Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Jun;37(3):430-432. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.430.
A Case Report of Long-Term Bisphosphonate Therapy and Atypical Stress Fracture of Bilateral Femur
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjko@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2219542
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.430
Abstract
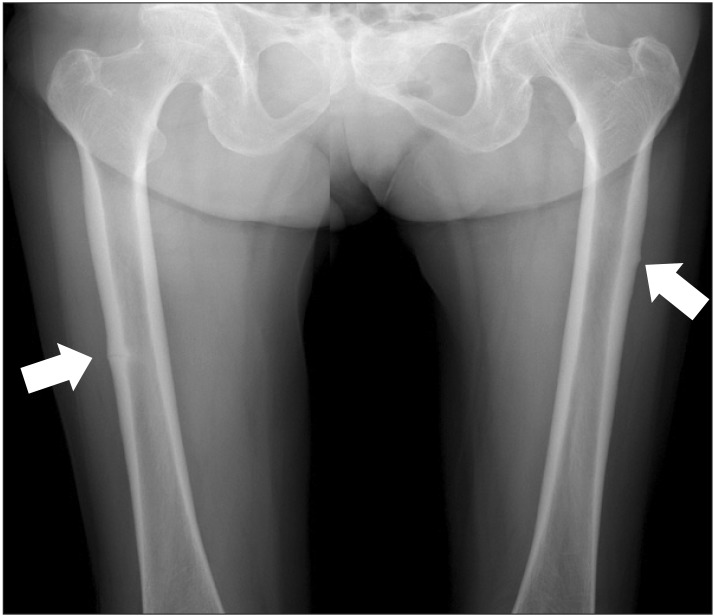
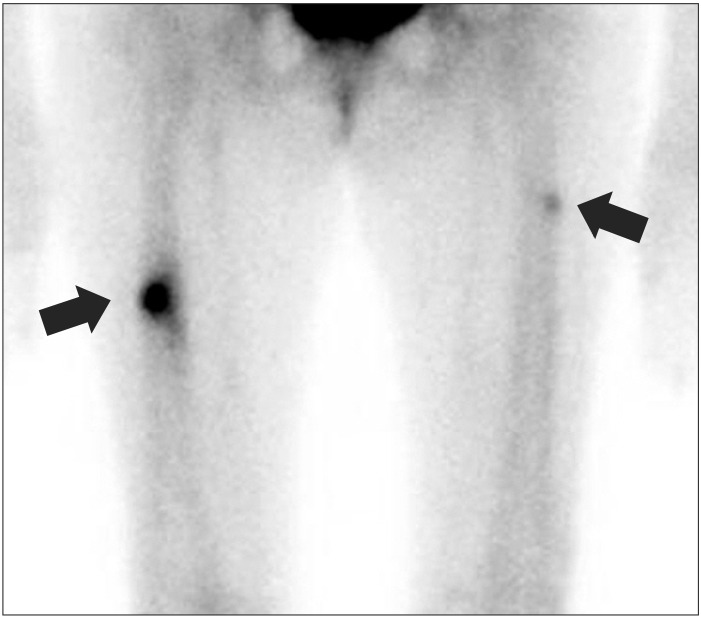
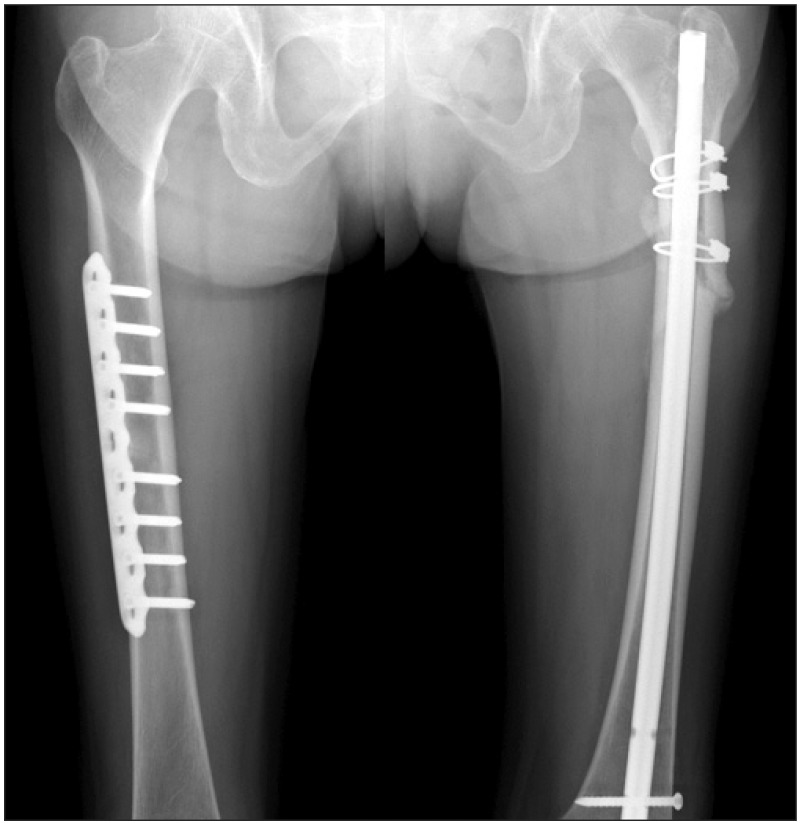
- Bisphosphonates are potent inhibitors of bone resorption and considered as a gold standard and are generally recommended as first-line therapy in patients with osteoporosis. Though bisphosphonates are shown to significantly reduce the risk of vertebral, non-vertebral and hip fractures, recent reports suggest a possible correlation between long-term bisphosphonate therapy and the occurrence of insufficiency fractures owing to prolonged bone turnover suppression. We report a patient with non-traumatic stress fractures of bilateral femoral shafts related to long-term bisphosphonate therapy indicating the need for a critical evaluation of patients with long-term bisphosphonate therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Reginster JY, Burlet N. Osteoporosis: a still increasing prevalence. Bone. 2006; 38(2 Suppl 1):S4–S9. PMID: 16455317.
Article2. Silverman S, Christiansen C. Individualizing osteoporosis therapy. Osteoporos Int. 2012; 23:797–809. PMID: 22218417.
Article3. Osugi K, Miwa S, Marukawa S, Marukawa K, Kawaguchi Y, Nakato S. Diaphyseal femoral fatigue fracture associated with bisphosphonate therapy: 3 more cases. Acta Orthop. 2011; 82:112–113. PMID: 21142824.4. Black DM, Schwartz AV, Ensrud KE, Cauley JA, Levis S, Quandt SA, et al. Effects of continuing or stopping alendronate after 5 years of treatment: the Fracture Intervention Trial Long-term Extension (FLEX): a randomized trial. JAMA. 2006; 296:2927–2938. PMID: 17190893.
Article5. Dell R, Greene D, Ott S, Silverman S, Eisemon E, Funahashi T, et al. A retrospective analysis of all atypical femur fractures seen in a large California HMO from the years 2007 to 2009. In : ASBMR 2010 Annual Meeting; Oct 15-19; Toronto, Canada. 2010.6. Vasikaran SD. Association of low-energy femoral fractures with prolonged bisphosphonate use: a case-control study. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20:1457–1458. PMID: 19436933.
Article7. Giusti A, Hamdy NA, Papapoulos SE. Atypical fractures of the femur and bisphosphonate therapy: a systematic review of case/case series studies. Bone. 2010; 47:169–180. PMID: 20493982.8. Watts NB, Diab DL. Long-term use of bisphosphonates in osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:1555–1565. PMID: 20173017.
Article9. Rizzoli R, Akesson K, Bouxsein M, Kanis JA, Napoli N, Papapoulos S, et al. Subtrochanteric fractures after long-term treatment with bisphosphonates: a European Society on Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis, and International Osteoporosis Foundation Working Group Report. Osteoporos Int. 2011; 22:373–390. PMID: 21085935.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insufficiency Fracture of Ipsilateral Femur Neck in Patient Treated with Long Term Bisphosphonate Treatment: A Case Report
- Atypical femoral neck fracture after prolonged bisphosphonate therapy
- Insufficiency Fracture of Simultaneously Bilateral Femur Neck in Patient Treated with Long-Term Bisphosphonate Treatment - A Case Report -
- Atypical Fracture-Like Insufficiency Fracture of the Tibia with Prolonged Bisphosphonate Drug: A Case Report
- Management Challenges in Atypical Femoral Fractures: A Case Report