Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
2011 Jun;14(2):181-186. 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.2.181.
A Case of Non-IgE-mediated Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Presenting as Ascites
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea. yonho.choe@samsung.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2276539
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.2.181
Abstract
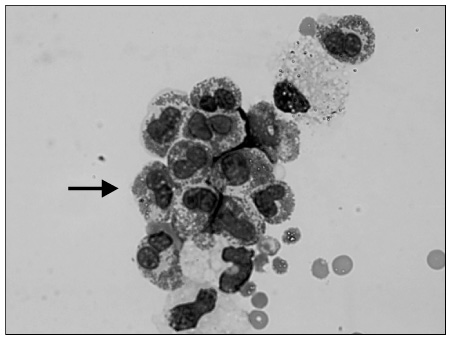
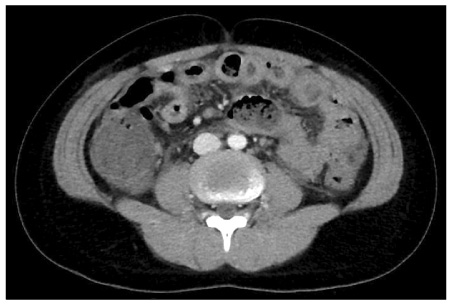
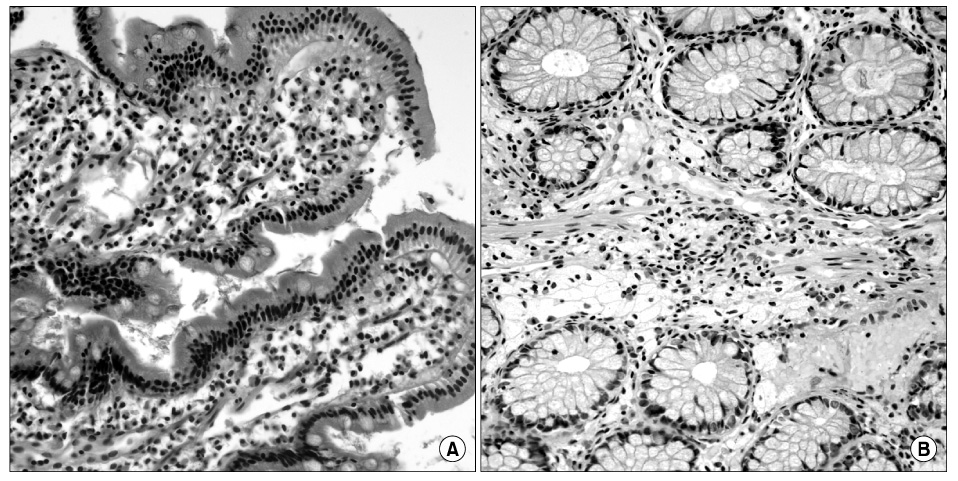
- Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare disease occurring especially in children, and shows various non-specific presentations with infiltration of eosinophils in the gastrointestinal organs. The pathophysiology of eosinophilic gastroenteritis is not yet clearly known, but allergic reactions are suspected to be related with the disease. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is categorized into the mucosal, muscularis and subserosal types based on which layer of the intestinal wall is involved. There are different clinical manifestations according to the involved layer. Most cases to date have responded well to steroid therapy. In this study, we diagnosed and treated a case of non-IgE-mediated, subserosal eosinophilic gastroenteritis in a child with abdominal pain, diarrhea and ascites.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorder Presenting as Intractable Vomiting and Ascites in a Young Girl
Ji Yoon Kwon, Ji Sun Huh, Bo Kyung Je, Kwang Dae Hong, Jee Hyun Lee
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2017;20(3):198-203. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.3.198.
Reference
-
1. Kim AS, Kim HJ, Choi YH. A case of eosinophilic ascites noted in eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1999. 19:271–274.2. Jeon EJ, Lee KM, Jung DY, Kim TH, Ji JS, Kim HK, et al. Clinical characteristics of 17 cases of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010. 55:361–367.
Article3. Kaijser R. Zur kenntnis der allergischen affectionen des verdauungskanals vom standpunkt des chirugen aus. Arch Klin Chir. 1937. 188:36–64.4. Talley NJ, Shorter RG, Phillips SF, Zinsmeister AR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a clinicopathological study of patients with disease of the mucosa, muscle layer, and subserosal tissues. Gut. 1990. 31:54–58.
Article5. Kim NI, Jo YJ, Song MH, Kim SH, Kim TH, Park YS, et al. Clinical features of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004. 44:217–223.6. Katz AJ, Twarog FJ, Zeiger RS, Falchuk ZM. Milk-sensitive and eosinophilic gastroenteropathy: similar clinical features with contrasting mechanisms and clinical course. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984. 74:72–78.
Article7. Park HS, Kim HS, Jang HJ. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis associated with food allergy and bronchial asthma. J Korean Med Sci. 1995. 10:216–219.
Article8. Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Di Lorenzo C, Putnam PE, Sigurdsson L, Mousa H, et al. The spectrum of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis beyond infancy: a clinical series of 30 children. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000. 95:1422–1430.
Article9. Guajardo JR, Plotnick LM, Fende JM, Collins MH, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophil-associated gastrointestinal disorders: a world-wide-web based registry. J Pediatr. 2002. 141:576–581.
Article10. Shifflet A, Forouhar F, Wu GY. Eosinophilic digestive diseases: eosinophilic esophagitis, gastroenteritis, and colitis. J Formos Med Assoc. 2009. 108:834–843.
Article11. Klein NC, Hargrove RL, Sleisenger MH, Jeffries GH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 1970. 49:299–319.
Article12. Kalantar SJ, Marks R, Lambert JR, Badov D, Talley NJ. Dyspepsia due to eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Dig Dis Sci. 1997. 42:2327–2332.13. Khan S. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2005. 19:177–198.
Article14. Daneshjoo R, N JT. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2002. 4:366–372.
Article15. Steffen RM, Wyllie R, Petras RE, Caulfield ME, Michener WM, Firor HV, et al. The spectrum of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Report of six pediatric cases and review of the literature. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1991. 30:404–411.16. Zora JA, O'Connell EJ, Sachs MI, Hoffman AD. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Allergy. 1984. 53:45–47.17. Fenoglio LM, Benedetti V, Rossi C, Anania A, Wulhfard K, Trapani M, et al. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with ascites: a case report and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2003. 48:1013–1020.18. Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, Gupta SK, Justinich C, Putnam PE, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007. 133:1342–1363.
Article19. DeBrosse CW, Case JW, Putnam PE, Collins MH, Rothenberg ME. Quantity and distribution of eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract of children. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2006. 9:210–218.
Article20. Um HJ, Kim BI, Park HD, Koo ES, Cho YK, Kim CS, et al. A case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis with diffuse small bowel edema and ascites. Korean J Med. 2000. 59:74–79.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis in a Child
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Presenting with Peritoneal Eosinpophilic Infiltration
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis with Eosinophilic Ascites
- Serosal Type Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
- A case of subserosal type of eosinophilic gastroenteritis with ascites