The Effect of Bedside Exercise Program on Stroke Patients with Dysphagia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gwangju Veterans Hospital, Gwangju 506-705, Korea. standupmd@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2266722
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.512
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To examine the effects of a bedside exercise program on the recovery of swallowing after a stroke. METHOD: Fifty stroke patients with dysphagia (<6 months post-stroke) were enrolled and classified into two groups, the experimental (25 subjects) and control groups (25 subjects). The control group was treated with conventional swallowing therapy. The experimental group received additional bedside exercise training, which consisted of oral, pharyngeal, laryngeal, and respiratory exercises, 1 hour per day for 2 months, and they were instructed regarding this program through the nursing intervention. All patients were assessed for their swallowing function by Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study (VFSS), using the New VFSS scale, the level of functional oral intake, the frequency of dysphagia complications, the presence (or not) of tube feeding, the mood state and quality of life before the treatment and at 2 months after the treatment.
RESULTS
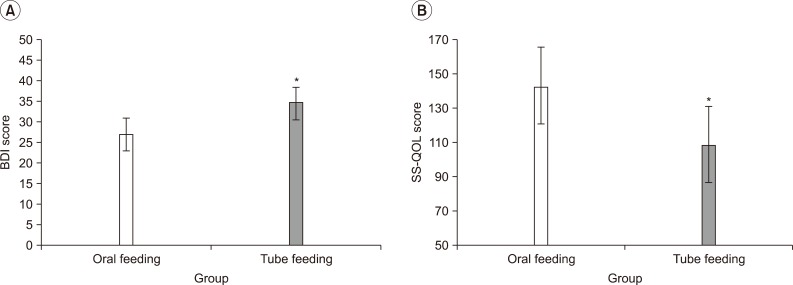
After 2 months of treatment, the experimental group showed a significant improvement in the swallowing function at the oral phase in the New VFSS Scale than that of the control group (p<0.05). Further, they also showed less depressive mood and better quality of life than the control group. However, there was no significant change in the incidence of dysphagia complication and the presence (or not) of tube feeding between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
Bedside exercise program showed an improvement of swallowing function and exhibited a positive secondary effect, such as mood state and quality of life, on subacute stroke patients with dysphagia. For improvement of rehabilitation results on subacute stroke patients with dysphagia, this study suggests that additional intensive bedside exercise would be necessary.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Effects of an educational program for improving the dietary quality of older adults at risk for dysphagia in South Korea
∗
Sooyoun Kwon, Youngmi Lee, Oksun Kim, Hae Ryun Park, Young Suk Lim, Chorong Kim, Hee Young Kim
J Nutr Health. 2018;51(5):445-454. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2018.51.5.445.Efficacy of a 4-Week Swallowing Rehabilitation Program Combined With Pyriform Sinus Ballooning in Patients With Post-stroke Dysphagia
Yong Kyun Kim, Kyun Yeon Lee, Sang-Heon Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(4):542-550. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.542.Clinical Practice Guidelines for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
Seoyon Yang, Jin-Woo Park, Kyunghoon Min, Yoon Se Lee, Young-Jin Song, Seong Hee Choi, Doo Young Kim, Seung Hak Lee, Hee Seung Yang, Wonjae Cha, Ji Won Kim, Byung-Mo Oh, Han Gil Seo, Min-Wook Kim, Hee-Soon Woo, Sung-Jong Park, Sungju Jee, Ju Sun Oh, Ki Deok Park, Young Ju Jin, Sungjun Han, DooHan Yoo, Bo Hae Kim, Hyun Haeng Lee, Yeo Hyung Kim, Min-Gu Kang, Eun-Jae Chung, Bo Ryun Kim, Tae-Woo Kim, Eun Jae Ko, Young Min Park, Hanaro Park, Min-Su Kim, Jungirl Seok, Sun Im, Sung-Hwa Ko, Seong Hoon Lim, Kee Wook Jung, Tae Hee Lee, Bo Young Hong, Woojeong Kim, Weon-Sun Shin, Young Chan Lee, Sung Joon Park, Jeonghyun Lim, Youngkook Kim, Jung Hwan Lee, Kang-Min Ahn, Jun-Young Paeng, JeongYun Park, Young Ae Song, Kyung Cheon Seo, Chang Hwan Ryu, Jae-Keun Cho, Jee-Ho Lee, Kyoung Hyo Choi
Ann Rehabil Med. 2023;47(Suppl 1):S1-S26. doi: 10.5535/arm.23069.
Reference
-
1. Katzan IL, Cebul RD, Husak SH, Dawson NV, Baker DW. The effect of pneumonia on mortality among patients hospitalized for acute stroke. Neurology. 2003; 60:620–625. PMID: 12601102.
Article2. Alberts MJ, Horner J, Gray L, Brazer SR. Aspiration after stroke: lesion analysis by brain MRI. Dysphagia. 1992; 7:170–173. PMID: 1499361.
Article3. Chokshi SK, Asper RF, Khandheria BK. Aspiration pneumonia: a review. Am Fam Physician. 1986; 33:195–202. PMID: 3513497.4. Grober ME. Dysphagia: diagnosis and management. 1997. 3rd ed. Newton: Butterworth-Heinemann;p. 139–143.5. Kikuchi R, Watabe N, Konno T, Mishima N, Sekizawa K, Sasaki H. High incidence of silent aspiration in elderly patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994; 150:251–253. PMID: 8025758.
