J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2007 Sep;14(3):201-207. 10.4078/jkra.2007.14.3.201.
The Suppressive Effect of Rifampicin in Animal Model of Hemophilic Synovitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. yhira@khu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3East-West Bone and Joint Research Institute, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2202168
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2007.14.3.201
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Hemophilic arthropathy, which results from recurrent intra-articular bleeding, is a proliferative synovitis, but the sequence of pathogenic events in hemophilic synovitis (HS) is not known in detail. To investigate the pathogenic mechanism of HS and to evaluate the suppressive effect of rifampicin for HS, we designed this study.
METHODS
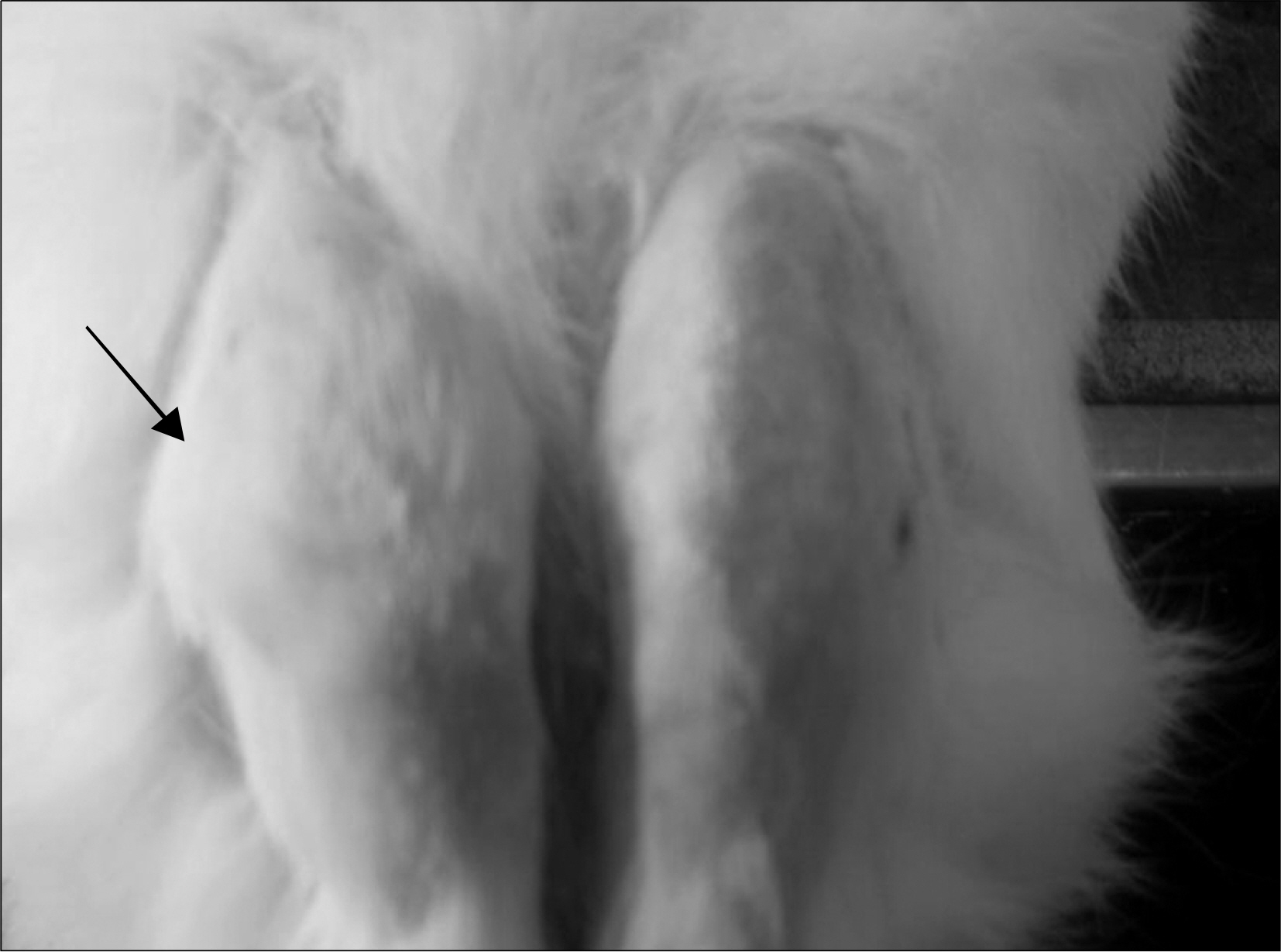
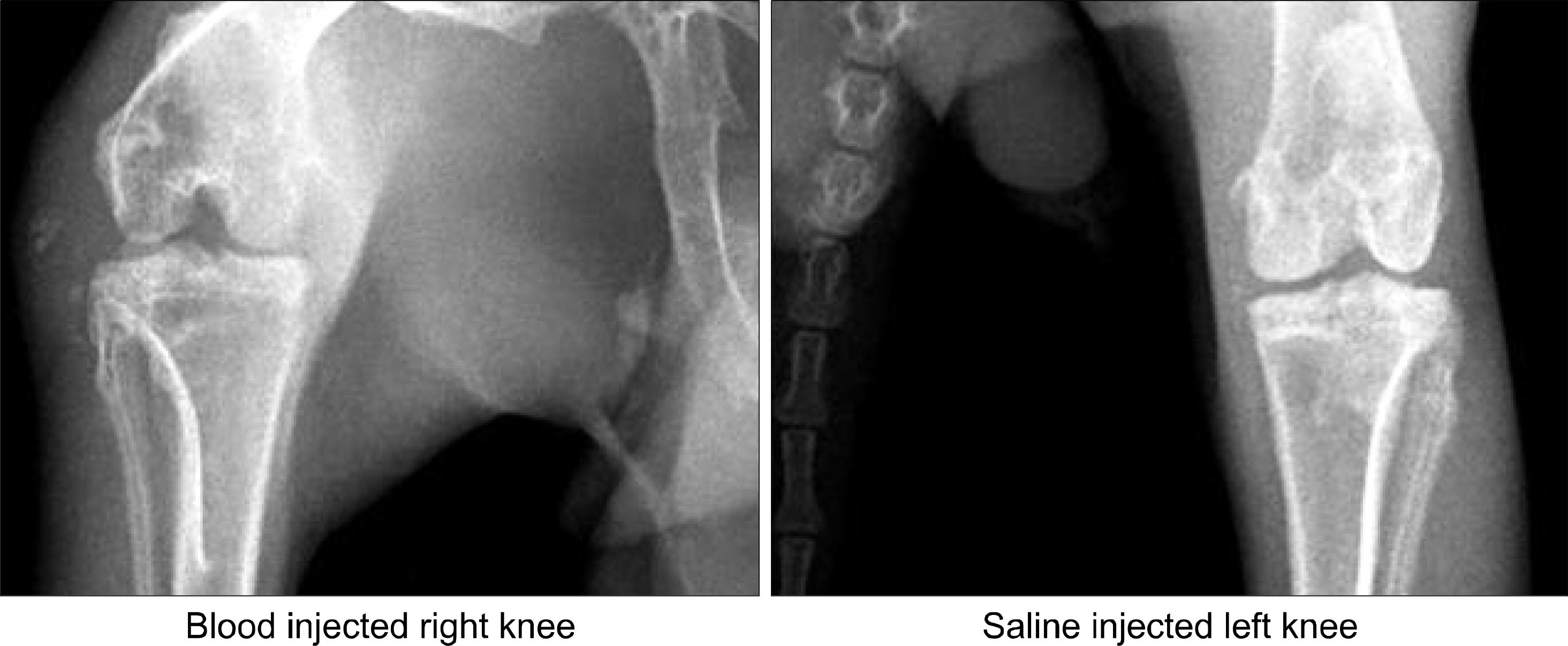
Twenty normal male New Zealand white rabbits weighing approximately 2,000 gm were used for this study. We injected 1 mL of autologous whole blood of the rabbits into the right knee joint and normal saline into the left knee joint (control) thrice a week for 10 weeks and sacrificed 10 of them. We injected 10 mg of rifampicin into the right knee joint of HS, which is 5 rabbits of remained 10, once a week from 11th week until 15th week. At 11th week and 20th week, the rabbits were sacrificed and both knee joints of each rabbit were opened, synovial membrane specimens were collected and examined pathologically and biologically such as mRNA of IL-1, TNF-alpha, MMP-1 and MMP-3 in hemophilic synovium using by real-time quantitative PCR method (comparative Ct method).
RESULTS
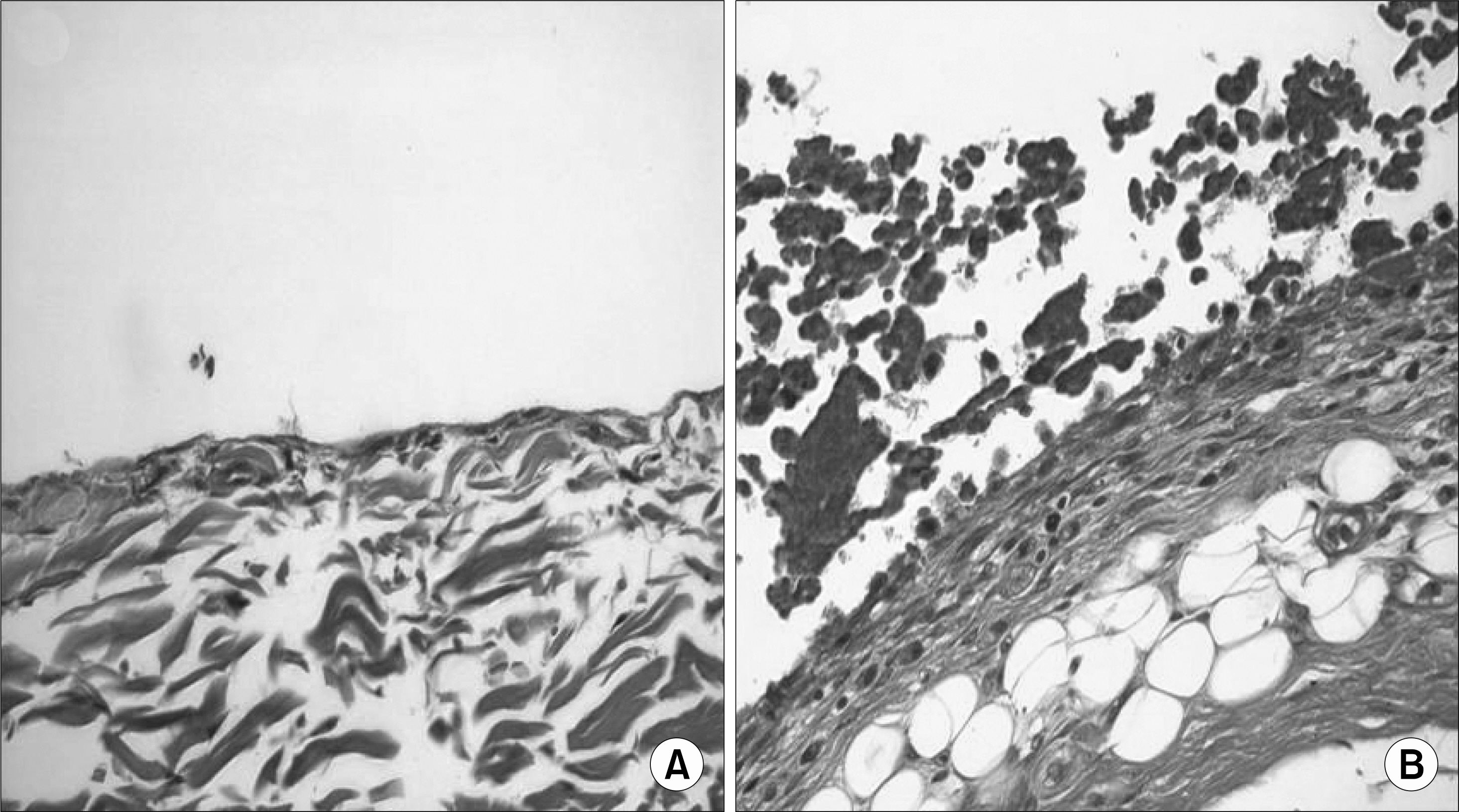
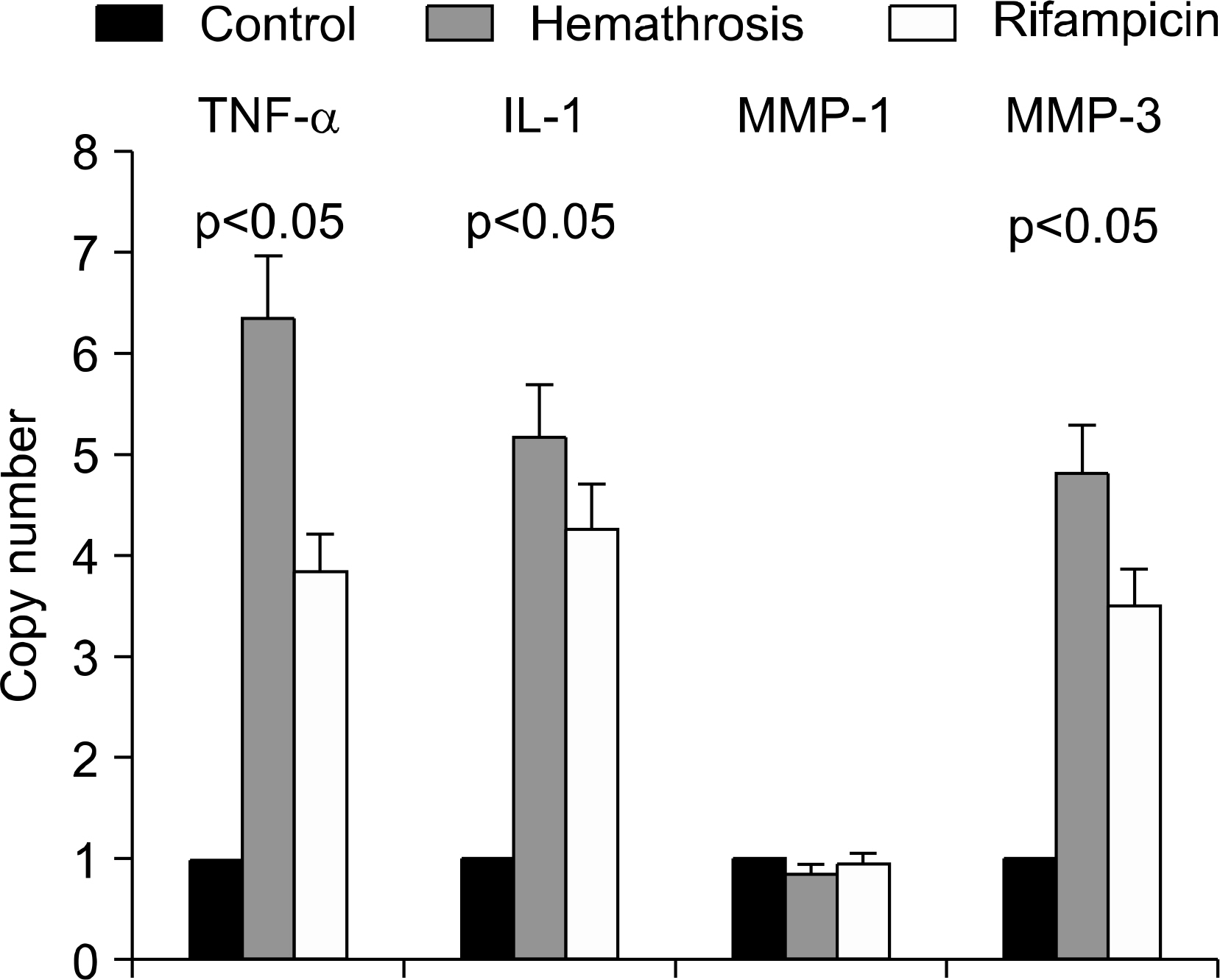
At 20th week, in rifampicin treated group showed decreased proliferative, and infiltrated mononuclear cells compared with control group. And mRNA of TNF-alpha, IL-1 and MMP-3 levels were decreased also.
CONCLUSION
In animal model of HS, histological changes showed the same as human hemophilic synovitis. And this study suggested that rifampicin has a controlling effect on the inflammatory process of HS by suppression of inflammatory cytokine production in the experimental hemophilic synovitis model.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Pathogenesis, early diagnosis, and prophylaxis for chronic hemophilic synovitis. Clin Orthop. 1997. 343:6–11.2). Arnold WD., Hilgartner MW. Haemophilic arthropathy. Current concepts of pathogenesis and management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:287–305.3). Madhok R., York J., Sturrock RD. Haemophilic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991. 50:588–91.
Article4). Aledort LM., Haschmeyer RH., Pettersson H. A longitudinal study of orthopaedic outcomes for severe factor-VIII-deficient haemophiliacs. The Orthopaedic Outcome Study Group. J Int Med. 1992. 236:391–9.5). Petrini P., Lindvall N., Egberg N., Blomback M. Prophylaxis with factor concentrates in preventing haemophilic arthopaghy. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1991. 13:280–7.6). Soreff J., Blomback M. Arthropathy in children with severe hemophilia A. Acta Paedriatr Scand. 1980. 69:667–73.
Article7). Roosendaal G., Vianen ME., Wenting MJ., van Rinsum AC., van den Berg HM., Lafeber FP, et al. Iron deposits and catabolic properties of synovial tissue from patients with haemophilia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998. 80:540–5.
Article8). Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Methods to treat chronic haemophilic synovitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991. 50:588–91.
Article9). Roosendaal G., Mauser-Bunschoten EP., de Kleijn P., Heijnen L., van den Berg HM., Van Rinsum AC, et al. Synovium in haemophilic arthropathy. Haemophilia. 1998. 4:502–5.10). Hooiveld MJ., Roosendaal G., Jacobs KM., Vianen ME., van den Berg HM., Bijlsma JW, et al. Initiation of degenerative joint damage by experimental bleeding combined with loading of the joint: a possible mechanism of hemophilic arthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:2024–31.
Article11). Roosendaal G., Vianen ME., van den Berg HM., Lafeber FP., Bijlsma JW. Cartilage damage as a result of hemarthrosis in a human in vitro model. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:1350–4.12). Roosendaal G., Vianen ME., Marx JJ., van den Berg HM., Lafeber FP., Bijlsma JW. Blood-induced joint damage: a human in vitro study. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:1025–32.
Article13). Caviglia HA., Fernandez-Palazzi F., Galatro G., Perez-Bianco R. Chemical synoviorthesis with rifampicin in hemophilia. Hemophilia. 2001. 7:26–30.14). Caviglia HA., Fernandez-Palazzi F., Maffei E., Galatro G., Barrionuevo A. Chemical synoviorthesis for hemophilic synovitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 343:30–6.
Article15). Stein H., Duthie RB. The pathogenesis of chronic haemophilic arthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981. 63-B:601–9.
Article16). Erken EHW. Radiocolloids in the management of hemophilic arthropathy in children and adolescents. Clin Orthop. 1991. 264:129–35.
Article17). Fernandez-Palazzi F., de Bosch NB., de Vargas AF. Radioactive synovectomy in haemophilic haemarthrosis. Follow-up of fifty cases. Scand J Haematol. 1984. 40(Suppl):s291–s300.
Article18). Fernandez-Palazzi F., Rivas S., Cibeira JL., Dib O., Viso R. Radioactive synoviorthesis in hemophilic synovitis. Materials, techniques, and dangers. Clin Orthop. 1996. 328:14–8.19). Greene WB: Synovectomy of the ankle for hemophilic arthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg. 1994. 76A:812–9.20). Mannucci PM., DeFranchis R., Torri G., Pietrogrande V. Role of synovectomy in hemophilic arthropathy. Isr J Med Sci. 1977. 13:983–7.21). Matsuda Y., Duthie RB. Surgical synovectomy for haemophilic arthropathy of the knee. Long-term follow-up. Scand J Haematol. 1984. 40((Suppl):):237–47.22). Soroa VE., del Huerto Velazquez Espeche M., Giannone C., Caviglia H., Galatros G., Fernandez D, et al. Effects of radiosynovectomy with p-32 colloid therapy in hemophilia and rheumatoid arthritis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2005. 20:344–8.
Article23). Merchan EC., Magallon M., Martin-Villar J., Galindo E., Ortega F., Pardo JA. Long term follow up of haemophilia arthropathy treated by Au-198 radiation synovectomy. Int ᄋrthop. 1993. 17:120–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical and Radiological Evaluation After Chemical Synovectomy With Rifampicin in Hemophilic Arthropathy: Korean Experience With a 2-Week Interval Protocol
- Rifampicin Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis-Like Response in vivo and in vitro
- Case Report of Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis Affection Knee Joint
- The Clinical Effect of Rifampicin for Retreatment Cases for Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- A Case of Pedunculated Localized Nodular Synovitis of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings