Assessment of Total/Specific IgE Levels Against 7 Inhalant Allergens in Children Aged 3 to 6 Years in Seoul, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Allergy TF, Department of Immunology and Pathology, Korea National Institute of Health, Cheongwon, Korea. jooshil@korea.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Childhood Asthma Atopy Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Allergy, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2260336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.3.162
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Childhood allergies are a serious problem, as they may lead to lifetime chronic disease. Determination of total and specific IgE levels is known to be a diagnostic tool for allergic sensitization; however, IgE levels are affected by various factors, such as age, sex, ethnicity, and geographic area. Thus, we evaluated the distribution of total and specific serum IgE levels against seven inhalant allergens in preschool children and examined their association with allergic diseases in Seoul, Korea.
METHODS
Total/specific serum IgE determination and skin prick tests for seven common allergens were performed on 509 children aged 3 to 6 years from 16 child care centers in Seoul, Korea. Demographic characteristics were surveyed from parents using a modified International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) questionnaire. A diagnosis of atopic dermatitis was made by physicians.
RESULTS
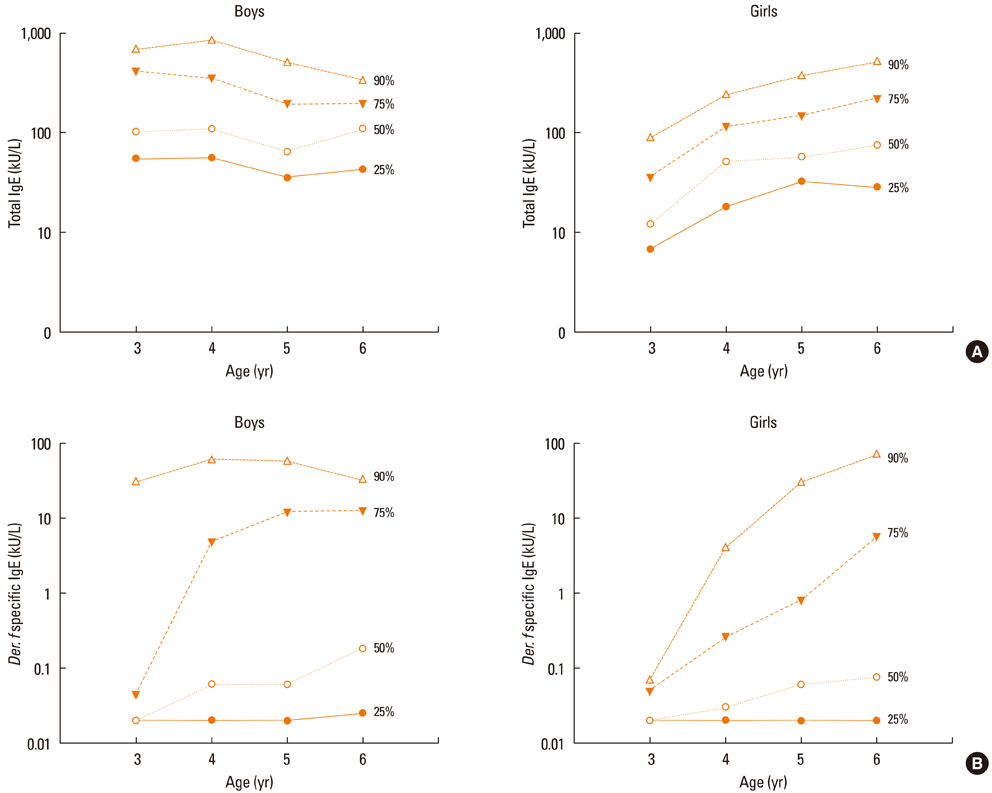
The geometric mean of total IgE was 80.48+/-3.80 kU/L in preschool children. IgE levels were higher in boys (boys, 102.34+/-3.52 kU/L; girls, 62.37+/-3.93 kU/L; P<0.001) and atopic subjects (atopic, 158.00+/-3.35 kU/L; non-atopic, 52.75+/-3.44 kU/L; P<0.001). An increased prevalence of atopy was associated with a high monthly household income (P=0.004) and higher maternal education level (above university-level education; P=0.009), as well as increased total IgE levels (P=0.036). Physician-diagnosed atopic dermatitis was associated with sensitization to inhalant allergens.
