Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2014 Jul;6(4):296-303. 10.4168/aair.2014.6.4.296.
Trends in Specific Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis: A Survey of Chinese ENT Specialists
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China. jspent@126.com
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Changzheng Hospital, The Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China.
- 3Editorial Office, Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, Beijing, China.
- 4Institute of Otorhinolaryngology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
- 5International Centre for Allergy Research, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
- KMID: 2260209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.4.296
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Specific immunotherapy (SIT) is a suitable but uncommon treatment option for allergic rhinitis (AR) in China. The current understanding and attitude of Chinese ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialists in regards to SIT is unclear. This study investigates current trends in the awareness and application status of SIT among Chinese ENT specialists.
METHODS
We performed a nationwide, cross-sectional survey with a specially designed questionnaire given to 800 ENT specialists in China. A member of the trained research group conducted face-to-face interviews with each respondent.
RESULTS
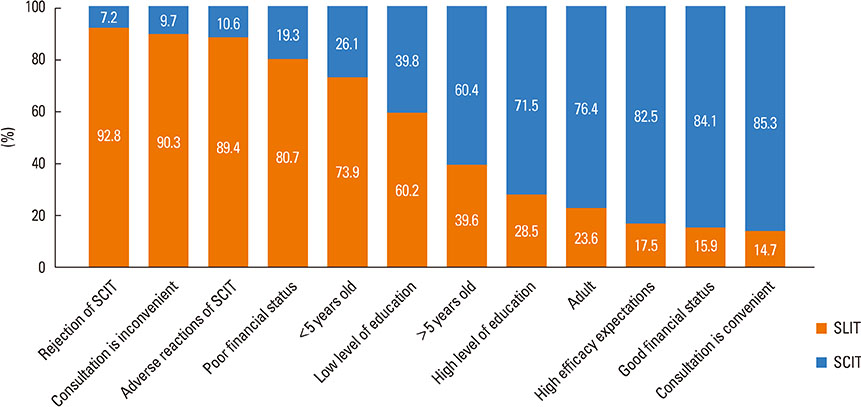
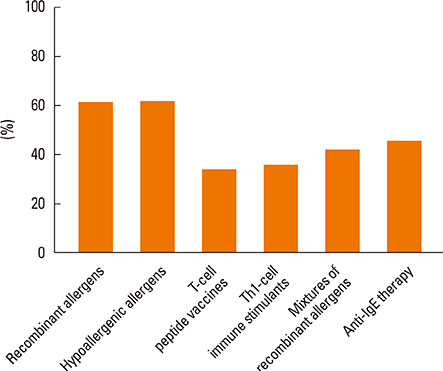
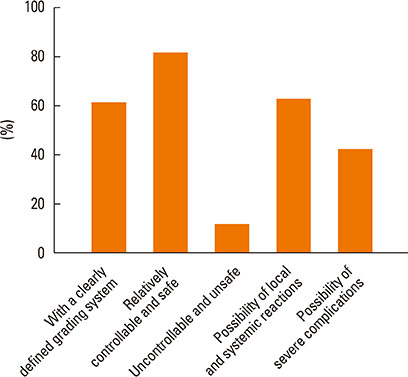
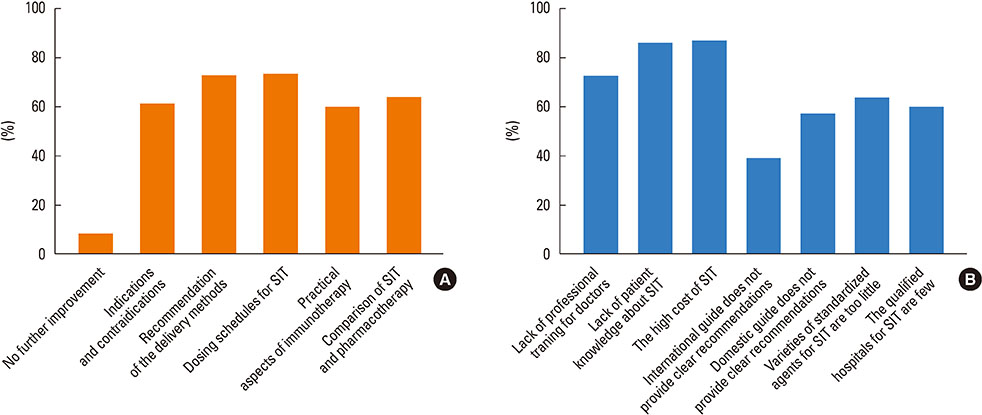
Most of the respondents considered AR (96.0%) and allergic asthma (96.0%) the most suitable indications for SIT. Of all respondents, 77.0% recommended the application of SIT as early as possible; in addition, SIT was considered 'relatively controllable and safe' by most respondents (80.6%). The highest allergen-positive rate in AR was associated with house dust mite (47.7%) and obvious differences existed among geographical regions. Conventional subcutaneous immunotherapy was the most highly recommended treatment option (96.2%). 'The high cost of SIT' (86.6%) and 'lack of patient knowledge of SIT' (85.2%) were probably the main reasons for the lower clinical use of SIT in China.
