Mirror Therapy for Phantom Limb Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea. mandell@naver.com
- KMID: 2278170
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.272
Abstract
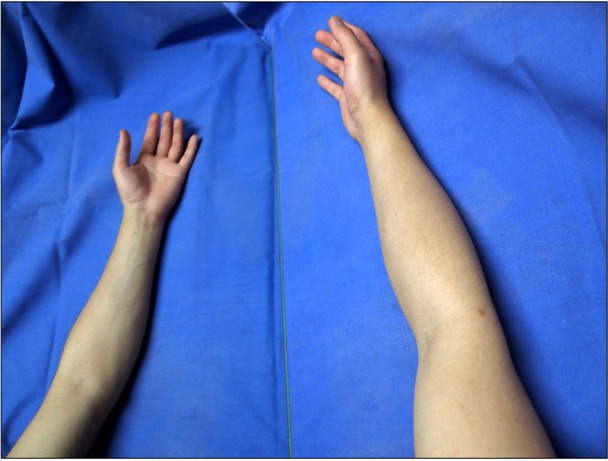
- Phantom limb pain is a painful sensation that is perceived in a body part that no longer exists. To control this pain, many methods have been used such as medication, physical treatment, nerve block, neuromodulation, surgical treatment and mirror therapy. However, until now, there effects have been uncertain. We report the successful reduction of phantom limb pain using mirror therapy when other treatments initially failed to control the pain.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Effects of different anesthetic techniques on the incidence of phantom limb pain after limb amputation: a population-based retrospective cohort study
Hyun-Seok Cho, Sooyoung Kim, Chan Sik Kim, Ye-Jee Kim, Jong-Hyuk Lee, Jeong-Gill Leem
Korean J Pain. 2020;33(3):267-274. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.3.267.Mirror Therapy as an Alternative Treatment for Phantom Limb Pain: A Short Literature Review
Farshad Hasanzadeh Kiabi, Mohammad Reza Habibi, Aria Soleimani, Amir Emami Zeydi
Korean J Pain. 2013;26(3):309-311. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.3.309.Spinal Cauda Equina Stimulation for Alternative Location of Spinal Cord Stimulation in Intractable Phantom Limb Pain Syndrome: A Case Report
Pil Moo Lee, Yun So, Jung Min Park, Chul Min Park, Hae Kyoung Kim, Jae Hun Kim
Korean J Pain. 2016;29(2):123-128. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.2.123.
Reference
-
1. Weinstein SM. Phantom limb pain and related disorders. Neurol Clin. 1998; 16:919–936. PMID: 9767070.
Article2. Carlen PL, Wall PD, Nadvorna H, Steinbach T. Phantom limbs and related phenomena in recent traumatic amputations. Neurology. 1978; 28:211–217. PMID: 564474.
Article3. Hayes C, Armstrong-Brown A, Burstal R. Perioperative intravenous ketamine infusion for the prevention of persistent post-amputation pain: a randomized, controlled trial. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2004; 32:330–338. PMID: 15264726.
Article4. Weeks SR, Anderson-Barnes VC, Tsao JW. Phantom limb pain: theories and therapies. Neurologist. 2010; 16:277–286. PMID: 20827116.5. Nikolajsen L, Ilkjaer S, Krøner K, Christensen JH, Jensen TS. The influence of preamputation pain on postamputation stump and phantom pain. Pain. 1997; 72:393–405. PMID: 9313280.
Article6. Cheong YK, Lee C, Son Y, Song YK, Kim TY, Lee SW. The trial of continuous intravenous infusion of ketamine in patients with phantom limb pain: a case report. Korean J Pain. 2006; 19:233–236.
Article7. Ramachandran VS, Rogers-Ramachandran D. Synaesthesia in phantom limbs induced with mirrors. Proc Biol Sci. 1996; 263:377–386. PMID: 8637922.
Article8. McCabe CS, Haigh RC, Halligan PW, Blake DR. Simulating sensory-motor incongruence in healthy volunteers: implications for a cortical model of pain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:509–516. PMID: 15644392.
Article9. Rizzolatti G, Fogassi L, Gallese V. Mirrors of the mind. Sci Am. 2006; 295:54–61. PMID: 17076084.10. Rossi S, Tecchio F, Pasqualetti P, Ulivelli M, Pizzella V, Romani GL, et al. Somatosensory processing during movement observation in humans. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002; 113:16–24. PMID: 11801420.
Article11. Ramachandran VS, Rogers-Ramachandran D. Sensations referred to a patient's phantom arm from another subjects intact arm: perceptual correlates of mirror neurons. Med Hypotheses. 2008; 70:1233–1234. PMID: 18329821.
Article12. Sumitani M, Miyauchi S, McCabe CS, Shibata M, Maeda L, Saitoh Y, et al. Mirror visual feedback alleviates deafferentation pain, depending on qualitative aspects of the pain: a preliminary report. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47:1038–1043. PMID: 18463143.
Article13. Rothgangel AS, Braun SM, Beurskens AJ, Seitz RJ, Wade DT. The clinical aspects of mirror therapy in rehabilitation: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Rehabil Res. 2011; 34:1–13. PMID: 21326041.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mirror Therapy as an Alternative Treatment for Phantom Limb Pain: A Short Literature Review
- Effect of Epidural Block with Meperidine in Patient with Phantom Limb Pain: A case report
- Phantom Phenomena in Traumatic Amputation
- Atypical Supernumerary Phantom Limb and Phantom Limb Pain in Two Patients with Pontine Hemorrhage
- Letter to the Editor: The Supernumerary Phantom Limb and Phantom Limb Pain-Important Facts