Ann Dermatol.
2014 Feb;26(1):111-113. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.1.111.
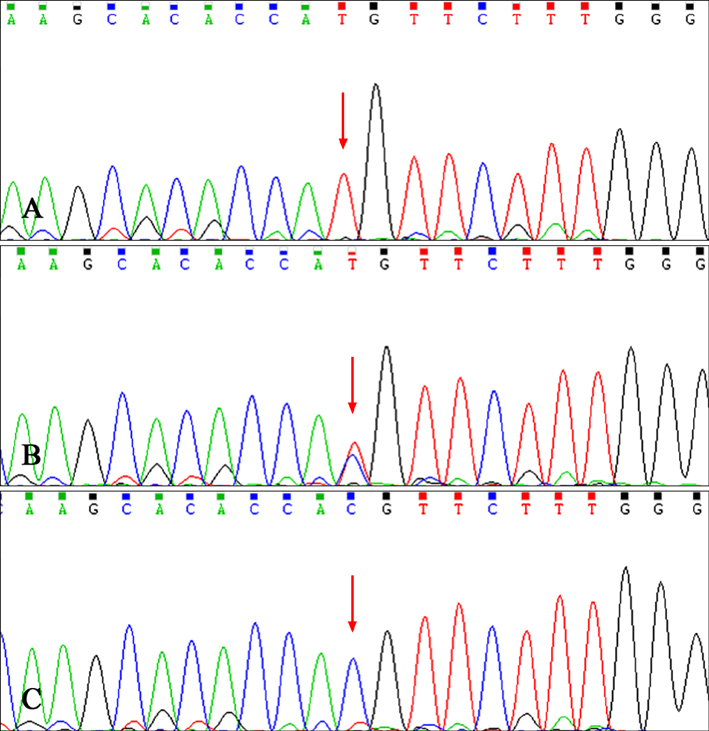
One Mutation of the ED1 Gene in a Chinese Han Family with X-Linked Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Dermatology, Anhui Medical University, Anhui, China. ayzxj@vip.sina.com
- 2The MOE Key Laboratory of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Anhui, China.
- 3Departments of Dermatology and Venereology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Anhui, China.
- KMID: 2265708
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.1.111
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang J, Han D, Song S, Wang Y, Zhao H, Pan S, et al. Correlation between the phenotypes and genotypes of X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and non-syndromic hypodontia caused by ectodysplasin-A mutations. Eur J Med Genet. 2011; 54:e377–e382.
Article2. Kere J, Srivastava AK, Montonen O, Zonana J, Thomas N, Ferguson B, et al. X-linked anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia is caused by mutation in a novel transmembrane protein. Nat Genet. 1996; 13:409–416.
Article3. Zhang H, Quan C, Sun LD, Lv HL, Gao M, Zhou FS, et al. A novel frameshift mutation of the EDA1 gene in a Chinese Han family with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009; 34:74–76.
Article4. Zhang XJ, Chen JJ, Song YX, Yang S, Xiong XY, Zhang AP, et al. Mutation analysis of the ED1 gene in two Chinese Han families with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Arch Dermatol Res. 2003; 295:38–42.
Article