Article6. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW, Kwon BS. The prediction of persistent dysphagia beyond six months after stroke. Dysphagia. 2008; 23:59–64. PMID: 17602263.
Article7. Smithard DG, O'Neill PA, England RE, Park CL, Wyatt R, Martin DF, Morris J. The natural history of dysphagia following a stroke. Dysphagia. 1997; 12:188–193. PMID: 9294937.
Article8. Howard L, Ament M, Fleming CR, Shike M, Steiger E. Cerrent use and clinical outcome of home parenteral and enteral nutrition therapies in the United States. Gastroenterology. 1995; 109:355–365. PMID: 7615183.9. Holas MA, DePippo KL, Reding MJ. Aspiration and relative risk of medical complications following stroke. Arch Neurol. 1994; 51:1051–1053. PMID: 7945003.
Article10. Horner J, Buoyer FG, Alberts MJ, Helms MJ. Dysphagia following brain-stem stroke. Clinical correlates and outcome. Arch Neurol. 1991; 48:1170–1173. PMID: 1953404.11. Horner J, Massey EW. Silent aspiration following stroke. Neurology. 1988; 38:317–319. PMID: 3340301.
Article12. Rosenbek JC, Robbins J, Fishback B, Levine RL. Effects of thermal application on dysphagia after stroke. J Speech Hear Res. 1991; 34:1257–1268. PMID: 1787707.
Article13. Hamdy S, Jilani S, Price V, Parker C, Hall N, Power M. Mudulation of human swallowing behaviour by thermal and chemical stimulation in health and after brain injury. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2003; 15:69–77. PMID: 12588471.14. Oh BM, Kim DY, Paik NJ. Recovery of swallowing function is accompanied by the expansion of the cortical map. Int J Neurosci. 2007; 117:1215–1227. PMID: 17654088.
Article15. Ludlow CL, Humbert I, Saxon K, Poletto C, Sonies B, Crujido L. Effects of surface electrical stimulation both at rest and during swallowing in chronic pharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2007; 22:1–10. PMID: 16718620.
Article16. Freed ML, Freed L, Chatburn RL, Christian M. Electrical stimulation for swallowing disorders caused by stroke. Respir Care. 2001; 46:466–474. PMID: 11309186.17. Park CL, O'Neil PA, Martin DF. A pilot exploratory study of oral electrical stimulation on swallow function following stroke: an innovative technique. Dysphagia. 1997; 12:161–166. PMID: 9190102.
Article18. Bulow M, Olsson R, Ekberg O. Videomanometric analysis of supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia. 2001; 16:190–195. PMID: 11453566.
Article19. Ding R, Larson CR, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW. Surface electromyographic and electroglottographic studies in normal subjects under two swallow conditions: normal and during the Mendelsohn maneuver. Dysphagia. 2002; 17:1–12. PMID: 11820381.20. Shaker R, Kern M, Bardan E, Taylor A, Stewart ET, Hoffmann RG, Arndorfer RC, Hofmann C, Bonnevier J. Augmentation of deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter opening in the elderly by exercise. Am J Physiol. 1997; 272:1518–1522.
Article21. Shaker R, Easterling C, Kern M, Nitschke T, Massey B, Daniels S, Grande B, Kazandjian M, Dikeman K. Rehabilitation of swallowing by exercise in tube-fed patients with pharyngeal dysphagia secondary to abnormal UES opening. Gastroenterology. 2002; 122:1314–1321. PMID: 11984518.
Article22. Logeman JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 1983. 2nd ed. San Diego: College Hill Press;p. 168–180.23. Jung SH, Lee KJ, Hong JB, Han TR. Validation of clinical dysphagia scale: based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005; 29:343–350.24. Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003; 114:2226–2244. PMID: 14652082.
Article25. Jean A. Brain stem control of swallowing: neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 2001; 81:929–969. PMID: 11274347.
Article26. Lund JP, Kolta A, Westberg KG, Scott G. Brainstem mechanisms underlying feeding begaviors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1998; 8:718–724. PMID: 9914242.27. Robbins JA, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, Taylor AJ. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:150–158. PMID: 17270511.
Article28. Lee CK, Kim JA. Pattern of post-stroke swallowing disorder according to the brain lesion. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25:193–201.29. Gillen R, Eberhardt TL, Tennen H, Affleck G, Groszmann Y. Screening for depression in stroke: relationship to rehabilitation efficiency. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 1999; 8:300–306. PMID: 17895179.
Article30. Gillen R, Tennen H, Mckee TE, Gernert-Dott P, Affleck G. Depressive symptoms and history of depression predict rehabilitation efficiency in stroke patiens. Arch phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:1645–1649. PMID: 11733876.31. Morris PL, Robinson RG, Andrzejewski P, Samuels J, Price TR. Association of depression with 10-year potstroke mortality. Am J Psychiatry. 1993; 150:124–129. PMID: 8417554.32. You YY, Ann CS. A study of the relationships between perceived rehabilitation-motivation and quality of life in patients after a cerebrovascular accident. J Korean Acad Occup Ther. 2009; 17:1–15.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiology, Natural Recovery, Long-term Outcome of Post Stroke Dysphagia
- Application of Non-invasive Brain Stimulation on Dysphagia after Stroke
- Clinical Utility of the Bedside Swallowing Evaluations for Dysphagia
- Post-Stroke Dysphagia: Incidence, Complications and Pattern Relates to Brain Lesion
- Effect of Oropharyngeal Sensory Stimulation Using Capsaicin in Acute Stroke Patients with Dysphagia