J Breast Cancer.
2015 Mar;18(1):16-21. 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.1.16.
Predictive Significance of p53, Ki-67, and Bcl-2 Expression for Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Breast Cancer Center, Gachon University Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery and Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hanw@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2286332
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2015.18.1.16
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) with pathologic complete response (pCR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) have superior survival outcomes compared to those with residual disease after NAC. This study investigated the value of three biomarkers, p53, Ki-67, and Bcl-2 for predicting pCR in NAC-treated patients with TNBC.
METHODS
Between 2003 and 2012, 198 patients with pathologically confirmed primary TNBC were treated with two different taxane-based chemotherapeutic regimens prior to surgery. Before NAC, expression of p53 (cutoff 25%), Ki-67 (cutoff 10%), and Bcl-2 (cutoff 10%) was assessed immunohistochemically in core biopsy specimens. The incidence of pCR was correlated with the expression of these biomarkers.
RESULTS
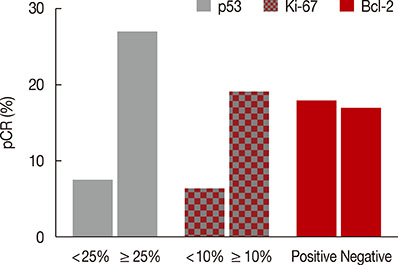
Overall, pCR occurred in 37 of the 198 patients (18.7%). A significant association was observed between the pCR rate and overexpression of the p53 and Ki-67 biomarkers. Multivariate analysis showed that only p53 expression was independently associated with pCR to NAC (odds ratio, 3.961; p=0.003). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of p53 expression for predicting pCR were 77.8%, 50.3%, 26.2%, and 90.9%, respectively. The pCR rate was the lowest (5.2%) in patients with low expression of both p53 and Ki-67, and it was the highest (25.8%) when both biomarkers showed high expression.
CONCLUSION
Expression of p53 was significantly associated with pCR after NAC in patients with TNBC, suggesting that this biomarker might be particularly valuable in identifying TNBC patients prone to have residual disease after NAC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Keam B, Im SA, Kim HJ, Oh DY, Kim JH, Lee SH, et al. Prognostic impact of clinicopathologic parameters in stage II/III breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant docetaxel and doxorubicin chemotherapy: paradoxical features of the triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007; 7:203.
Article2. Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, André F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:1275–1281.
Article3. Bozzetti C, Musolino A, Camisa R, Bisagni G, Flora M, Bassano C, et al. Evaluation of HER-2/neu amplification and other biological markers as predictors of response to neoadjuvant anthracycline-based chemotherapy in primary breast cancer: the role of anthracycline dose intensity. Am J Clin Oncol. 2006; 29:171–177.
Article4. Penault-Llorca F, Abrial C, Raoelfils I, Chollet P, Cayre A, Mouret-Reynier MA, et al. Changes and predictive and prognostic value of the mitotic index, Ki-67, cyclin D1, and cyclo-oxygenase-2 in 710 operable breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncologist. 2008; 13:1235–1245.
Article5. Ohmori T, Podack ER, Nishio K, Takahashi M, Miyahara Y, Takeda Y, et al. Apoptosis of lung cancer cells caused by some anti-cancer agents (MMC, CPT-11, ADM) is inhibited by bcl-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993; 192:30–36.
Article6. Tiezzi DG, Andrade JM, Ribeiro-Silva A, Zola FE, Marana HR, Tiezzi MG. HER-2, p53, p21 and hormonal receptors proteins expression as predictive factors of response and prognosis in locally advanced breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant docetaxel plus epirubicin combination. BMC Cancer. 2007; 7:36.
Article7. Anelli A, Brentani RR, Gadelha AP, Amorim De Albuquerque A, Soares F. Correlation of p53 status with outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy using paclitaxel and doxorubicin in stage IIIB breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:428–432.
Article8. Kandioler-Eckersberger D, Ludwig C, Rudas M, Kappel S, Janschek E, Wenzel C, et al. TP53 mutation and p53 overexpression for prediction of response to neoadjuvant treatment in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:50–56.9. Yonemori K, Tsuta K, Shimizu C, Hatanaka Y, Hashizume K, Ono M, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of PTEN and phosphorylated Akt are not correlated with clinical outcome in breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab-containing neo-adjuvant chemotherapy. Med Oncol. 2009; 26:344–349.
Article10. Jung SY, Han W, Lee JW, Ko E, Kim E, Yu JH, et al. Ki-67 expression gives additional prognostic information on St. Gallen 2007 and Adjuvant! Online risk categories in early breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:1112–1121.
Article11. von Minckwitz G, Sinn HP, Raab G, Loibl S, Blohmer JU, Eidtmann H, et al. Clinical response after two cycles compared to HER2, Ki-67, p53, and bcl-2 in independently predicting a pathological complete response after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with operable carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. 2008; 10:R30.
Article12. Bottini A, Berruti A, Bersiga A, Brizzi MP, Brunelli A, Gorzegno G, et al. p53 but not bcl-2 immunostaining is predictive of poor clinical complete response to primary chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:2751–2758.13. Mieog JS, van der Hage JA, van de Vijuer MJ, van de Velde CJ. Cooperating Investigators of the EORTC. Tumour response to preoperative anthracycline-based chemotherapy in operable breast cancer: the predictive role of p53 expression. Eur J Cancer. 2006; 42:1369–1379.
Article14. Tan DS, Marchió C, Jones RL, Savage K, Smith IE, Dowsett M, et al. Triple negative breast cancer: molecular profiling and prognostic impact in adjuvant anthracycline-treated patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008; 111:27–44.
Article15. Keam B, Im SA, Lee KH, Han SW, Oh DY, Kim JH, et al. Ki-67 can be used for further classification of triple negative breast cancer into two subtypes with different response and prognosis. Breast Cancer Res. 2011; 13:R22.
Article16. Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:2329–2334.
Article17. Chen MB, Zhu YQ, Xu JY, Wang LQ, Liu CY, Ji ZY, et al. Value of TP53 status for predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e39655.
Article18. Dumay A, Feugeas JP, Wittmer E, Lehmann-Che J, Bertheau P, Espié M, et al. Distinct tumor protein p53 mutants in breast cancer subgroups. Int J Cancer. 2013; 132:1227–1231.19. Sakuma K, Kurosumi M, Oba H, Kobayashi Y, Takei H, Inoue K, et al. Pathological tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy using anthracycline and taxanes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2011; 2:257–264.
Article20. Bertheau P, Espié M, Turpin E, Lehmann J, Plassa LF, Varna M, et al. TP53 status and response to chemotherapy in breast cancer. Pathobiology. 2008; 132–139.21. Wang TT, Phang JM. Effects of estrogen on apoptotic pathways in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:2487–2489.22. Gasparini G, Barbareschi M, Doglioni C, Palma PD, Mauri FA, Boracchi P, et al. Expression of bcl-2 protein predicts efficacy of adjuvant treatments in operable node-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1995; 1:189–198.23. van Slooten HJ, Clahsen PC, van Dierendonck JH, Duval C, Pallud C, Mandard AM, et al. Expression of Bcl-2 in node-negative breast cancer is associated with various prognostic factors, but does not predict response to one course of perioperative chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1996; 74:78–85.
Article24. Guarneri V, Piacentini F, Ficarra G, Frassoldati A, D'Amico R, Giovannelli S, et al. A prognostic model based on nodal status and Ki-67 predicts the risk of recurrence and death in breast cancer patients with residual disease after preoperative chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:1193–1198.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ki-67 as a Predictor of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients
- Differences in prognosis by p53 expression after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer
- Pathologic Findings of Residual Tumor according to the Response Rate after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
- Outcome of triple-negative breast cancer in patients with or without markers regulating cell cycle and cell death
- Expression of Immunohistochemical Markers before and after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Carcinoma, and Their Use as Predictors of Response