CONCLUSIONS
Most cases showed that the opinions of Chinese ENT specialists appeared to be in agreement with recent SIT progress and international guidelines; however, many areas still need to enhance the standardization and use of SIT in China. Clinical guidelines for SIT require improvement; in addition, Chinese ENT specialists need continuing medical education on SIT.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Survey of Korean Physicians’ Prescription Patterns for Allergic Rhinitis
Min Young Seo, Dong-Kyu Kim, Hye Mi Jee, Young Min Ahn, Yong Min Kim, Sang Duk Hong
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;10(4):332-337. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2017.00143.
Reference
-
1. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, Zuberbier T, Baena-Cagnani CE, Canonica GW, van Weel C, Agache I, Aït-Khaled N, Bachert C, Blaiss MS, Bonini S, Boulet LP, Bousquet PJ, Camargos P, Carlsen KH, Chen Y, Custovic A, Dahl R, Demoly P, Douagui H, Durham SR, van Wijk RG, Kalayci O, Kaliner MA, Kim YY, Kowalski ML, Kuna P, Le LT, Lemiere C, Li J, Lockey RF, Mavale-Manuel S, Meltzer EO, Mohammad Y, Mullol J, Naclerio R, O'Hehir RE, Ohta K, Ouedraogo S, Palkonen S, Papadopoulos N, Passalacqua G, Pawankar R, Popov TA, Rabe KF, Rosado-Pinto J, Scadding GK, Simons FE, Toskala E, Valovirta E, van Cauwenberge P, Wang DY, Wickman M, Yawn BP, Yorgancioglu A, Yusuf OM, Zar H, Annesi-Maesano I, Bateman ED, Ben Kheder A, Boakye DA, Bouchard J, Burney P, Busse WW, Chan-Yeung M, Chavannes NH, Chuchalin A, Dolen WK, Emuzyte R, Grouse L, Humbert M, Jackson C, Johnston SL, Keith PK, Kemp JP, Klossek JM, Larenas-Linnemann D, Lipworth B, Malo JL, Marshall GD, Naspitz C, Nekam K, Niggemann B, Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Okamoto Y, Orru MP, Potter P, Price D, Stoloff SW, Vandenplas O, Viegi G, Williams D. World Health Organization. GA2LEN. AllerGen. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA2LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.2. Alvarez-Cuesta E, Bousquet J, Canonica GW, Durham SR, Malling HJ, Valovirta E. EAACI, Immunotherapy Task Force. Standards for practical allergen-specific immunotherapy. Allergy. 2006; 61:Suppl 82. 1–20.3. Akkoc T, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Update in the mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotheraphy. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:11–20.4. Noon L. Prophylactic inoculation against hay fever. Lancet. 1911; 177:1572–1573.5. Pajno GB, Barberio G, De Luca F, Morabito L, Parmiani S. Prevention of new sensitizations in asthmatic children monosensitized to house dust mite by specific immunotherapy. A six-year follow-up study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:1392–1397.6. Jacobsen L, Niggemann B, Dreborg S, Ferdousi HA, Halken S, Høst A, Koivikko A, Norberg LA, Valovirta E, Wahn U, Möller C. (The PAT investigator group). Specific immunotherapy has long-term preventive effect of seasonal and perennial asthma: 10-year follow-up on the PAT study. Allergy. 2007; 62:943–948.7. Durham SR, Emminger W, Kapp A, Colombo G, de Monchy JG, Rak S, Scadding GK, Andersen JS, Riis B, Dahl R. Long-term clinical efficacy in grass pollen-induced rhinoconjunctivitis after treatment with SQ-standardized grass allergy immunotherapy tablet. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:131–138.e1-7.8. Allergen immunotherapy: therapeutic vaccines for allergic diseases. Geneva: January 27-29 1997. Allergy. 1998; 53:1–42.9. Canonica GW, Bousquet J, Casale T, Lockey RF, Baena-Cagnani CE, Pawankar R, Potter PC, Bousquet PJ, Cox LS, Durham SR, Nelson HS, Passalacqua G, Ryan DP, Brozek JL, Compalati E, Dahl R, Delgado L, van Wijk RG, Gower RG, Ledford DK, Filho NR, Valovirta EJ, Yusuf OM, Zuberbier T, Akhanda W, Almarales RC, Ansotegui I, Bonifazi F, Ceuppens J, Chivato T, Dimova D, Dumitrascu D, Fontana L, Katelaris CH, Kaulsay R, Kuna P, Larenas-Linnemann D, Manoussakis M, Nekam K, Nunes C, O'Hehir R, Olaguibel JM, Onder NB, Park JW, Priftanji A, Puy R, Sarmiento L, Scadding G, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Seberova E, Sepiashvili R, Solé D, Togias A, Tomino C, Toskala E, Van Beever H, Vieths S. Sub-lingual immunotherapy: World Allergy Organization Position Paper 2009. Allergy. 2009; 64:Suppl 91. 1–59.10. Walker SM, Durham SR, Till SJ, Roberts G, Corrigan CJ, Leech SC, Krishna MT, Rajakulasingham RK, Williams A, Chantrell J, Dixon L, Frew AJ, Nasser SM. British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology. Immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:1177–1200.11. Li J, Sun B, Huang Y, Lin X, Zhao D, Tan G, Wu J, Zhao H, Cao L, Zhong N. China Alliance of Research on Respiratory Allergic Disease. A multicentre study assessing the prevalence of sensitizations in patients with asthma and/or rhinitis in China. Allergy. 2009; 64:1083–1092.12. Shi HB, Cheng L, Enomoto T, Takahashi Y, Sahashi N, Shirakawa T, Miyoshi A. Recent advances in pollen survey and pollinosis research in China. Jpn J Palynol. 2002; 48:109–127.13. Zhu L, Lu JH, Xie Q, Wu YL, Zhu LP, Cheng L. Compliance and safety evaluation of subcutaneous versus sublingual immunotherapy in mite-sensitized patients with allergic rhinitis. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010; 45:444–449.14. Zhu L, Zhu LP, Chen RX, Tao QL, Lu JH, Cheng L. Clinical efficacy of subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy in mite-sensitized patients with allergic rhinitis. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011; 46:986–991.15. Calderón MA, Cox L, Casale TB, Moingeon P, Demoly P. Multiple-allergen and single-allergen immunotherapy strategies in polysensitized patients: looking at the published evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:929–934.16. Jutel M, Jaeger L, Suck R, Meyer H, Fiebig H, Cromwell O. Allergen-specific immunotherapy with recombinant grass pollen allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 116:608–613.17. Nelson HS. Multiallergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:763–769.18. Amar SM, Harbeck RJ, Sills M, Silveira LJ, O'Brien H, Nelson HS. Response to sublingual immunotherapy with grass pollen extract: monotherapy versus combination in a multiallergen extract. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:150–156.e1-5.19. Adkinson NF Jr, Eggleston PA, Eney D, Goldstein EO, Schuberth KC, Bacon JR, Hamilton RG, Weiss ME, Arshad H, Meinert CL, Tonascia J, Wheeler B. A controlled trial of immunotherapy for asthma in allergic children. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:324–331.20. Eifan AO, Keles S, Bahceciler NN, Barlan IB. Anaphylaxis to multiple pollen allergen sublingual immunotherapy. Allergy. 2007; 62:567–568.21. Dunsky EH, Goldstein MF, Dvorin DJ, Belecanech GA. Anaphylaxis to sublingual immunotherapy. Allergy. 2006; 61:1235.22. Cox L, Nelson H, Lockey R, Calabria C, Chacko T, Finegold I, Nelson M, Weber R, Bernstein DI, Blessing-Moore J, Khan DA, Lang DM, Nicklas RA, Oppenheimer J, Portnoy JM, Randolph C, Schuller DE, Spector SL, Tilles S, Wallace D. Allergen immunotherapy: a practice parameter third update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:S1–S55.23. Cohn JR, Pizzi A. Determinants of patient compliance with allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993; 91:734–737.24. Cox L. Accelerated immunotherapy schedules: review of efficacy and safety. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006; 97:126–137.25. Finegold I. Allergen immunotherapy: present and future. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007; 28:44–49.26. Cox LS. Shooting for a faster approach to the immunotherapy target: will cluster become conventional? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009; 102:177–178.27. Schubert R, Eickmeier O, Garn H, Baer PC, Mueller T, Schulze J, Rose MA, Rosewich M, Renz H, Zielen S. Safety and immunogenicity of a cluster specific immunotherapy in children with bronchial asthma and mite allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009; 148:251–260.28. Zhang L, Wang C, Han D, Wang X, Zhao Y, Liu J. Comparative study of cluster and conventional immunotherapy schedules with dermatophagoides pteronyssinus in the treatment of persistent allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009; 148:161–169.29. Copenhaver CC, Parker A, Patch S. Systemic reactions with aeroallergen cluster immunotherapy in a clinical practice. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011; 107:441–447.30. More DR, Hagan LL. Factors affecting compliance with allergen immunotherapy at a military medical center. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002; 88:391–394.31. Radulovic S, Wilson D, Calderon M, Durham S. Systematic reviews of sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT). Allergy. 2011; 66:740–752.32. Wang DH, Chen L, Cheng L, Li KN, Yuan H, Lu JH, Li H. Fast onset of action of sublingual immunotherapy in house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:1334–1340.33. Valenta R, Linhart B, Swoboda I, Niederberger V. Recombinant allergens for allergen-specific immunotherapy: 10 years anniversary of immunotherapy with recombinant allergens. Allergy. 2011; 66:775–783.34. Larché M. Update on the current status of peptide immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:906–909.35. Valenta R, Campana R, Marth K, van Hage M. Allergen-specific immunotherapy: from therapeutic vaccines to prophylactic approaches. J Intern Med. 2012; 272:144–157.36. Cox L, Larenas-Linnemann D, Lockey RF, Passalacqua G. Speaking the same language: the World Allergy Organization subcutaneous immunotherapy systemic reaction grading system. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:569–574. 574.e1–574.e7.37. Akdis C, Papadopoulos N, Cardona V. Fighting allergies beyond symptoms: the European Declaration on Immunotherapy. Eur J Immunol. 2011; 41:2802–2804.38. Ariano R, Berto P, Tracci D, Incorvaia C, Frati F. Pharmacoeconomics of allergen immunotherapy compared with symptomatic drug treatment in patients with allergic rhinitis and asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2006; 27:159–163.39. Omnes LF, Bousquet J, Scheinmann P, Neukirch F, Jasso-Mosqueda G, Chicoye A, Champion L, Fadel R. Pharmacoeconomic assessment of specific immunotherapy versus current symptomatic treatment for allergic rhinitis and asthma in France. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 39:148–156.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Allergen Specific Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis
- Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis
- The status quo and unmet needs in the management of allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis: a Malaysian perspective
- Sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis
- Allergen Specific Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis