Ann Dermatol.
2013 Nov;25(4):524-525. 10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.524.
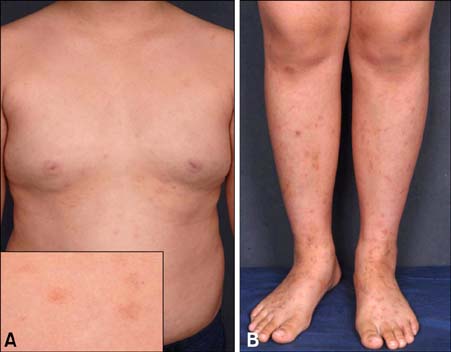
Generalized Schamberg Disease in a Child
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hykang@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2265084
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.524
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Torrelo A, Requena C, Mediero IG, Zambrano A. Schamberg's purpura in children: a review of 13 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003; 48:31–33.
Article2. Zvulunov A, Avinoach I, Hatskelzon L, Halevy S. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis (Schamberg's purpura) in an infant. Dermatol Online J. 1999; 5:2.
Article3. Can B, Turkoglu Z, Kavala M, Zindanci I, Kural E. Successful treatment of generalized childhood Schamberg's disease with narrowband ultraviolet B therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2011; 27:216–218.
Article4. Milea M, Dimov HA, Cribier B. Generalized Schamberg's disease treated with PUVA in a child. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2007; 134:378–380.5. Mun JH, Jwa SW, Song M, Kim HS, Ko HC, Kim BS, et al. Extensive pigmented purpuric dermatosis successfully treated with pentoxifylline. Ann Dermatol. 2012; 24:363–365.
Article