J Korean Surg Soc.
2012 Mar;82(3):143-148. 10.4174/jkss.2012.82.3.143.
Can serum interleukin-2 receptor alpha predict lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sungkimm@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 2212215
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.82.3.143
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although local resection like endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer is accepted as a treatment option, one of the most important drawbacks of such an approach is the inability to predictlymph node metastasis. The aim of this study was to evaluate the serum soluble receptor alpha for interleukin-2 (IL-2Ralpha) level as a predictor of lymph node metastasis in the patients with early gastric cancer.
METHODS
Assessment of pre-operative serum IL-2Ralpha levels was performed on 86 patients with early gastric cancer treated by gastrectomies combined with D2 lymph node resections and 20 healthy controls at Samsung Medical Center. Data on patient age and gender, tumor size, depth of invasion, histologic differentiation, and endoscopic findings were reviewed post-operatively. The submucosal lesions were divided into three layers (sm1, sm2, and sm3) in accordance with the depth of invasion.
RESULTS
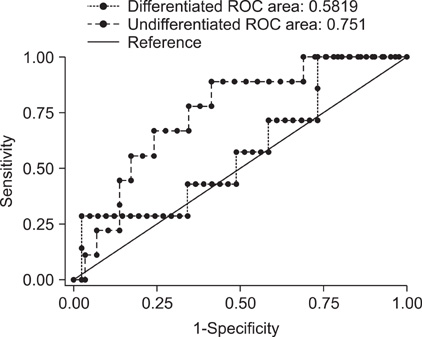
Lymph node metastasis was observed in 16 patients (18.6%). Statistically, the serum IL-2Ralpha level was an important predictive factor of lymph node metastasis in undifferentiated gastric cancer, and the cut-off point for the predictive value of serum IL-2Ralpha level was 200 U/mL.
CONCLUSION
The serum IL-2Ralpha level might be a good predictor of lymph node metastasis in undifferentiated early gastric cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim MG, Kim BS, Kim TH, Kim KC, Yook JH, Oh ST, et al. Surgical treatment for patients who underwent endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)/endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) of early gastric cancer (EGC). J Korean Surg Soc. 2011. 80:165–171.2. Kitano S, Iso Y, Moriyama M, Sugimachi K. Laparoscopyassisted Billroth I gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1994. 4:146–148.3. Heo GU, Kim MC, Jung GJ, Choi SR. Robotic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: preliminary results. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 76:301–306.4. Lee JH, Kim JJ. Endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer: Experiences in Korea. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. 13:3657–3661.5. Nitti D, Marchet A, Olivieri M, Ambrosi A, Mencarelli R, Farinati F, et al. Lymphadenectomy in patients with gastric cancer. A critical review. Suppl Tumori. 2003. 2:S35–S38.6. Yanai H, Noguchi T, Mizumachi S, Tokiyama H, Nakamura H, Tada M, et al. A blind comparison of the effectiveness of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in staging early gastric cancer. Gut. 1999. 44:361–365.7. Smith KA. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science. 1988. 240:1169–1176.8. Saito H, Tsujitani S, Katano K, Ikeguchi M, Maeta M, Kaibara N. Levels of serum-soluble receptor for interleukin-2 in patients with colorectal cancer. Surg Today. 1998. 28:1115–1117.9. Fukuya T, Honda H, Hayashi T, Kaneko K, Tateshi Y, Ro T, et al. Lymph-node metastases: efficacy for detection with helical CT in patients with gastric cancer. Radiology. 1995. 197:705–711.10. Dehn TC, Reznek RH, Nockler IB, White FE. The pre-operative assessment of advanced gastric cancer by computed tomography. Br J Surg. 1984. 71:413–417.11. Dorfman RE, Alpern MB, Gross BH, Sandler MA. Upper abdominal lymph nodes: criteria for normal size determined with CT. Radiology. 1991. 180:319–322.12. Dittler HJ, Siewert JR. Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in gastric carcinoma. Endoscopy. 1993. 25:162–166.13. Maehara Y, Okuyama T, Oshiro T, Baba H, Anai H, Akazawa K, et al. Early carcinoma of the stomach. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1993. 177:593–597.14. Tsujitani S, Oka S, Saito H, Kondo A, Ikeguchi M, Maeta M, et al. Less invasive surgery for early gastric cancer based on the low probability of lymph node metastasis. Surgery. 1999. 125:148–154.15. Abe N, Watanabe T, Suzuki K, Machida H, Toda H, Nakaya Y, et al. Risk factors predictive of lymph node metastasis in depressed early gastric cancer. Am J Surg. 2002. 183:168–172.16. Wu CY, Chen JT, Chen GH, Yeh HZ. Lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer: a clinicopathological analysis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002. 49:1465–1468.17. Folli S, Morgagni P, Roviello F, De Manzoni G, Marrelli D, Saragoni L, et al. Risk factors for lymph node metastases and their prognostic significance in early gastric cancer (EGC) for the Italian Research Group for Gastric Cancer (IRGGC). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2001. 31:495–499.18. Murakami S, Sakata H, Tsuji Y, Okubo K, Hamada S, Hirayama R. Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a predictor of lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. Dig Surg. 2002. 19:9–13.19. Forones NM, Mandowsky SV, Lourenço LG. Serum levels of interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha correlate to tumor progression in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001. 48:1199–1201.20. Maeta M, Saito H, Katano K, Kondo A, Tsujitani S, Makino M, et al. A progressive postoperative increase in the serum level of soluble receptors for interleukin-2 is an indicator of a poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Int J Mol Med. 1998. 1:113–116.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of Lymph Node Metastasis in Early Gastric Cancer
- Risk Factors Affecting Lymph Node Metastasis and Recurrence in Early Gastric Cancer
- A Clinical Analysis of the Characteristics of the Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Gastrics Cancer
- A Rare Case of Lymph Node Metastasis from Early Gastric Cancer
- Correlation Between Expression of p53, Bcl-2 Protein and Ki-67 Labelling Index and Lymph Node Metastasis in Early Gastric Cancer