Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2013 Jun;6(2):78-81.
Analysis of Facial Deformities in Korean Leprosy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea. hlpch@paran.com
- 2Nano Bio Regenerative Medical Institute, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea. iloveu59@hallym.or.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The clinical features of various facial deformities in Korean leprosy patients were evaluated according to the type of leprosy.
METHODS
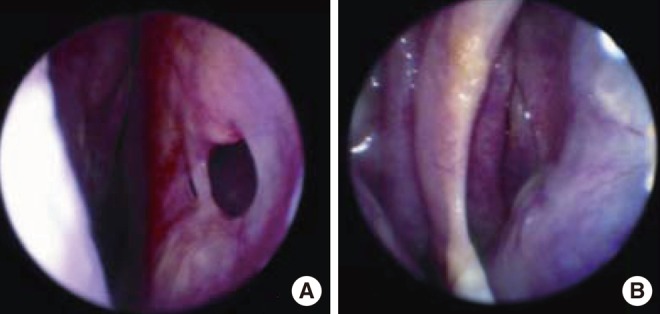
One hundred ninety six patients with leprosy were examined for various facial deformities using a nasal speculum, endoscope, and digital camera. The frequency and severity of external nasal deformities and septal perforations were evaluated according to the type of leprosy. Eye deformities, ear deformities, and facial palsy were also assessed.
RESULTS
Seventy-one patients (36.2%) displayed external nasal deformities: 28 minimal contractures, three cartilage contractures, two bony-cartilage contractures, and 38 skin defects. The external nasal deformity and severe form deformity in lepromatous types were more frequent compared to other types (P<0.05 for each variable). Twenty-three patients (9%) displayed septal perforations, among whom 11 had cartilaginous perforations and 12 had bony-cartilaginous perforations. The frequency of septal and bony-cartilaginous perforations did not differ significantly between the types of leprosy (P>0.05 for each variable). Sixty-one patients (31.1%) had eye deformities and 19 patients (9.7%) had facial nerve palsy, common in the borderline type. No cases of ear deformities were observed.
CONCLUSION
Korean patients had characteristic deformities according to the type of leprosy. They were different from those seen in the prior analyses of Caucasian populations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Binford CH, Meyers WM, Walsh GP. Leprosy. JAMA. 1982; 4. 247(16):2283–2292. PMID: 7040711.
Article2. Gupta A, Seiden AM. Nasal leprosy: case study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; 11. 129(5):608–610. PMID: 14595291.
Article3. Barton RP. Clinical manifestation of leprous rhinitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976; Jan-Feb. 85(1 Pt 1):74–82. PMID: 1259317.4. Abulafia J, Vignale RA. Leprosy: pathogenesis updated. Int J Dermatol. 1999; 5. 38(5):321–334. PMID: 10369539.
Article6. Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity: a five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966; Jul-Sep. 34(3):255–273. PMID: 5950347.7. Barton RP. A clinical study of the nose in lepromatous leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1974; 6. 45(2):135–144. PMID: 4421363.
Article8. Davey TF, Rees RJ. The nasal dicharge in leprosy: clinical and bacteriological aspects. Lepr Rev. 1974; 6. 45(2):121–134. PMID: 4608620.9. Davey TF, Barton RP. Multiple nasal smears in early lepromatous leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1974; 6. 45(2):158–165. PMID: 4608404.
Article10. House JW, Brackmann DE. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985; 4. 93(2):146–147. PMID: 3921901.
Article11. Shehata MA, Abou-Zeid SA, El-Arini AF. Leprosy of the nose clinical reassessment. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1974; Oct-Dec. 42(4):436–445. PMID: 4617723.12. Antia NH. Reconstruction of the face in leprosy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1963; 2. 32:71–98. PMID: 14013322.13. Reichart P. Facial and oral manifestations in leprosy: an evaluation of seventy cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1976; 3. 41(3):385–399. PMID: 1061926.14. McDougall AC, Rees RJ, Weddell AG, Kanan MW. The histopathology of lepromatous leprosy in the nose. J Pathol. 1975; 4. 115(4):215–226. PMID: 1099180.