Ann Dermatol.
2010 Aug;22(3):349-352. 10.5021/ad.2010.22.3.349.
Recalcitrant Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Omalizumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. chhuh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2265375
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.3.349
Abstract
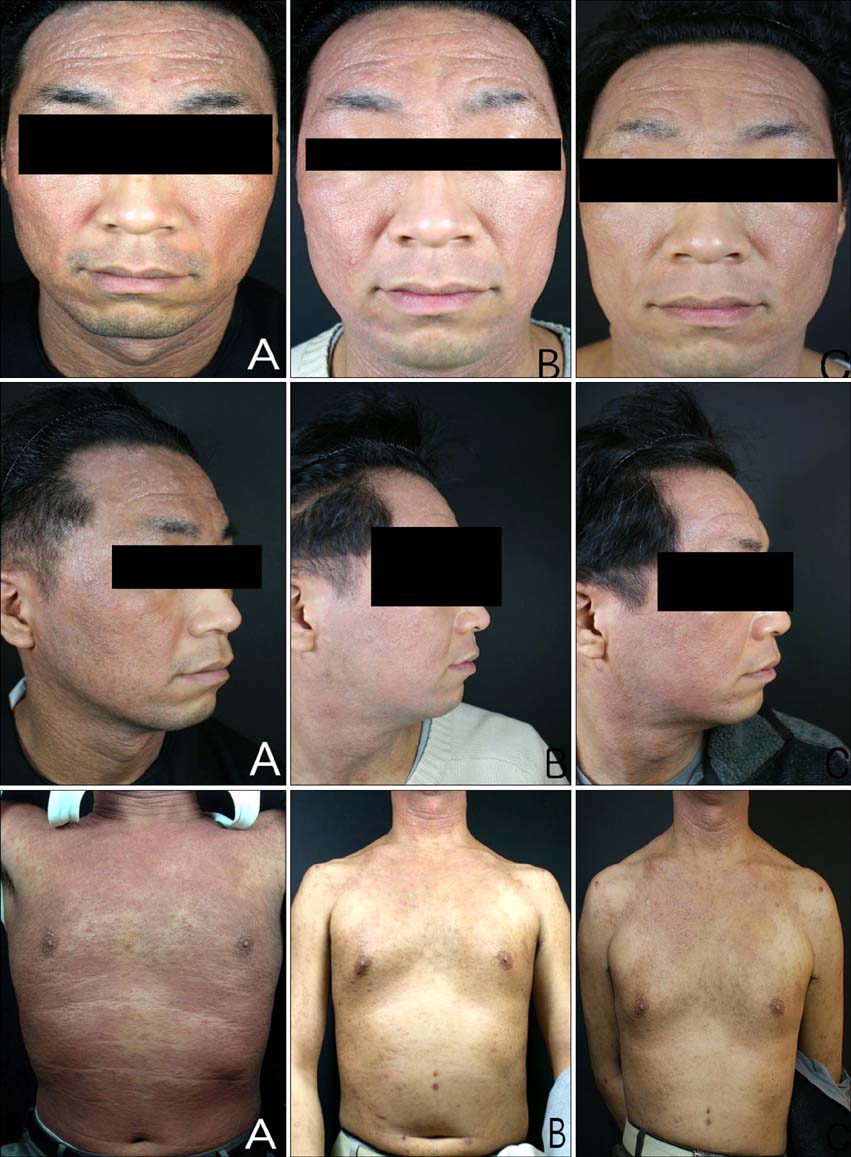
- Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic cutaneous inflammatory disease. Various categories of therapeutic medications are used for treating AD. Omalizumab is a monoclonal anti-IgE antibody that binds to IgE molecules at the high-affinity receptor (FcepsilonRI) binding site. Therefore, omalizumab can be used as a potential new systemic treatment agent for recalcitrant AD patients with elevated IgE levels. A 34-year-old man had been treated for AD with several topical and oral agents. However, he was refractory to these therapies and his serum IgE levels were very high. We treated him with omalizumab. After 8 months of the treatment, his symptoms were notably improved and the SCORAD index was decreased. Thus, we report on the first case of recalcitrant AD that was successfully treated with omalizumab in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Akdis CA, Akdis M, Bieber T, Bindslev-Jensen C, Boguniewicz M, Eigenmann P, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adults: European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/PRACTALL Consensus Report. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 118:152–169.
Article2. Lee BH, Park CK, Kim HO, Park CW, Lee CH. A case of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis treated with dapsone. Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:1626–1630.3. Kuanprasert N, Herbert O, Barnetson RS. Clinical improvement and significant reduction of total serum IgE in patients suffering from severe atopic dermatitis treated with oral azathioprine. Australas J Dermatol. 2002. 43:125–127.
Article4. Neuber K, Schwartz I, Itschert G, Dieck AT. Treatment of atopic eczema with oral mycophenolate mofetil. Br J Dermatol. 2000. 143:385–391.
Article5. Jolles S, Hughes J, Rustin M. The treatment of atopic dermatitis with adjunctive high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin: a report of three patients and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol. 2000. 142:551–554.
Article6. Krathen RA, Hsu S. Failure of omalizumab for treatment of severe adult atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005. 53:338–340.
Article7. Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:1483–1494.
Article8. Stingl G. IgE-mediated, Fc(epsilon)RI-dependent allergen presentation: a pathogenetic factor in atopic dermatitis? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001. 45:S17–S20.9. Lane JE, Cheyney JM, Lane TN, Kent DE, Cohen DJ. Treatment of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis with omalizumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 54:68–72.
Article10. Lowe PJ, Tannenbaum S, Gautier A, Jimenez P. Relationship between omalizumab pharmacokinetics, IgE pharmacodynamics and symptoms in patients with severe persistent allergic (IgE-mediated) asthma. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. 68:61–76.
Article11. Salvin RG, Ferioli C, Tannenbaum SJ, Mrtin C, Blogg M, Lowe PJ. Asthma symptom re-emergence after omalizumab withdrawal correlates well with increasing IgE and decreasing pharmacokinetic concentration. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 123:107–113.12. Vigo PG, Girgis KR, Pfuetze BL, Critchlow ME, Fisher J, Hussain I. Efficacy of anti-IgE therapy in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:168–170.
Article13. Nowak D. Management of asthma with anti-immunoglobulin E: A review of clinical trials of omalizumab. Respir Med. 2006. 100:1907–1917.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Omalizumab and unmet needs in severe asthma and allergic comorbidities in Japanese children
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability
- Three Cases of Facial Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Topical Pimecrolimus (Elidel)
- Serum IgE Level in Patients of Atopic Dermatitis and Atopic Dermatitis with Molluscum Contagiosum
- Atopic dermatitis