Cancer Res Treat.
2010 Sep;42(3):180-184.
Novel Sunitinib Strategy in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma on Hemodialysis: Intermittent Dose of Sunitinib after Hemodialysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rha7655@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
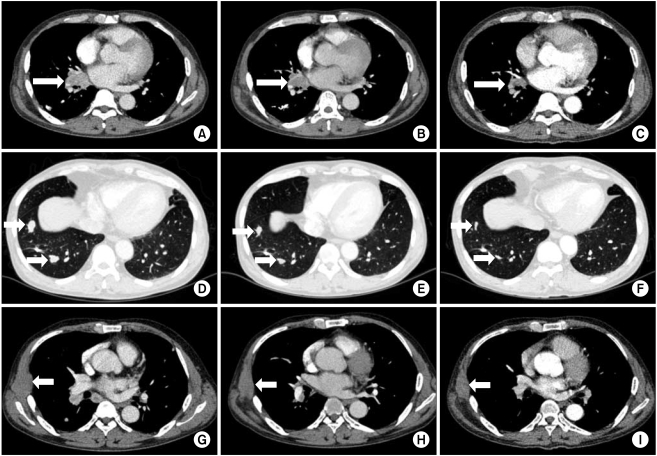
- The proper dose and schedule of sunitinib have yet to be established for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) on hemodialysis. We reviewed two patients with metastatic RCC on hemodialysis who had been treated with sunitinib in Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine. Fifty milligrams of sunitinib was administered intermittently after each hemodialysis session (3 or 4 times a week). Overall responses were partial response in both cases. Progression-free survivals were 16 and 6 months, respectively, at the time of reporting (April 2010). Both subjects tolerated the treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Keith DS, Torres VE, King BF, Zincki H, Farrow GM. Renal cell carcinoma in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994; 4:1661–1669. PMID: 8011975.
Article2. Hughson MD, Buchwald D, Fox M. Renal neoplasia and acquired cystic kidney disease in patients receiving long-term dialysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986; 110:592–601. PMID: 3521533.3. Peces R, Martinez-Ara J, Miguel JL, Arrieta J, Costero O, Gorriz JL, et al. Renal cell carcinoma co-existent with other renal disease: clinico-pathological features in predialysis patients and those receiving dialysis or renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004; 19:2789–2796. PMID: 15316098.
Article4. Janus N, Thariat J, Boulanger H, Deray G, Launay-Vacher V. Proposal for dosage adjustment and timing of chemotherapy in hemodialyzed patients. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21:1395–1403. PMID: 20118214.
Article5. Escudier B. Sorafenib in kidney cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007; 18(Suppl 9):ix90–ix93. PMID: 17631603.6. Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007; 370:2103–2111. PMID: 18156031.
Article7. Motzer RJ, Hudes GR, Curti BD, McDermott DF, Escudier BJ, Negrier S, et al. Phase I/II trial of temsirolimus combined with interferon alfa for advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:3958–3964. PMID: 17761980.
Article8. Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Rosenberg J, Bukowski RM, Curti BD, George DJ, et al. Sunitinib efficacy against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2007; 178:1883–1887. PMID: 17868732.
Article9. Faivre S, Delbaldo C, Vera K, Robert C, Lozahic S, Lassau N, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel oral multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:25–35. PMID: 16314617.
Article10. Zastrow S, Froehner M, Platzek I, Novotny V, Wirth MP. Treatment of metastatic renal cell cancer with sunitinib during chronic hemodialysis. Urology. 2009; 73:868–870. PMID: 19167044.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intolerance to Sunitinib Treatment in Hemodialysis Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Hypoglycemic Coma in a Patient with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Sunitinib
- A Case of Sunitinib-Induced Destructive Thyroiditis
- A case of thyrotoxicosis after sunitinib treatment
- Sunitinib-induced hypothyroidism