J Rheum Dis.
2013 Feb;20(1):48-51. 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.48.
Adult-onset Cyclic Neutropenia Diagnosed in a Patient with Acute Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. yn35@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Borame Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2223049
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.48
Abstract
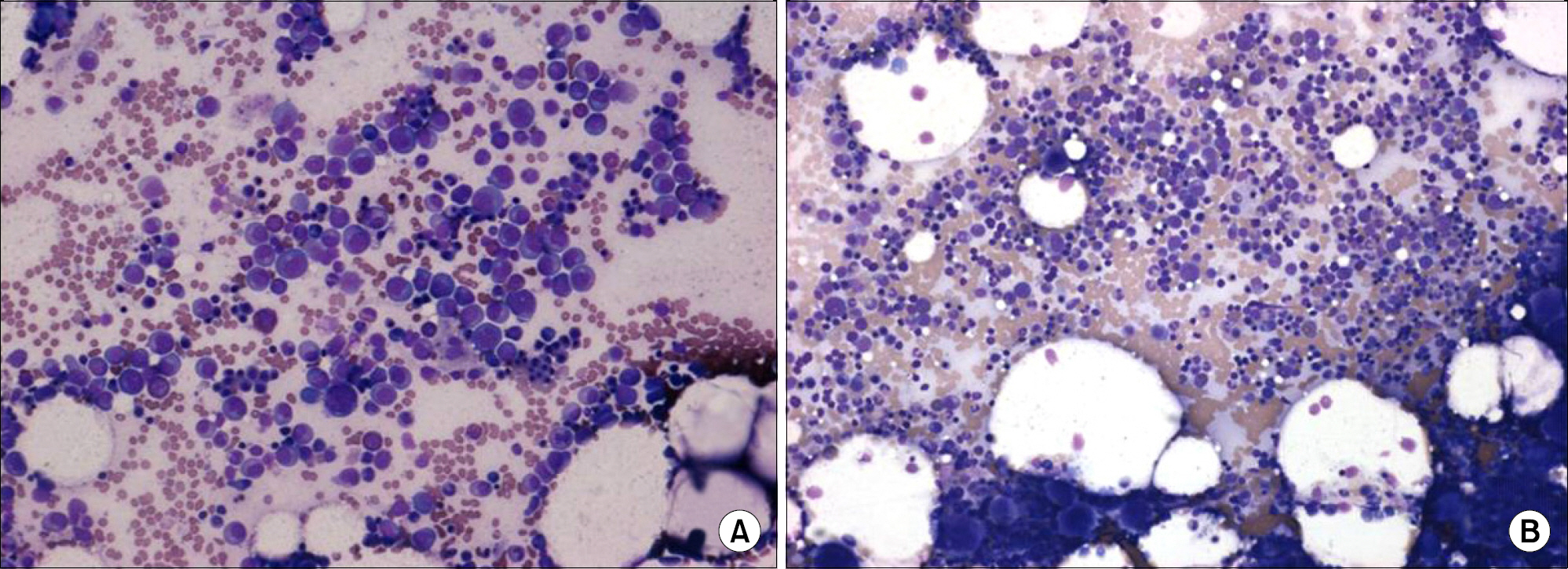
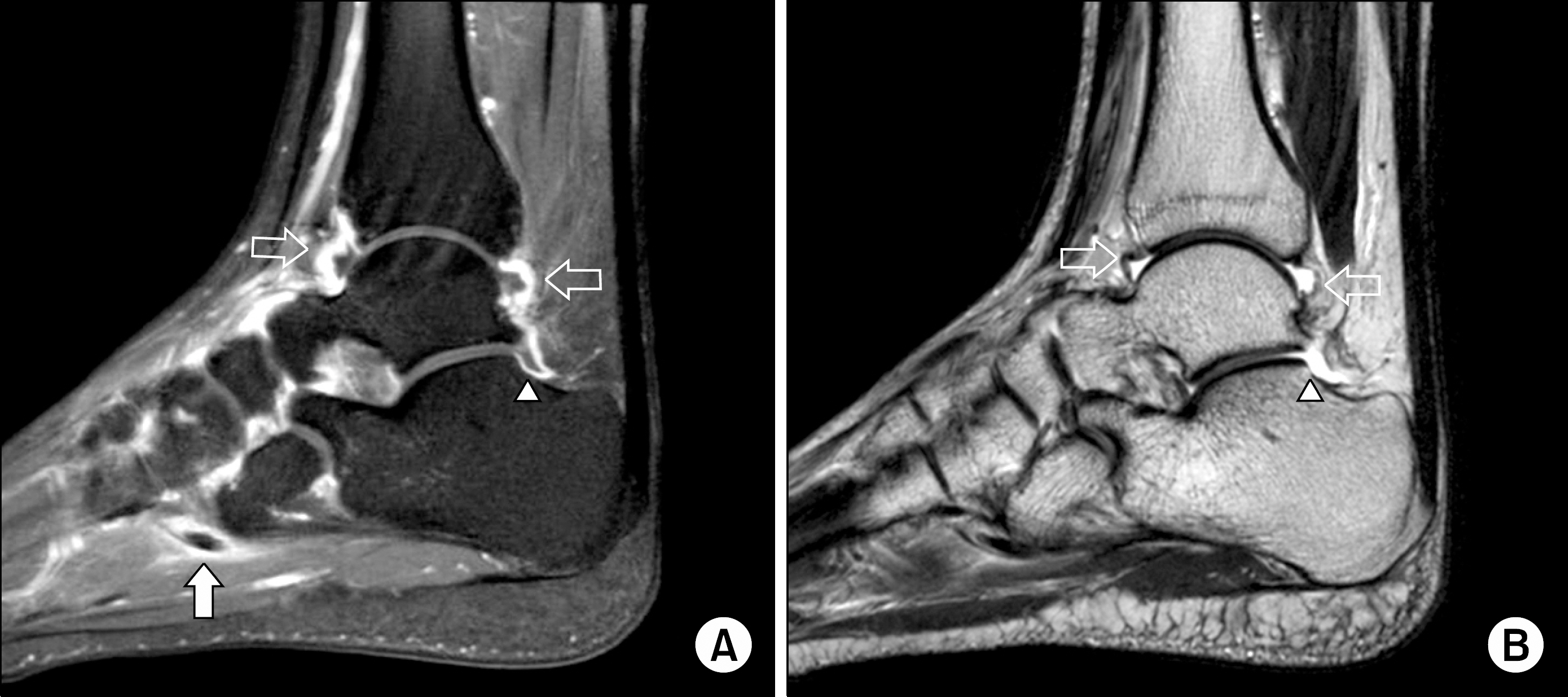
- Cyclic neutropenia (CN) is a rare disorder characterized by repetitive episodes of neutropenia and is generally associated with fever, oral mucosal ulcers, and bacterial infections in the neutropenic episodes. It usually manifests initially in infancy or childhood as an autosomal dominant or sporadic condition; however, adult-onset CN may have an autoimmune etiology. Here, we report the first case of a 22-year old man with CN in Korea. He developed acute arthralgia and fever 4 weeks after an episode of lower gastrointestinal symptoms. Serial blood cell counts showed recurrent neutropenia at 3 week intervals. Further, laboratory examination for neutropenia, including neutrophil elastase gene sequencing, did not reveal any abnormality. His arthritis and periarthritis fluctuated during his course. Under the diagnosis of CN, he received regular G-CSF therapy with partial improvement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Aprikyan AA, Dale DC. Mutations in the neutrophil elastase gene in cyclic and congenital neutropenia. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001; 13:535–8.
Article2. Dale DC, Bolyard AA, Aprikyan A. Cyclic neutropenia. Semin Hematol. 2002; 39:89–94.
Article3. Loughran TP Jr, Clark EA, Price TH, Hammond WP. Adult-onset cyclic neutropenia is associated with increased large granular lymphocytes. Blood. 1986; 68:1082–7.
Article4. Loughran TP Jr, Hammond WP 4th. Adult-onset cyclic neutropenia is a benign neoplasm associated with clonal proliferation of large granular lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1986; 164:2089–94.
Article5. Dale DC, Hammond WP 4th. Cyclic neutropenia: a clinical review. Blood Rev. 1988; 2:178–85.
Article6. Cha YH, Lee HS, Ahn YM, Koo MS. A case of cyclic neutropenia. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1993; 36:1009–15.7. Oh SM, Kim HS, Kwak JY, Yim CY. A case of cyclic hematopoiesis. Korean J Hematol. 1997; 32:428–32.8. Storek J, Glaspy JA, Grody WW, Susi E, Slater ED. Adult-onset cyclic neutropenia responsive to cyclosporine therapy in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis. Am J Hematol. 1993; 43:139–43.
Article9. Palmer SE, Stephens K, Dale DC. Genetics, phenotype, and natural history of autosomal dominant cyclic hematopoiesis. Am J Med Genet. 1996; 66:413–22.
Article10. Barnes C, Gerstle JT, Freedman MH, Carcao MD. Clostridium septicum myonecrosis in congenital neutropenia. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:e757–60.
Article11. Rodgers GM, Shuman MA. Acquired cyclic neutropenia: successful treatment with prednisone. Am J Hematol. 1982; 13:83–9.
Article12. Selleri C, Catalano L, Alfinito F, De Rosa G, Vaglio S, Rotoli B. Cyclosporin A in adult-onset cyclic neutropenia.13. Young GA, Iland HJ, Deveridge SF, Forrest PR, Vincent PC. Steroid responsive cyclical neutropenia. Blut. 1984; 48:153–9.
Article14. Heussner P, Haase D, Kanz L, Fonatsch C, Welte K, Freund M. G-CSF in the longterm treatment of cyclic neutropenia and chronic idiopathic neutropenia in adult patients. Int J Hematol. 1995; 62:225–34.15. Horwitz MS, Duan Z, Korkmaz B, Lee HH, Mealiffe ME, Salipante SJ. Neutrophil elastase in cyclic and severe congenital neutropenia. Blood. 2007; 109:1817–24.
Article