Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2010 Jun;14(3):127-132. 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.3.127.
Modulation of Presynaptic GABA Release by Oxidative Stress in Mechanically-isolated Rat Cerebral Cortical Neurons
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Biomedical Science Institute and Medical Research Center for Reactive Oxygen Species, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul 130-701, Korea. ywcho@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2285392
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.3.127
Abstract
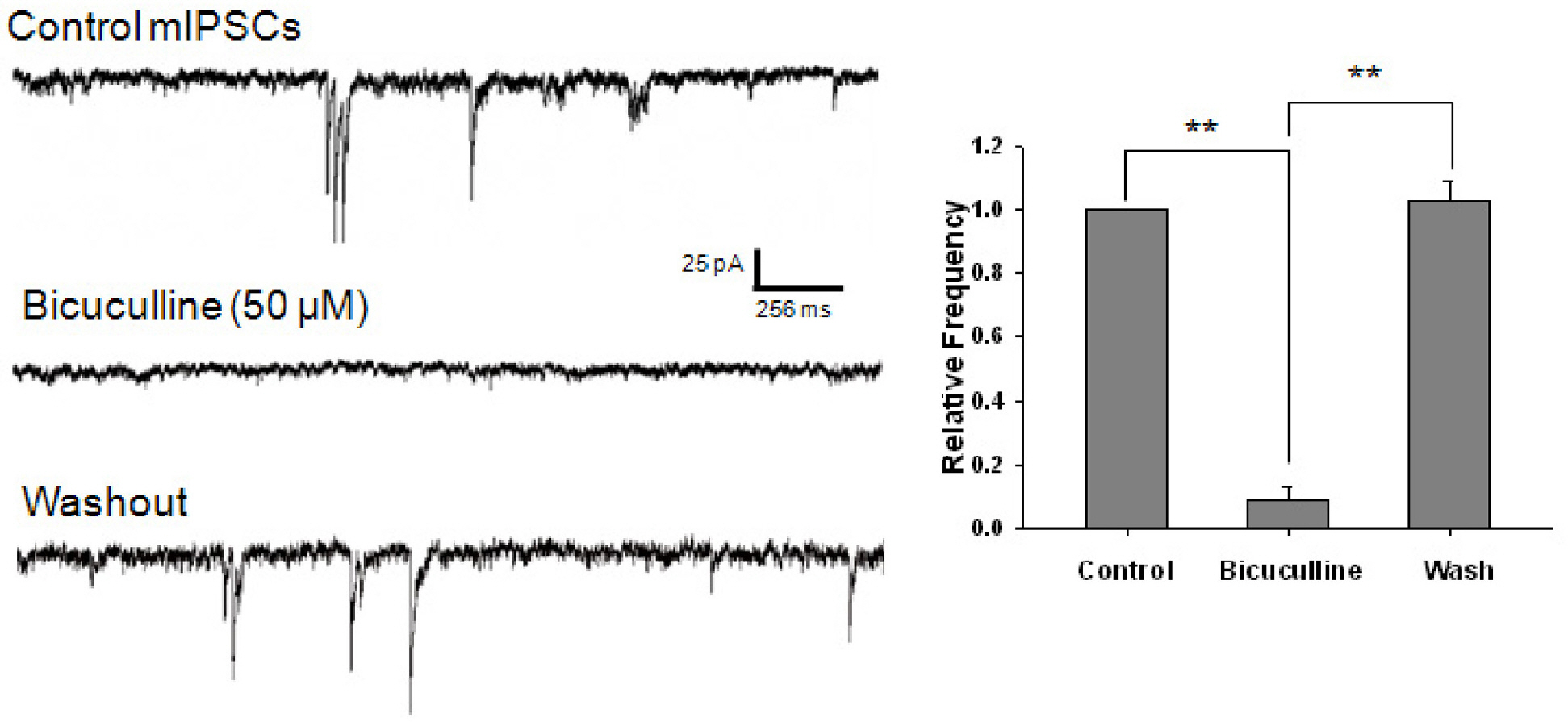
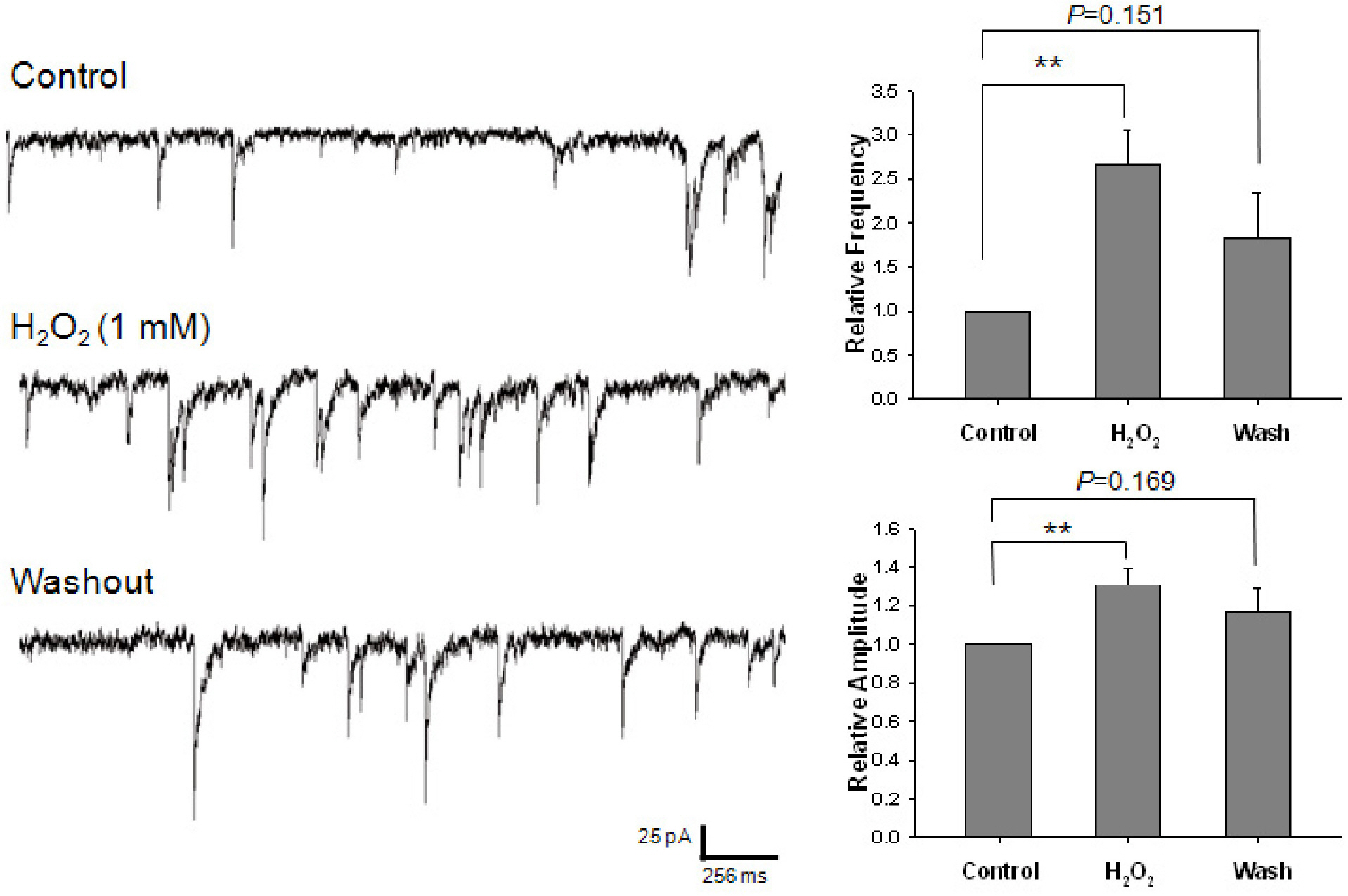
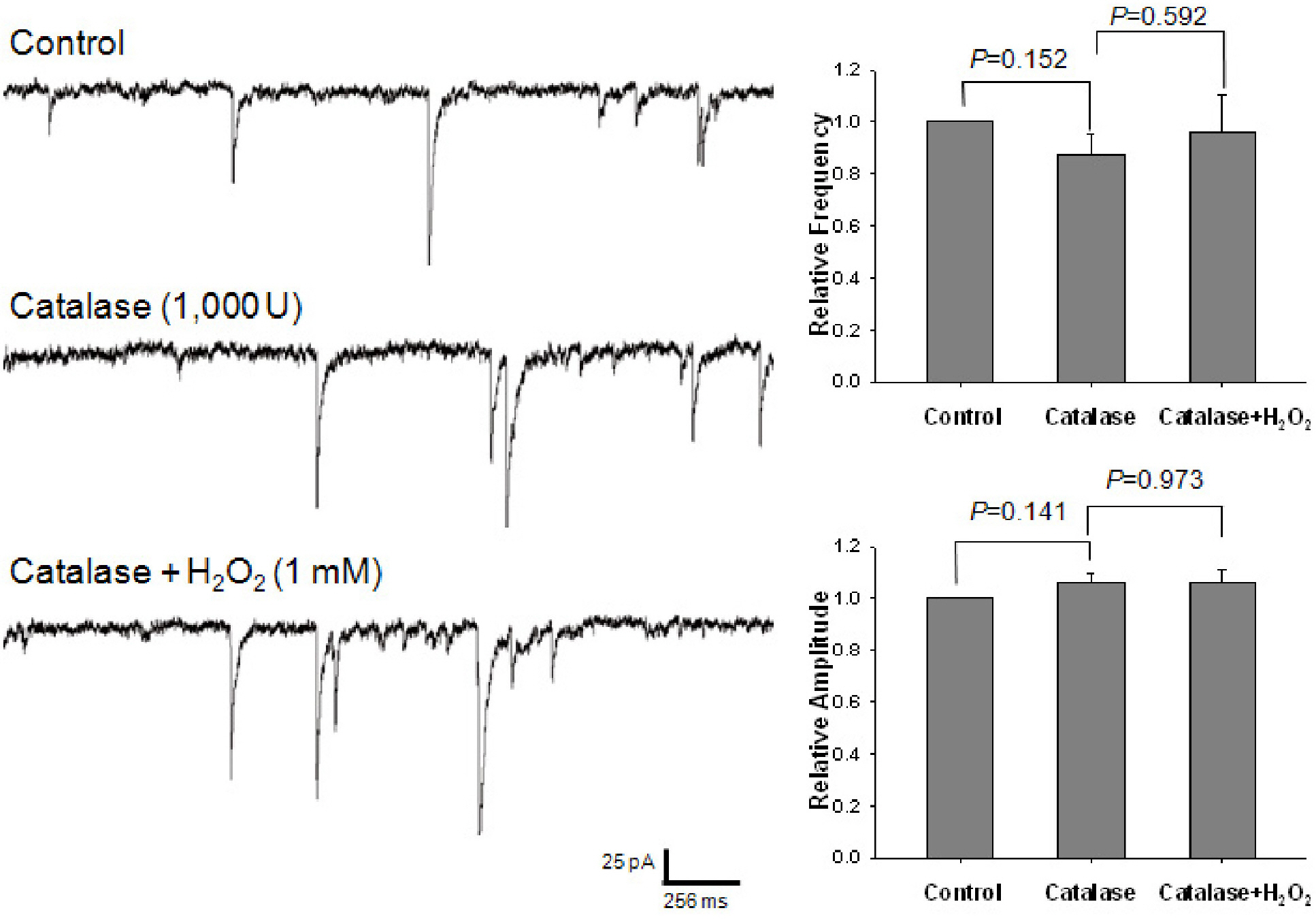
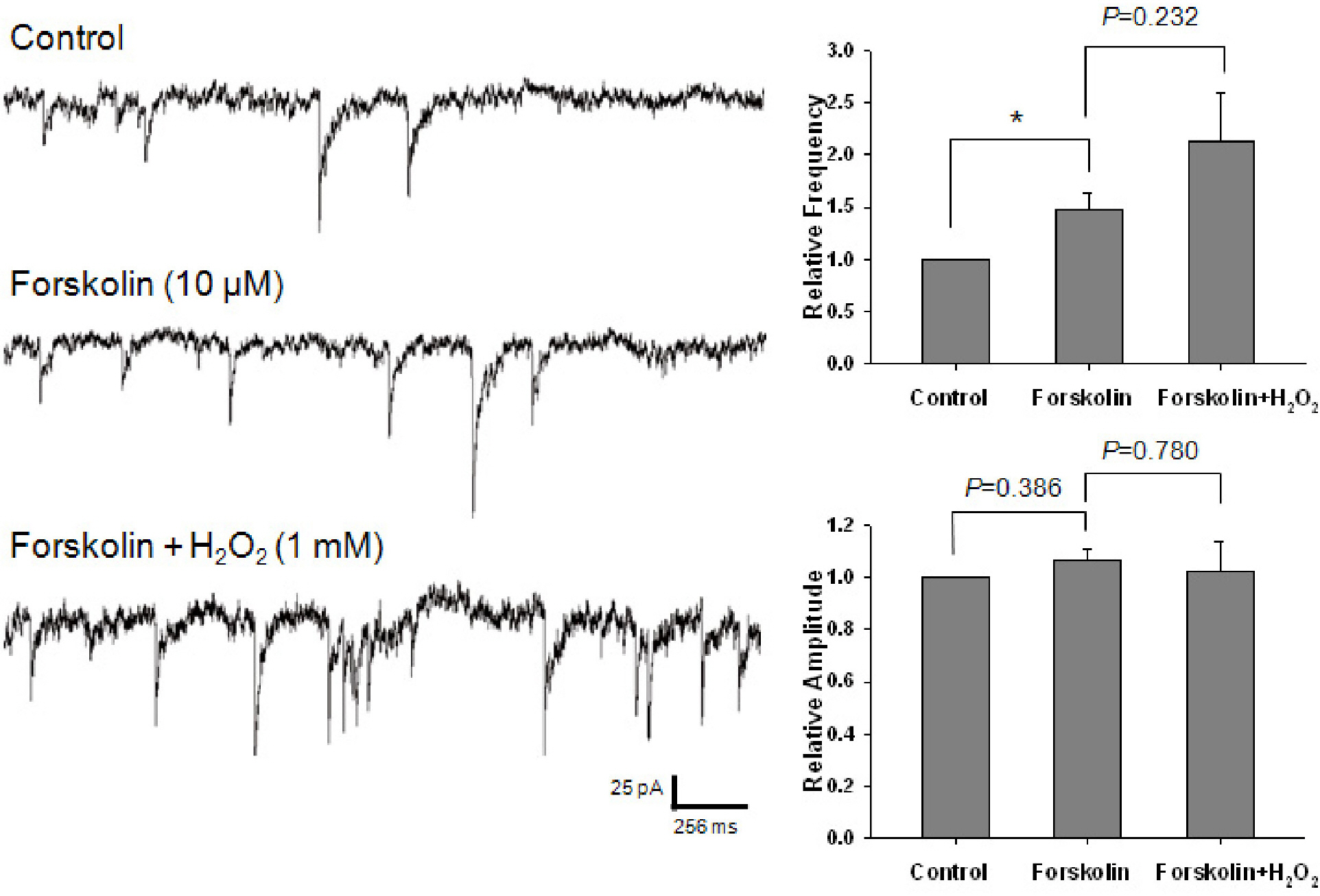
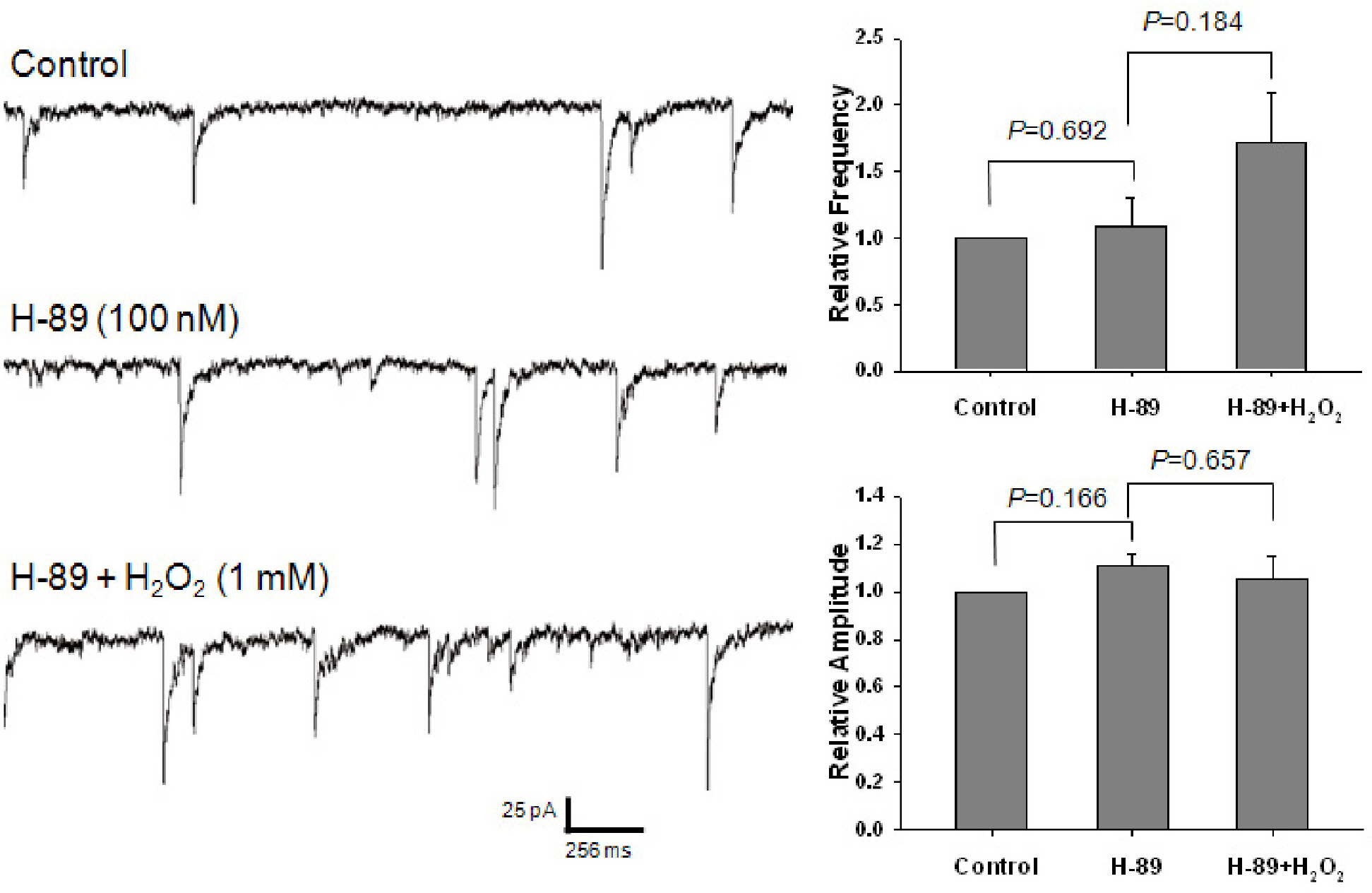
- Reactive oxygen species (ROS), which include hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the superoxide anion (O2-.), and the hydroxyl radical (OH.), are