Ann Dermatol.
2013 Nov;25(4):508-510. 10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.508.
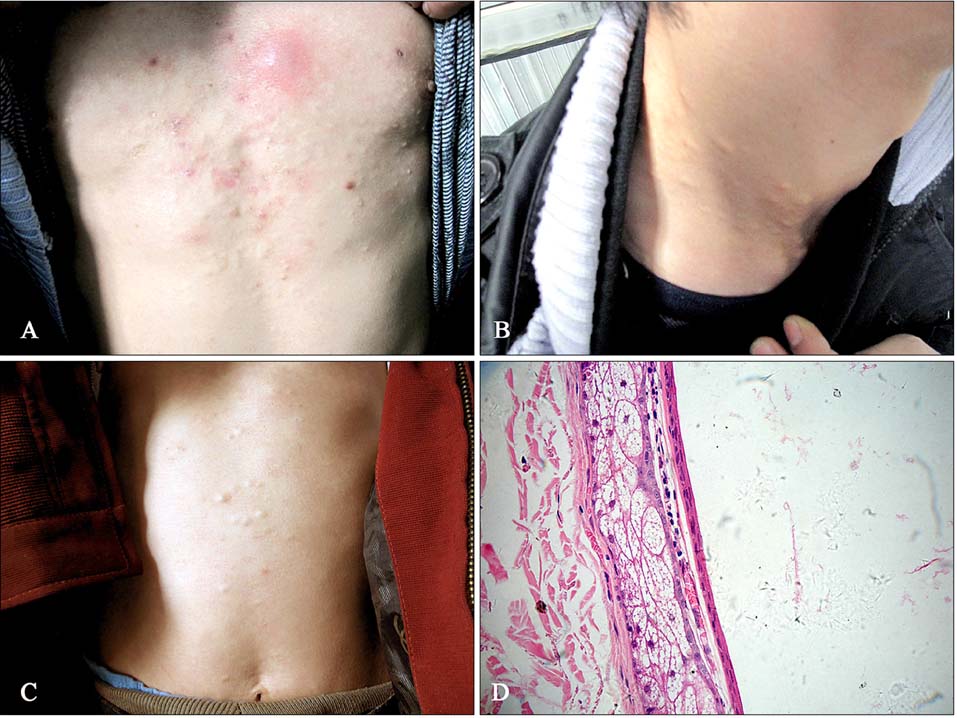
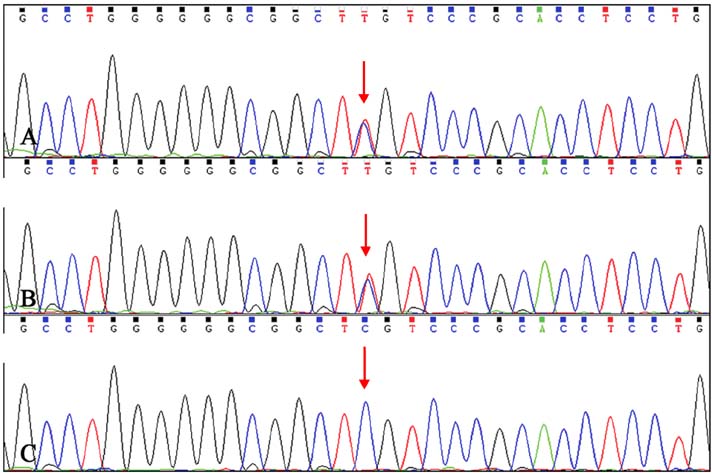
A Novel Missense Mutation of Keratin 17 Gene in a Chinese Family with Steatocystoma Multiplex
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Dermatology, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China. ayzxj@vip.sina.com
- 2The MOE Key Laboratory of Dermatology, Hefei, Anhui, China.
- 3Department of Dermatology and Venereology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China.
- KMID: 2265077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.508
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moritz DL, Silverman RA. Steatocystoma multiplex treated with isotretinoin: a delayed response. Cutis. 1988; 42:437–439.2. Smith FJ, Corden LD, Rugg EL, Ratnavel R, Leigh IM, Moss C, et al. Missense mutations in keratin 17 cause either pachyonychia congenita type 2 or a phenotype resembling steatocystoma multiplex. J Invest Dermatol. 1997; 108:220–223.
Article3. Covello SP, Smith FJ, Sillevis Smitt JH, Paller AS, Munro CS, Jonkman MF, et al. Keratin 17 mutations cause either steatocystoma multiplex or pachyonychia congenita type 2. Br J Dermatol. 1998; 139:475–480.
Article4. McLean WH, Rugg EL, Lunny DP, Morley SM, Lane EB, Swensson O, et al. Keratin 16 and keratin 17 mutations cause pachyonychia congenita. Nat Genet. 1995; 9:273–278.
Article5. Smith FJ, Jonkman MF, van Goor H, Coleman CM, Covello SP, Uitto J, et al. A mutation in human keratin K6b produces a phenocopy of the K17 disorder pachyonychia congenita type 2. Hum Mol Genet. 1998; 7:1143–1148.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Steatocystoma multiplex: A case report of a rare entity
- Huge Steatocystoma Multiplex with New Point Mutation in the Exon 1 of KRT 17 Gene
- Steatocystoma Multiplex in a Family
- A Case of Steatocystoma Multiplex on the Face in a Family
- A Case of Steatocystoma Multiplex: Successful Treatment with Mini-incisions