CONCLUSIONS
Total IgE levels were very high as compared with those in previous reports from other countries. The most common sensitized allergen was Dermatophagoides farinae, and the positive response rate peaked at age 3 years and was maintained thereafter, particularly in boys. Specific IgE levels for seven inhalant allergens varied with age in preschool children. Although further investigations are needed with a broad range of ages and various allergens, the distribution of the total and specific serum IgE levels in preschool children might help to serve as a reference value to diagnose atopy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Insulin Resistance Increases Serum Immunoglobulin E Sensitization in Premenopausal Women
Seung Eun Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Kyungdo Han, Eun Hee Koh
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):175-182. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0150.Sensitization patterns to common allergens in Korean children younger than 6 years of age presenting with typical symptoms or signs of allergic diseases: a single center study
Jung Won Yoon, Sang Min Lee, Joon Hwan Kim, Na Yeon Kim, Ji Hyeon Baek, Hey-Sung Baek, Hye Mi Jee, Hyeung Yoon Kim, Sun Hee Choi, Ki Eun Kim, Hye Yung Yum, Man Yong Han, Jintack Kim, Youn Ho Shin
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014;2(4):272-276. doi: 10.4168/aard.2014.2.4.272.The change in food allergy prevalence of elementary school children in Seoul since the last 20 years and the risk factor analysis
Yeong-Ho Kim, So-Yeon Lee, Eun Lee, Hyun-Ju Cho, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ji-Won Kwon, Song-I Yang, Eun-Jin Kim, Jeom-Kyu Lee, Soo-Jong Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(4):276-283. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.4.276.Allergen sensitization and vitamin D status in young Korean children with urticaria
Jeong Bong Lee, Shin Hae Lee, Man Yong Han, Jung Won Yoon
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(3):153-158. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.3.153.Factors associated with chronic and recurrent rhinosinusitis in preschool children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Hyung Ho Yun, Young Min Ahn, Hyun-Jung Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(3):168-173. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.3.168.
Reference
-
1. Gustafsson D, Sjöberg O, Foucard T. Development of allergies and asthma in infants and young children with atopic dermatitis--a prospective follow-up to 7 years of age. Allergy. 2000. 55:240–245.2. Stupka E, deShazo R. Asthma in seniors: Part 1. Evidence for underdiagnosis, undertreatment, and increasing morbidity and mortality. Am J Med. 2009. 122:6–11.3. Burgess JA, Dharmage SC, Byrnes GB, Matheson MC, Gurrin LC, Wharton CL, Johns DP, Abramson MJ, Hopper JL, Walters EH. Childhood eczema and asthma incidence and persistence: a cohort study from childhood to middle age. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 122:280–285.4. Stern DA, Morgan WJ, Halonen M, Wright AL, Martinez FD. Wheezing and bronchial hyper-responsiveness in early childhood as predictors of newly diagnosed asthma in early adulthood: a longitudinal birth-cohort study. Lancet. 2008. 372:1058–1064.5. Martin PE, Matheson MC, Gurrin L, Burgess JA, Osborne N, Lowe AJ, Morrison S, Mészáros D, Giles GG, Abramson MJ, Walters EH, Allen KJ, Dharmage SC. Childhood eczema and rhinitis predict atopic but not nonatopic adult asthma: a prospective cohort study over 4 decades. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. 127:1473–1479.e1.6. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering committee. Steering committee. Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC. Lancet. 1998. 351:1225–1232.7. Ellwood P, Asher MI, Beasley R, Clayton TO, Stewart AW. ISAAC Steering Committee. The international study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC): phase three rationale and methods. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2005. 9:10–16.8. Hamilton RG. Rich RR, Fleisher TA, Shearer WT, Schroeder HW, Frew AJ, Weyand CM, editors. Assessment of human allergic diseases. Clinical immunology: principles and practice. 2008. 3rd ed. London: Mosby Elsevier Ltd;1471–1484.9. Carosso A, Bugiani M, Migliore E, Antò JM, DeMarco R. Reference values of total serum IgE and their significance in the diagnosis of allergy in young European adults. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007. 142:230–238.10. Zetterström O, Johansson SG. IgE concentrations measured by PRIST in serum of healthy adults and in patients with respiratory allergy. A diagnostic approach. Allergy. 1981. 36:537–547.11. Criqui MH, Seibles JA, Hamburger RN, Coughlin SS, Gabriel S. Epidemiology of immunoglobulin E levels in a defined population. Ann Allergy. 1990. 64:308–313.12. Grigoreas C, Pappas D, Galatas ID, Kollias G, Papadimos S, Papadakis P. Serum total IgE levels in a representative sample of a Greek population. I. Correlation with age, sex, and skin reactivity to common aeroallergens. Allergy. 1993. 48:142–146.13. Jarvis D, Luczynska C, Chinn S, Burney P. The association of age, gender and smoking with total IgE and specific IgE. Clin Exp Allergy. 1995. 25:1083–1091.14. Burney P, Malmberg E, Chinn S, Jarvis D, Luczynska C, Lai E. The distribution of total and specific serum IgE in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997. 99:314–322.15. Kjellman NI, Nilsson L. From food allergy and atopic dermatitis to respiratory allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1998. 9:13–17.16. Sigurs N, Hattevig G, Kjellman B, Kjellman NI, Nilsson L, Björkstén B. Appearance of atopic disease in relation to serum IgE antibodies in children followed up from birth for 4 to 15 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994. 94:757–763.17. Burr ML, Merrett TG, Dunstan FD, Maguire MJ. The development of allergy in high-risk children. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997. 27:1247–1253.18. Kulig M, Bergmann R, Tacke U, Wahn U, Guggenmoos-Holzmann I. Long-lasting sensitization to food during the first two years precedes allergic airway disease. The MAS Study Group, Germany. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1998. 9:61–67.19. Kurukulaaratchy RJ, Matthews S, Arshad SH. Defining childhood atopic phenotypes to investigate the association of atopic sensitization with allergic disease. Allergy. 2005. 60:1280–1286.20. Song Y, Kwon JW, Kim BJ, Kim BS, Kim JH, Kim HB, Lee SY, Yu J, Yu SM, Hong SJ. Relationship between allergic rhinitis and asthma in high school students in Korea. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2010. 20:30–40.21. Kwon JW, Seo JH, Yu J, Kim BJ, Kim HB, Lee SY, Kim WK, Kim KW, Ji HM, Kim KE, Shin YJ, Kim MH, Kim H, Hong SJ. Relationship between the prevalence of allergic rhinitis and allergen sensitization in children of Songpa area, Seoul. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011. 21:47–55.22. Mediaty A, Neuber K. Total and specific serum IgE decreases with age in patients with allergic rhinitis, asthma and insect allergy but not in patients with atopic dermatitis. Immun Ageing. 2005. 2:9.23. Barbee RA, Brown WG, Kaltenborn W, Halonen M. Allergen skin-test reactivity in a community population sample: correlation with age, histamine skin reactions and total serum immunoglobulin E. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981. 68:15–19.24. Barbee RA, Halonen M, Lebowitz M, Burrows B. Distribution of IgE in a community population sample: correlations with age, sex, and allergen skin test reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981. 68:106–111.25. Barbee RA, Halonen M, Kaltenborn W, Lebowitz M, Burrows B. A longitudinal study of serum IgE in a community cohort: correlations with age, sex, smoking, and atopic status. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987. 79:919–927.26. Barbee RA, Kaltenborn W, Lebowitz MD, Burrows B. Longitudinal changes in allergen skin test reactivity in a community population sample. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987. 79:16–24.27. Freidhoff LR, Meyers DA, Bias WB, Chase GA, Hussain R, Marsh DG. A genetic-epidemiologic study of human immune responsiveness to allergens in an industrial population: I. Epidemiology of reported allergy and skin-test positivity. Am J Med Genet. 1981. 9:323–340.28. Freidhoff LR, Meyers DA, Marsh DG. A genetic-epidemiologic study of human immune responsiveness to allergens in an industrial population. II. The associations among skin sensitivity, total serum IgE, age, sex, and the reporting of allergies in a stratified random sample. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984. 73:490–499.29. Arbes SJ Jr, Gergen PJ, Elliott L, Zeldin DC. Prevalences of positive skin test responses to 10 common allergens in the US population: results from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 116:377–383.30. Gergen PJ, Arbes SJ Jr, Calatroni A, Mitchell HE, Zeldin DC. Total IgE levels and asthma prevalence in the US population: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 124:447–453.31. Pastorello EA, Incorvaia C, Ortolani C, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Romagnani S, Tursi A, Zanussi C. Studies on the relationship between the level of specific IgE antibodies and the clinical expression of allergy: I. Definition of levels distinguishing patients with symptomatic from patients with asymptomatic allergy to common aeroallergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995. 96:580–587.32. Ricci G, Capelli M, Miniero R, Menna G, Zannarini L, Dillon P, Masi M. A comparison of different allergometric tests, skin prick test, Pharmacia UniCAP and ADVIA Centaur, for diagnosis of allergic diseases in children. Allergy. 2003. 58:38–45.33. Grundbacher FJ, Massie FS. Levels of immunoglobulin G, M, A, and E at various ages in allergic and nonallergic black and white individuals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985. 75:651–658.34. Litonjua AA, Celedón JC, Hausmann J, Nikolov M, Sredl D, Ryan L, Platts-Mills TA, Weiss ST, Gold DR. Variation in total and specific IgE: effects of ethnicity and socioeconomic status. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 115:751–757.35. Wittig HJ, Belloit J, De Fillippi I, Royal G. Age-related serum immunoglobulin E levels in healthy subjects and in patients with allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980. 66:305–313.36. Moorman JE, Zahran H, Truman BI, Molla MT. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Current asthma prevalence - United States, 2006-2008. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2011. 60:Suppl. 84–86.37. Heinrich J, Popescu MA, Wjst M, Goldstein IF, Wichmann HE. Atopy in children and parental social class. Am J Public Health. 1998. 88:1319–1324.38. Baqueiro T, Pontes-de-carvalho L, Carvalho FM, Santos NM, Alcântara-Neves NM. Medical Student's Group. Asthma and rhinitis symptoms in individuals from different socioeconomic levels in a Brazilian city. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007. 28:362–367.39. Omenaas E, Bakke P, Elsayed S, Hanoa R, Gulsvik A. Total and specific serum IgE levels in adults: relationship to sex, age and environmental factors. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994. 24:530–539.40. Kerkhof M, Droste JH, de Monchy JG, Schouten JP, Rijcken B. Distribution of total serum IgE and specific IgE to common aeroallergens by sex and age, and their relationship to each other in a random sample of the Dutch general population aged 20-70 years. Dutch ECRHS Group, European Community Respiratory Health Study. Allergy. 1996. 51:770–776.41. Wuthrich B, Schindler C, Medici TC, Zellweger JP, Leuenberger P. IgE levels, atopy markers and hay fever in relation to age, sex and smoking status in a normal adult Swiss population. SAPALDIA (Swiss Study on Air Pollution and Lung Diseases in Adults) Team. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1996. 111:396–402.42. Kulig M, Tacke U, Forster J, Edenharter G, Bergmann R, Lau S, Wahn V, Zepp F, Wahn U. Serum IgE levels during the first 6 years of life. J Pediatr. 1999. 134:453–458.43. Malinowska E, Kaczmarski M. Total IgE levels in children under three years of age. Med Sci Monit. 2002. 8:CR113–CR118.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Relationship between Total Serum IgE, Allergen-Specific IgE, and Skin Prick Test in Children with Atopic Asthma
- Relationship between Total Serum IgE Level and Allergic Sensitization/Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness in Preschool Children with Asthma
- The Age Impact on Serum Total and Allergen-Specific IgE
- Blood eosinophil counts as a biomarker for allergen sensitization in childhood allergic diseases in comparison with total IgE
- Comparison of MAST-CLA System Results between Children and Adults with Atopic Dermatitis (2005~2012, Gangwon, Yeongseo Province)