Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Jun;37(3):426-429. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.426.
The Effect of Balloon Dilation at the Vallecular Using Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study on Patient Who Has a Dysphagia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. kmt137@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2219541
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.426
Abstract
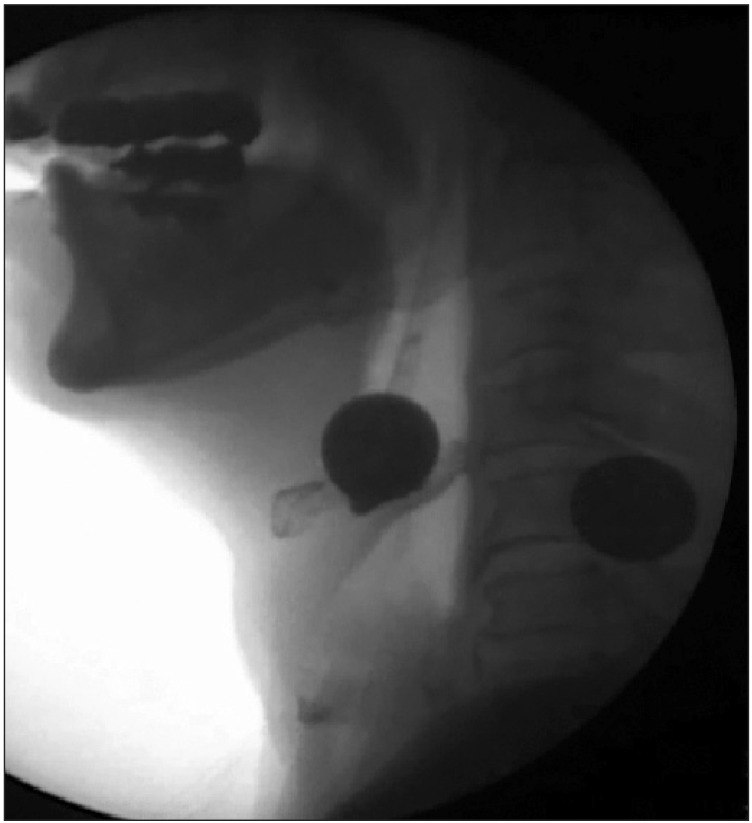
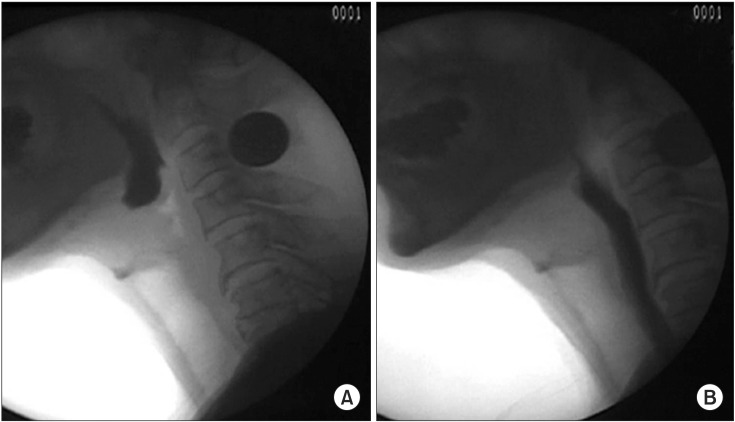
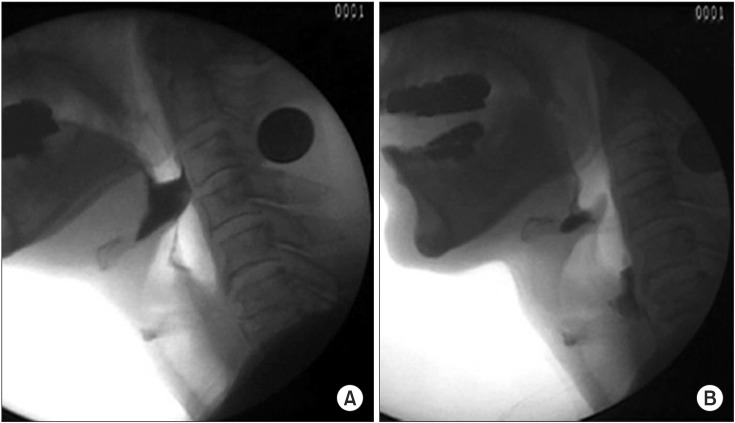
- Authors have previously experienced the effect of balloon dilation at the vallecular by utilizing the video-fluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) and the urethral catheter to physically stretch and spread in the direction of the posterior inferior towards the patients who have claimed for dysphagia symptoms due to epiglottic dysfunction. A 72-year-old male patient has been diagnosed with rectal cancer and have been treated with an ileocolostomy after the intubation. After the removal of tracheal intubation, the patient complained of dysphagia. Foods and drinks could not be transmigrated into the esophagus due to the inability of the epiglottis to bend backward in the direction of posterior inferior on VFSS. The epiglottis was physically stretched and spread in the direction of posterior inferior by utilizing the balloon attached to a urethral catheter. After stretching and spreading the epiglottis in the direction of posterior inferior, the bolus remaining in the epiglottic vallecula was decreased. For a patient who is experiencing dysphagia due to an epiglottis disorder, it seems that an epiglottis balloon dilation supported by VFSS and a urethral catheter may be appropriate for the treatment of dysphagia symptoms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Vallecular Ballooning in Stroke Patients With Dysphagia
Yong Kyun Kim, Sang-heon Lee, Jang-won Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(2):231-238. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.231.
Reference
-
1. Kim HJ, Yun DH, Kim SH, Kim DY, Kim HS, Kim HJ. Endoscopic botulinum toxin injection for the treatment of dysphagia caused by cricopharyngeal hypertonicity: a case report. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2006; 30:398–401.2. Garon BR, Huang Z, Hommeyer M, Eckmann D, Stern GA, Ormiston C. Epiglottic dysfunction: abnormal epiglottic movement patterns. Dysphagia. 2002; 17:57–68. PMID: 11820387.