generated as by-products of oxidative metabolism in cells. The cerebral cortex has been found to be particularly vulnerable to production of ROS associated with conditions such as ischemia-reperfusion, Parkinson's disease, and aging. To investigate the effect of ROS on inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission, we examined the electrophysiological mechanisms of the modulatory effect of H2O2 on GABAergic miniature inhibitory postsynaptic current (mIPSCs) in mechanically isolated rat cerebral cortical neurons retaining intact synaptic boutons. The membrane potential was voltage-clamped at -60 mV and mIPSCs were recorded and analyzed. Superfusion of 1-mM H2O2 gradually potentiated mIPSCs. This potentiating effect of H2O2 was blocked by the pretreatment with either 10,000-unit/mL catalase or 300-micrometer N-acetyl-cysteine. The potentiating effect of H2O2 was occluded by an adenylate cyclase activator, forskolin, and was blocked by a protein kinase A inhibitor, N-(2-[p-bromocinnamylamino] ethyl)-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide hydrochloride. This study indicates that oxidative stress may potentiate presynaptic GABA release through the mechanism of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent pathways, which may result in the inhibition of the cerebral cortex neuronal activity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenylyl Cyclases
Aging
Animals
Catalase
Cerebral Cortex
Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein Kinases
Forskolin
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydroxyl Radical
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials
Membrane Potentials
Neurons
Oxidative Stress
Parkinson Disease
Presynaptic Terminals
Rats
Reactive Oxygen Species
Superoxides
Synaptic Transmission
Catalase
Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein Kinases
Forskolin
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydroxyl Radical
Reactive Oxygen Species
Superoxides
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978; 201:875–880.
Article2. Halliwell B. Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1992; 59:1609–1623.
Article3. Beckman JS, Beckman TW, Chen J, Marshall PA, Freeman BA. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990; 87:1620–1624.
Article4. Dreher D, Junod AF. Differential effects of superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radical on intracellular calcium in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1995; 162:147–153.
Article5. Lewen A, Matz P, Chan PH. Free radical pathways in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000; 17:871–890.6. Ames BN, Shigenaga MK. Oxidants are a major contributor to aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992; 663:85–96.
Article7. Chandra J, Samali A, Orrenius S. Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000; 29:323–333.
Article8. Golino P, Ragni M, Cirillo P, Avvedimento VE, Feliciello A, Esposito N, Scognamiglio A, Trimarco B, Iaccarino G, Condorelli M, Chiariello M, Ambrosio G. Effects of tissue factor induced by oxygen free radicals on coronary flow during reperfusion. Nat Med. 1996; 2:35–40.
Article9. Kvaltinova Z, Lukovic L, Stolc S. Effect of incomplete ischemia and reperfusion of the rat brain on the density and affinity of alpha-adrenergic binding sites in the cerebral cortex. Prevention of changes by stobadine and vitamin E. Neuropharmacology. 1993; 32:785–791.10. Joseph JA, Erat S, Denisova N, Villalobos-Molina R. Receptor- and age-selective effects of dopamine oxidation on receptor-G protein interactions in the striatum. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998; 24:827–834.
Article11. Muakkassah-Kelly SF, Andresen JW, Shih JC, Hochstein P. Decreased [3H]serotonin and [3H]spiperone binding consequent to lipid peroxidation in rat cortical membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982; 104:1003–1010.
Article12. Sah R, Schwartz-Bloom RD. Optical imaging reveals elevated intracellular chloride in hippocampal pyramidal neurons after oxidative stress. J Neurosci. 1999; 19:9209–9217.
Article13. Schwartz RD. The GABAA receptor-gated ion channel: biochemical and pharmacological studies of structure and function. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988; 37:3369–3375.
Article14. van der Want JJ, Nunes Cardozo JJ, van der TC. GABAergic neurons and circuits in the pretectal nuclei and the accessory optic system of mammals. Prog Brain Res. 1992; 90:283–305.15. Finkel T. Oxygen radicals and signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998; 10:248–253.
Article16. Denu JM, Tanner KG. Specific and reversible inactivation of protein tyrosine phosphatases by hydrogen peroxide: evidence for a sulfenic acid intermediate and implications for redox regulation. Biochemistry. 1998; 37:5633–5642.
Article17. Nakamura K, Hori T, Sato N, Sugie K, Kawakami T, Yodoi J. Redox regulation of a src family protein tyrosine kinase p56lck in T cells. Oncogene. 1993; 8:3133–3139.18. Klann E, Roberson ED, Knapp LT, Sweatt JD. A role for superoxide in protein kinase C activation and induction of long-term potentiation. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:4516–4522.
Article19. Whisler RL, Goyette MA, Grants IS, Newhouse YG. Sublethal levels of oxidant stress stimulate multiple serine/threonine kinases and suppress protein phosphatases in Jurkat T cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995; 319:23–35.
Article20. Rego AC, Santos MS, Oliveira CR. Oxidative stress, hypoxia, and ischemia-like conditions increase the release of endogenous amino acids by distinct mechanisms in cultured retinal cells. J Neurochem. 1996; 66:2506–2516.
Article21. Saransaari P, Oja SS. Release of endogenous glutamate, aspartate, GABA, and taurine from hippocampal slices from adult and developing mice under cell-damaging conditions. Neurochem Res. 1998; 23:563–570.22. Takahashi A, Mikami M, Yang J. Hydrogen peroxide increases GABAergic mIPSC through presynaptic release of calcium from IP3 receptor-sensitive stores in spinal cord substantia gelatinosa neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2007; 25:705–716.
Article23. Akaike N, Moorhouse AJ. Techniques: applications of the nerve-bouton preparation in neuropharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003; 24:44–47.
Article24. Hahm ET, Lee JJ, Min BI, Cho YW. Opioid inhibition of GABAergic neurotransmission in mechanically isolated rat periaqueductal gray neurons. Neurosci Res. 2004; 50:343–354.
Article25. Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981; 391:85–100.
Article26. Min BI, Kim CJ, Rhee JS, Akaike N. Modulation of glycine-induced chloride current in acutely dissociated rat periaqueductal gray neurons by μ-opioid agonist DAGO. Brain Res. 1996; 734:72–78.27. Lin HH, Chen CH, Hsieh WK, Chiu TH, Lai CC. Hydrogen peroxide increases the activity of rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vivo and in vitro. Neuroscience. 2003; 121:641–647.28. Volterra A, Trotti D, Racagni G. Glutamate uptake is inhibited by arachidonic acid and oxygen radicals via two distinct and additive mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol. 1994; 46:986–992.29. Mailly F, Marin P, Israel M, Glowinski J, Premont J. Increase in external glutamate and NMDA receptor activation contribute to H2O2-induced neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem. 1999; 73:1181–1188.30. Lee MK, Yeo H, Kim J, Markelonis GJ, Oh TH, Kim YC. Cynandione A from Cynanchum wilfordii protects cultured cortical neurons from toxicity induced by H2O2, L-glutamate, and kainate. J Neurosci Res. 2000; 59:259–264.31. Yum DS, Cho JH, Choi IS, Nakamura M, Lee JJ, Lee MG, Choi BJ, Choi JK, Jang IS. Adenosine A1 receptors inhibit GABA-ergic transmission in rat tuberomammillary nucleus neurons. J Neurochem. 2008; 106:361–371.32. Lee JJ, Hahm ET, Lee CH, Cho YW. Serotonergic modulation of GABAergic and glutamatergic synaptic transmission in mechanically isolated rat medial preoptic area neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008; 33:340–352.
Article33. Jeong HJ, Jang IS, Nabekura J, Akaike N. Adenosine A1 receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition of GABAergic transmission in immature rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2003; 89:1214–1222.
Article34. Schwartz-Bloom RD, Sah R. gamma-Aminobutyric acid(A) neurotransmission and cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 2001; 77:353–371.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nitric Oxide Modulation of GABAergic Synaptic Transmission in Mechanically Isolated Rat Auditory Cortical Neurons
- Effects of Zinc on Spontaneous Miniature GABA Release in Rat Hippocampal CA3 Pyramidal Neurons
- Muscarine M2 Receptor-mediated Presynaptic Inhibition of GABAergic Transmission in Rat Meynert Neurons
- Effect of GABA on the contratility of small intestine isolated from rat
- Experimental Demonstration of Corticostriatal Synapses in the Rat Neostriatum