Korean J Pain.
2011 Mar;24(1):1-6. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.1.
Application of Botulinum Toxin in Pain Management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. anesthe@skku.edu
- KMID: 2278090
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.1
Abstract
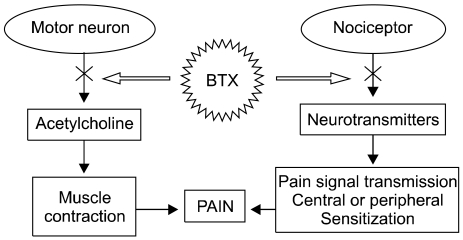
- Botulinum toxin has been used for the treatment of many clinical disorders by producing temporary skeletal muscle relaxation. In pain management, botulinum toxin has demonstrated an analgesic effect by reducing muscular hyperactivity, but recent studies suggest this neurotoxin could have direct analgesic mechanisms different from its neuromuscular actions. At the moment, botulinum toxin is widely investigated and used in many painful diseases such as myofascial syndrome, headaches, arthritis, and neuropathic pain. Further studies are needed to understand the exact analgesic mechanisms, efficacy and complications of botulinum toxin in chronic pain disorders.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The pharmacological management of neuropathic pain
Youngkwon Ko, Yoon Hee Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2012;55(6):582-592. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2012.55.6.582.
Reference
-
1. Lew MF. Review of the FDA-approved uses of botulinum toxins, including data suggesting efficacy in pain reduction. Clin J Pain. 2002; 18(6 Suppl):S142–S146. PMID: 12569961.
Article2. Colhado OC, Boeing M, Ortega LB. Botulinum toxin in pain treatment. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2009; 59:366–381. PMID: 19488551.
Article3. Setler PE. Therapeutic use of botulinum toxins: background and history. Clin J Pain. 2002; 18(6 Suppl):S119–S124. PMID: 12569958.
Article4. Freund B, Schwartz M. Temporal relationship of muscle weakness and pain reduction in subjects treated with botulinum toxin A. J Pain. 2003; 4:159–165. PMID: 14622713.
Article5. Factor SA, Molho ES, Evans S, Feustel PJ. Efficacy and safety of repeated doses of botulinum toxin type B in type A resistant and responsive cervical dystonia. Mov Disord. 2005; 20:1152–1160. PMID: 15954134.
Article6. Comella CL, Jankovic J, Shannon KM, Tsui J, Swenson M, Leurgans S, et al. Comparison of botulinum toxin serotypes A and B for the treatment of cervical dystonia. Neurology. 2005; 65:1423–1429. PMID: 16275831.
Article7. Apostol C, Abdi S, Moeller-Bertram T, Smith HS, Argoff CE, Wallace M. Smith HS, editor. Botulinum toxins for the treatment of pain. Current therapy in pain. 2009. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 489–498.
Article8. Arezzo JC. Possible mechanisms for the effects of botulinum toxin on pain. Clin J Pain. 2002; 18(6 Suppl):S125–S132. PMID: 12569959.
Article9. Sycha T, Samal D, Chizh B, Lehr S, Gustorff B, Schnider P, et al. A lack of antinociceptive or antiinflammatory effect of botulinum toxin A in an inflammatory human pain model. Anesth Analg. 2006; 102:509–516. PMID: 16428552.
Article10. Göbel H, Heinze A, Heinze-Kuhn K, Austermann K. Botulinum toxin A in the treatment of headache syndromes and pericranial pain syndromes. Pain. 2001; 91:195–199. PMID: 11275374.
Article11. Kamanli A, Kaya A, Ardicoglu O, Ozgocmen S, Zengin FO, Bayik Y. Comparison of lidocaine injection, Botulinum toxin injection, and dry needling to trigger points in myofascial pain syndrome. Rheumatol Int. 2005; 25:604–611. PMID: 15372199.
Article12. Fishman LM, Konnoth C, Rozner B. Botulinum neurotoxin type B and physical therapy in the treatment of piriformis syndrome: a dose-finding study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83:42–50. PMID: 14709974.
Article13. Lang AM. Botulinum toxin type B in piriformis syndrome. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83:198–202. PMID: 15043354.
Article14. Göbel H, Heinze A, Reichel G, Hefter H, Benecke R. Dysport myofascial pain study group. Efficacy and safety of a single botulinum type A toxin complex treatment (Dysport) for the relief of upper back myofascial pain syndrome: results from a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled multicentre study. Pain. 2006; 125:82–88. PMID: 16750294.
Article15. von Lindern JJ, Niederhagen B, Bergé S, Appel T. Type A botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic facial pain associated with masticatory hyperactivity. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:774–778. PMID: 12856249.
Article16. Babcock MS, Foster L, Pasquina P, Jabbari B. Treatment of pain attributed to plantar fasciitis with botulinum toxin a: a short-term, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 84:649–654. PMID: 16141740.
Article17. Foster L, Clapp L, Erickson M, Jabbari B. Botulinum toxin A and chronic low back pain: a randomized, double-blind study. Neurology. 2001; 56:1290–1293. PMID: 11376175.
Article18. Difazio M, Jabbari B. A focused review of the use of botulinum toxins for low back pain. Clin J Pain. 2002; 18(6 Suppl):S155–S162. PMID: 12569963.
Article19. Silberstein S, Mathew N, Saper J, Jenkins S. Botulinum toxin type A as a migraine preventive treatment. For the BOTOX Migraine Clinical Research Group. Headache. 2000; 40:445–450. PMID: 10849039.
Article20. Silberstein SD, Göbel H, Jensen R, Elkind AH, Degryse R, Walcott JM, et al. Botulinum toxin type A in the prophylactic treatment of chronic tension-type headache: a multicentre, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Cephalalgia. 2006; 26:790–800. PMID: 16776693.
Article21. Evers S, Vollmer-Haase J, Schwaag S, Rahmann A, Husstedt IW, Frese A. Botulinum toxin A in the prophylactic treatment of migraine--a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2004; 24:838–843. PMID: 15377314.
Article22. Smuts JA, Schultz D, Barnard A. Mechanism of action of botulinum toxin type A in migraine prevention: a pilot study. Headache. 2004; 44:801–805. PMID: 15330827.
Article23. Freund BJ, Schwartz M. Use of botulinum toxin in chronic whiplash-associated disorder. Clin J Pain. 2002; 18(6 Suppl):S163–S168. PMID: 12569964.
Article24. Mahowald ML, Krug HE, Singh JA, Dykstra D. Jankovic J, Albanese A, Atassi MZ, Dolly JO, Hallett M, Mayer NH, editors. Botulinum toxin for osteoarticular pain. Botulinum toxin. Therapeutic clinical practice and science. 2009. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 295–306.
Article25. Smith PP, Smith CP. Jankovic J, Albanese A, Atassi MZ, Dolly JO, Hallett M, Mayer NH, editors. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndromes. Botulinum toxin. Therapeutic clinical practice and science. 2009. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 257–268.
Article26. Hallett M. Jankovic J, Albanese A, Atassi MZ, Dolly JO, Hallett M, Mayer NH, editors. Potential new therapeutic indications for botulinum neurotoxins. Botulinum toxin. Therapeutic clinical practice and science. 2009. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 367–372.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of botulinum toxin in maxillofacial field: Part III. Ancillary treatment for maxillofacial surgery and summary
- Botulinum Toxin-Type A in Cervical Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A report of 3 cases
- Botulinum Toxin Injection Treatment for Facial Spasm
- A clinical study on the use of botulinum toxin type a in maxillofacial area
- Botulinum Toxin Injection Therapy for Lingual Dystonia: A Case Report