Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2013 Sep;1(3):284-287. 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.284.
Anaphylaxis due to fentanyl during radiofrequency ablation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kwonhs21@naver.com
- KMID: 2262973
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.284
Abstract
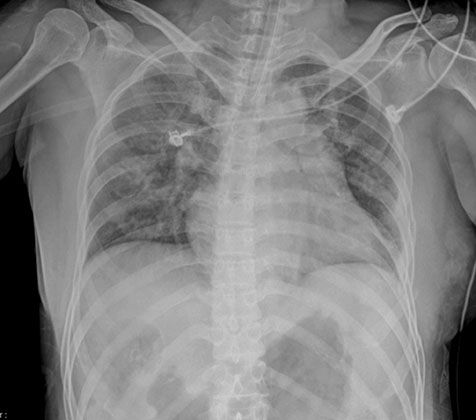
- This case report describes a life-threatening anaphylaxis to fentanyl during radiofrequency ablation (RFA). A 50-year-old woman with hepatocellular carcinoma was admitted for RFA. She denied any history of adverse drug reactions or past adverse anesthetic reaction. Physical examination, vital signs, any laboratory findings were all within normal limits. Ten minutes after intravenous administration of 50 mcg of fentanyl before starting RFA, she developed generalized erythema and sudden onset of bronchospasm followed by respiratory arrest. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) commenced with 100% oxygen and intravenous administration of epinephrine 1 mg. After 5 minutes of CPR, she had the return of spontaneous circulation. Chest X-ray revealed pulmonary edema which resolved over two days. She recovered completely and was discharged home. After six weeks, intradermal tests performed with fentanyl, remifentanyl, midazolam, and profopol. Among those, only fentanyl induced positive skin response. Fentanyl induced anaphylaxis was diagnosed for this case, and fentanyl was avoided in the subsequent general anesthesia for liver transplantation. This case suggested that fentanyl could induce anaphylaxis combined with uncommon comorbidities like pulmonary edema.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Intravenous
Anaphylaxis
Anesthesia, General
Bronchial Spasm
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Comorbidity
Drug Toxicity
Epinephrine
Erythema
Female
Fentanyl
Humans
Intradermal Tests
Liver Transplantation
Midazolam
Middle Aged
Oxygen
Physical Examination
Pulmonary Edema
Skin
Skin Tests
Thorax
Vital Signs
Epinephrine
Fentanyl
Midazolam
Oxygen
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hepner DL, Castells MC. Anaphylaxis during the perioperative period. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:1381–1395.
Article2. Mertes PM, Laxenaire MC, Alla F. Groupe d'Etudes des Réactions Anaphylactoïdes Peranesthésiques. Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions occurring during anesthesia in France in 1999-2000. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:536–545.
Article3. Blunk JA, Schmelz M, Zeck S, Skov P, Likar R, Koppert W. Opioid-induced mast cell activation and vascular responses is not mediated by mu-opioid receptors: an in vivo microdialysis study in human skin. Anesth Analg. 2004; 98:364–370.4. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilo MB, El-Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, et al. World allergy organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:13–37.
Article5. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim TW, Kwon JW, Lee SM, Kim SH, et al. Epidemiologic and clinical features of anaphylaxis in Korea. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:31–36.
Article6. Milojevic I, Simic D, Markovic M, Atanaskovic-Markovic M, Milosevic K, Trifunovic B. Anaphylactic reaction during general anaesthesia associated with positive skin test to fentanyl. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2009; 37:502–503.7. Cummings KC 3rd, Arnaut K. Case report: fentanyl-associated intraoperative anaphylaxis with pulmonary edema. Can J Anaesth. 2007; 54:301–306.
Article8. Fukuda T, Dohi S. Anaphylactic reaction to fentanyl or preservative. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1986; 33:826–827.
Article9. Bennett MJ, Anderson LK, McMillan JC, Ebertz JM, Hanifin JM, Hirshman CA. Anaphylactic reaction during anaesthesia associated with positive intradermal skin test to fentanyl. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1986; 33:75–78.
Article10. Joo J, Bae H, Lee J. Intraoperative allergic reaction to fentanyl: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2009; 57:776–779.
Article11. Levy JH, Brister NW, Shearin A, Ziegler J, Hug CC Jr, Adelson DM, et al. Wheal and flare responses to opioids in humans. Anesthesiology. 1989; 70:756–760.
Article12. Zucker-Pinchoff B, Ramanathan S. Anaphylactic reaction to epidural fentanyl. Anesthesiology. 1989; 71:599–601.
Article13. Konarzewski W, De'Ath S. Unrecognised fatal anaphylactic reaction to propofol or fentanyl. Anaesthesia. 2001; 56:497–498.
Article14. Nava Gómez M, Rojas Perez EM, Parra Martinez ES, Lopez-Lopez JR, Madrid Roldan MA. Transanesthetic anaphylactic shock induced by propofol and fentanyl: case report. Rev Alerg Mex. 2007; 54:140–143.15. Belso N, Kui R, Szegesdi I, Kakuja M, Kapitany K, Kemeny L, et al. Propofol and fentanyl induced perioperative anaphylaxis. Br J Anaesth. 2011; 106:283–284.
Article16. Schwartz LB, Metcalfe DD, Miller JS, Earl H, Sullivan T. Tryptase levels as an indicator of mast-cell activation in systemic anaphylaxis and mastocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1987; 316:1622–1626.
Article17. Dewachter P, Lefebvre D, Kalaboka S, Bloch-Morot E. An anaphylactic reaction to transdermal delivered fentanyl. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009; 53:1092–1093.
Article18. Ebo DG, Fisher MM, Hagendorens MM, Bridts CH, Stevens WJ. Anaphylaxis during anaesthesia: diagnostic approach. Allergy. 2007; 62:471–487.
Article19. Gallerani M, Manzoli N, Fellin R, Simonato M, Orzincolo C. Anaphylactic shock and acute pulmonary edema after a single oral dose of acetazolamide. Am J Emerg Med. 2002; 20:371–372.
Article20. Low I, Stables S. Anaphylactic deaths in Auckland, New Zealand: a review of coronial autopsies from 1985 to 2005. Pathology. 2006; 38:328–332.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Chronic Radiodermatitis following Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Cysts: Case Report
- Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas
- Successful Management of Atrio-Esophageal Fistula after Cardiac Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation
- Microwave thermosphere versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we approaching the time to end the debate?