Article3. Kim JC, Kim JS, Jung JH, Kim YK. The effect of balloon dilatation through video-fluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) in stroke patients with cricopharyngeal dysfunction. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:23–26.4. Solt J, Bajor J, Moizs M, Grexa E. Primary cricopharyngeal achalasia and its dilatation with balloon catheter. Orv Hetil. 2000; 141:2287–2292. PMID: 11076494.5. Solt J, Bajor J, Moizs M, Grexa E, Horvath PO. Primary cricopharyngeal dysfunction: treatment with balloon catheter dilatation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:767–771. PMID: 11726859.
Article6. Sinn DH, Choi YS, Kim JH, Kim ER, Son HJ, Kim JJ, et al. Change in cross-sectional area of esophageal muscle does not correlate with the outcome of achalasia after pneumatic balloon dilatation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:539–543. PMID: 20370731.
Article7. Alderliesten J, Conchillo JM, Leeuwenburgh I, Steyerberg EW, Kuipers EJ. Predictors for outcome of failure of balloon dilatation in patients with achalasia. Gut. 2011; 60:10–16. PMID: 21068135.
Article8. Jung C, Michaud L, Mougenot JF, Lamblin MD, Philippe-Chomette P, Cargill G, et al. Treatments for pediatric achalasia: Heller myotomy or pneumatic dilatation? Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010; 34:202–208. PMID: 20303225.
Article9. Garon BR, Huang Z, Hommeyer M, Eckmann D, Stern GA, Ormiston C. Epiglottic dysfunction: abnormal epiglottic movement patterns. Dysphagia. 2002; 17:57–68. PMID: 11820387.
Article10. Han TR, Bang MS, Paik NJ, Jeon JY, Kim SJ, Lee HJ. Digital image motion analysis of the pharyngeal movement during swallowing in dysphagia patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2002; 26:693–698.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Vallecular Ballooning in Stroke Patients With Dysphagia
- Instrumental Assessment of Swallowing
- Scoring System in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study
- Development of a New Scale for Pharyngeal Residue Using Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study and Fiberoptic Endoscopy
- The Effect of Balloon Dilatation through Video-Fluoroscopic Swallowing Study (VFSS) in Stroke Patients with Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction