J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Oct;52(10):1173-1181. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.10.1173.
Clinical Results of Bacterial Endophthalmitis: Bacterial Culture and Visual Acuity Outcomes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. parkjm@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Korea Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2214999
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.10.1173
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical characteristics of bacterial culture, and visual outcome in patients with acute endophthalmitis.
METHODS
Clinical records of patients treated for acute endophthalmitis in GNUH from 2000 to 2009 were reviewed. The specimens for culture were obtained from the anterior chamber or vitreous. Clinical outcome measures were bacterial culture, culture rate, and final visual acuity.
RESULTS
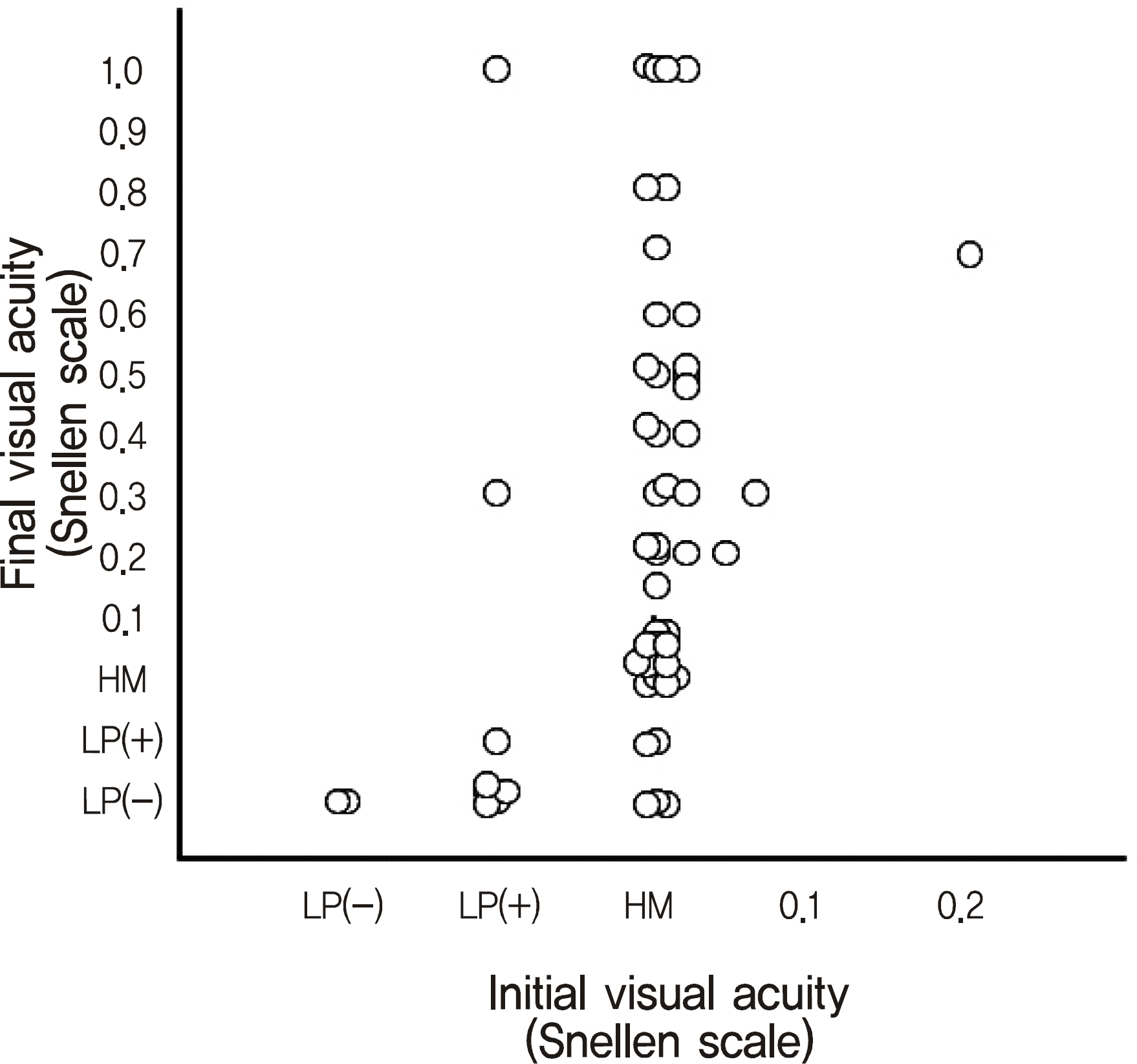
Cultures (total 59 cases) showed bacterial growth in 37 cases (63%). Among 35 cases vitreous specimens, bacteria growth was found in 22 cases (63%), and from the 27 anterior chamber specimens, 12 cases (44%) were culture positive. From these 37 bacterial-positive cultures, 11 (30%) were coagulase negative Staphylococcus species, 16 (43.0%) were other Gram-positive species, 9 (24%) were Gram-negative species, and 1 (3%) produced a polymicrobial culture. Final visual acuity above 0.5 was achieved in 16 of 59 (27%) cases and coagulase negative Staphylococcus species had the greatest proportion being 5 of 11 (45%).
CONCLUSIONS
The bacterial culture positivity rate in bacterial endophthalmitis was 63%, and the culture yield rate from the vitreous was higher than the anterior chamber aqueous samples. Coagulase negative Staphylococcus species were the most common causative organisms and showed the best final visual outcome in endophthalmitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Vitrectomy versus Intravitreal Antibiotic Injection to Treat Acute Endophthalmitis Developing after Cataract Surgery
Jung Yup Kim, Joo Eun Lee, Kang Yeun Pak
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(1):37-43. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.1.37.Factors Affecting Final Visual Acuity in Infectious Endophthalmitis Following Cataract Surgery
Kyung Tae Kang, Kwang Soo Kim, Yu Cheol Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(7):1025-1031. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.7.1025.The Effectiveness of Pediatric Blood Culture Bottle in Endophthalmitis
Kyong Ho Kim, Han Jo Kwon, Sung Who Park, Ik Soo Byon, Ji Eun Lee, Boo Sup Oum, Kyung Hwa Shin
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(9):1365-1370. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.9.1365.
Reference
-
References
1. Chung SE, Ham DI. Visual prognosis of culture-proven bacterial endophthalmitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1292–7.2. Results of the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study: A randomized trial of immediate vitrectomy and of intravenous antibiotics for the treatment of postoperative bacterial endophthalmitis. Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study Group. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995; 113:1479–96.3. Hwang JH, Cho NC. Prognostic factors in patients with endogenous endophthalmitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:858–63.
Article4. Pijl BJ, Theelen T, Tilanus MA, et al. Acute endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: 250 consecutive cases treated at a tertiary referral center in the Netherlands. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 149:482–7.
Article5. Nussenblatt RB, Palestine AG, Chan CC, Roberge F. Standardization of vitreal inflammatory activity in intermediate and posterior uveitis. Ophthalmology. 1985; 92:467–71.6. Olson RJ. Reducing the risk of postoperative endophthalmitis. Surv Ophthalmol. 2004; 49:S55–61.
Article7. Lee SB, Han JW, Chung SK, Baek NH. Factors associated with visual outcomes of postoperative endophthalmitis following cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1618–23.8. Kresloff MS, Castellarin AA, Zarbin MA. Endophthalmitis. Surv Ophthalmol. 1998; 43:193–224.
Article9. Binder MI, Chua J, Kaiser PK, et al. Endogenous endophthalmitis: an 18-year review of culture-positive cases at a tertiary care center. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003; 82:97–105.10. Ness T, Serr A. Diagnostics for endophthalmitis. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2008; 225:44–9.11. Barza M, Pavan PR, Doft BH, et al. Evaluation of microbiological diagnostic techniques in postoperative endophthalmitis in the Ebdophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997; 115:1142–50.12. Chiquet C, Maurin M, Thuret G, et al. Analysis of diluted vitreous samples from vitrectomy is useful in eyes with severe acute postoperative endophthalmitis. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:2437–41.
Article13. Sharma S, Jalali S, Adiraju MV, et al. Sensitivity and predictability of vitreous cytology, biopsy, and membrane filter culture in endophthalmitis. Retina. 1996; 16:525–9.
Article14. Kim WJ, Kweon EY, Lee DW, Cho NC. Postoperative endophthalmitis following cataract surgery over an eight-year period. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1771–8.
Article15. Laatikainen L, Tarkkanen A. Early vitrectomy in the treatment of postoperative purulent endophthalmitis. Acta Ophthalmol. 1987; 65:455–60.
Article16. Kuhn F, Gini G. Ten years after are findings of the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study still relevant today? Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005; 243:1197–9.
Article17. Anand AR, Therese KL, Madhavan HN. Spectrum of aetiological agents of postoperative endophthalmitis and antibiotic susceptibility of bacterial isolates. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2000; 48:123–8.18. Bispo PJ, Melo GB, d'Azevedo PA, et al. Culture proven bacterial endophthalmitis: a 6-year review. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2008; 71:617–22.19. Major JC Jr, Engelbert M, Flynn HW Jr, et al. Staphylococcus aureus endophthalmitis: antibiotic susceptibilities, methicillin resistance, and clinical outcomes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 149:278–83.
Article20. Duggirala A, Joseph J, Sharma S, et al. Activity of newer fluoroquinolones against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria isolated from ocular infections: an in vitro comparison. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2007; 55:15–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Bacterial Endophthalmitis Following Penetrating Keratoplasty
- Visual Prognosis of Culture-Proven Bacterial Endophthalmitis
- Factors Associated with Visual Outcomes of Postoperative Endophthalmitis Following Cataract Surgery
- Factors Affecting Final Visual Acuity in Infectious Endophthalmitis Following Cataract Surgery
- Bacterial Bacterial Culture and Clinical Characteristics of Infectious Endophthalmitis in Western Gyeongsangnam-do