller Fisher syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1992; 31:677–679.
Article17. Willison HJ, Yuki N. Peripheral neuropathies and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain. 2002; 125(Pt 12):2591–2625.
Article18. Hughes RA, Newsom-Davis JM, Perkin GD, Pierce JM. Controlled trial prednisolone in acute polyneuropathy. Lancet. 1978; 2:750–753.19. Hadden RD, Cornblath DR, Hughes RA, Zielasek J, Hartung HP, Toyka KV, Plasma Exchange/Sandoglobulin Guillain-Barré Syndrome Trial Group, et al. Electrophysiological classification of Guillain-Barré syndrome: clinical associations and outcome. Ann Neurol. 1998; 44:780–788.
Article20. Ho TW, Mishu B, Li CY, Gao CY, Cornblath DR, Griffin JW, et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome in northern China. Relationship to Campylobacter jejuni infection and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain. 1995; 118(Pt 3):597–605.
Article21. Oh SJ, Kim DE, Kuruoglu HR. What is the best diagnostic index of conduction block and temporal dispersion? Muscle Nerve. 1994; 17:489–493.
Article22. Ogawara K, Kuwabara S, Mori M, Hattori T, Koga M, Yuki N. Axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome: relation to anti-ganglioside antibodies and Campylobacter jejuni infection in Japan. Ann Neurol. 2000; 48:624–631.
Article23. Odaka M, Yuki N, Yoshino H, Kiso M, Ishida H, Hirata K. Antibodies to GD1alpha and to GQ1beta in Guillain-Barré syndrome and the related disorders. J Neurol Sci. 1999; 165:126–132.
Article24. Ho TW, Willison HJ, Nachamkin I, Li CY, Veitch J, Ung H, et al. Anti-GD1a antibody is associated with axonal but not demyelinating forms of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1999; 45:168–173.
Article25. Willison HJ. Gangliosides as targets for autoimmune injury to the nervous system. J Neurochem. 2007; 103:Suppl 1. 143–149.
Article26. Susuki K, Rasband MN, Tohyama K, Koibuchi K, Okamoto S, Funakoshi K, et al. Anti-GM1 antibodies cause complement-mediated disruption of sodium channel clusters in peripheral motor nerve fibers. J Neurosci. 2007; 27:3956–3967.
Article27. Susuki K, Baba H, Tohyama K, Kanai K, Kuwabara S, Hirata K, et al. Gangliosides contribute to stability of paranodal junctions and ion channel clusters in myelinated nerve fibers. Glia. 2007; 55:746–757.
Article28. Kashihara K, Shiro Y, Koga M, Yuki N. IgG anti-GT1a antibodies which do not cross react with GQ1b ganglioside in a pharyngeal-cervical-brachial variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998; 65:799.
Article29. Koga M, Yuki N, Ariga T, Morimatsu M, Hirata K. Is IgG anti-GT1a antibody associated with pharyngeal-cervical-brachial weakness or oropharyngeal palsy in Guillain-Barré syndrome? J Neuroimmunol. 1998; 86:74–79.
Article30. Susuki K, Koga M, Hirata K, Isogai E, Yuki N. A Guillain-Barré syndrome variant with prominent facial diplegia. J Neurol. 2009; 256:1899–1905.
Article31. Gong Y, Tagawa Y, Lunn MP, Laroy W, Heffer-Lauc M, Li CY, et al. Localization of major gangliosides in the PNS: implications for immune neuropathies. Brain. 2002; 125(Pt 11):2491–2506.
Article32. Galassi G, Susuki K, Quaglino D, Yuki N. Post-infectious acute ataxia and facial diplegia associated with anti-GD1a IgG antibody. Eur J Neurol. 2004; 11:790–791.
Article33. Kim SY, Kim JK, Suh CK. Polycranial neuropathy and sensory ataxia with IgG anti-GD1a antibody as a variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Clin Neurosci. 2013; 20:473–475.
Article34. Kuwabara S, Yuki N, Koga M, Hattori T, Matsuura D, Miyake M, et al. IgG anti-GM1 antibody is associated with reversible conduction failure and axonal degeneration in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1998; 44:202–208.
Article35. Kim JK, Kim DS, Kusunoki S, Kim SJ, Yoo BG. Acute pure motor demyelinating neuropathy with hyperreflexia and anti-GalNAc-GD1a antibodies. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012; 114:1345–1347.
Article36. Hong YH, Sung JJ, Oh MY, Moon HJ, Park KS, Lee KW. Axonal conduction block at intermediate nerve segments in pure motor Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2011; 16:37–46.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome With anti-GM1 and GD1b Antibodies Following Acute Hepatitis A
- A Variant Guillain-Barré Syndrome with Anti-Ganglioside Complex Antibody
- Elevated in Anti-GQ1b and Anti-GT1a IgG Antibody Titers in an Overlap Case of Pharyngeal-Cervical-Brachial Variant of Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Miller-Fisher Syndrome
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome With Antibody to Ganglioside GT1a
- Overlap syndrome of Miller-Fisher syndrome/Pharyngeal-Cervical-Brachial variant-Guillain Barre Syndrome with anti-ganglioside complex antibodies