J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2013 Sep;18(3):103-110. 10.12790/jkssh.2013.18.3.103.
Outcomes of Unstable Extraarticular Metacarpal Fractures Treated with Low Profile Titanium Plate System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ljhos69@naver.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2194139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2013.18.3.103
Abstract
- PURPOSE
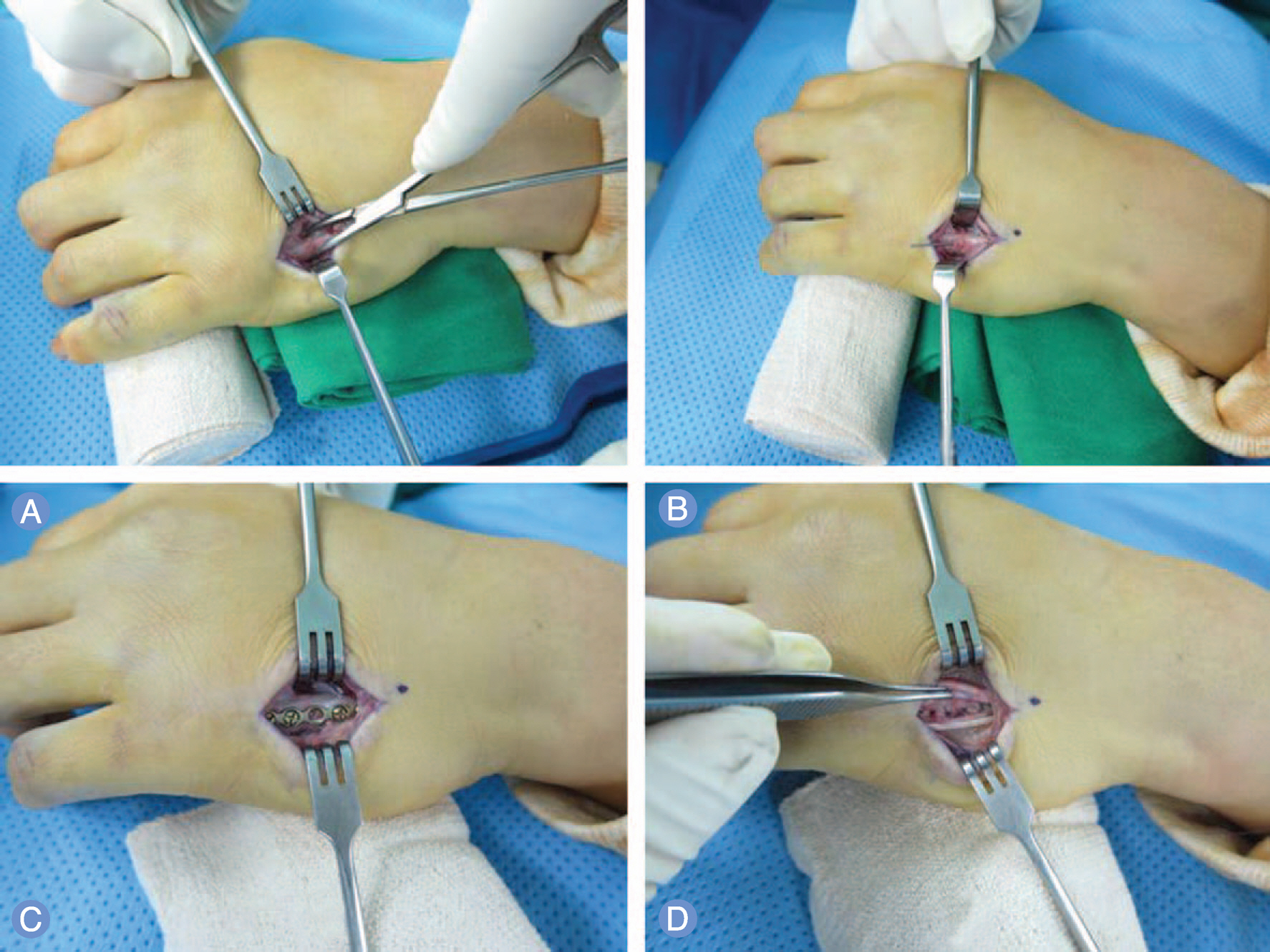
The purpose of this study was to evaluate clinical results for open reduction and internal fixation of unstable extraarticular metacarpal fractures using low profile titanium plates.
METHODS
Sixty-two consecutive patients (76 metacarpals) with unstable extraarticular metacarpal fractures who prospectively underwent internal fixation with plating were enrolled. Minimum follow-up was 1 year. There were 48 males and 14 females; average age was 39 years (range, 15-71 years). The location of the fractures was shaft in 65 metacarpals and the type was transverse in 22 cases, oblique in 46 cases, and communited in 8 cases. Of the 62 patients, 11 were open; 9 of these had additional soft tissue injury. The surgical outcome was assessed by clinical and radiographic outcomes and complications.
RESULTS
Bone union was successfully achieved in all patients on the average period of 6.4 weeks. The final range of total active motion was excellent for 64 cases, good for 6 cases, fair for 5 cases, and poor for 1 case. Postoperative complications occurred in 9 patients (15 metacarpals). Statistical analysis revealed that patient age, occupation, multiple metacarpal fractures, and soft tissue injury were significantly correlated with incidence of complications at last follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Low profile titanium plating showed the low complication rate and good results in treating unstable extraarticular metacarpal fractures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Firoozbakhsh KK, Moneim MS, Howey T, Castaneda E, Pirela-Cruz MA. Comparative fatigue strengths and stabilities of metacarpal internal fixation techniques. J Hand Surg Am. 1993; 18:1059–68.
Article2. Ford DJ, el-Hadidi S, Lunn PG, Burke FD. Fractures of the metacarpals: treatment by A. O. screw and plate fixation. J Hand Surg Br. 1987; 12:34–7.
Article3. Gonzalez MH, Igram CM, Hall RF Jr. Flexible intramedullary nailing for metacarpal fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1995; 20:382–7.
Article4. Prevel CD, McCarty M, Katona T, et al. Comparative biomechanical stability of titanium bone fixation systems in metacarpal fractures. Ann Plast Surg. 1995; 35:6–14.
Article5. Waris E, Ashammakhi N, Happonen H, et al. Bioabsor-bable miniplating versus metallic fixation for metacarpal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (410):310–9.
Article6. Waris E, Ashammakhi N, Raatikainen T, Tormala P, Santavirta S, Konttinen YT. Self-reinforced bioabsorbable versus metallic fixation systems for metacarpal and phalangeal fractures: a biomechanical study. J Hand Surg Am. 2002; 27:902–9.
Article7. Bach HG, Gonzalez MH, Hall RF Jr. Locked intramedullary nailing of metacarpal fractures secondary to gunshot wounds. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:1083–7.
Article8. Orbay J. Intramedullary nailing of metacarpal shaft fractures. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2005; 9:69–73.
Article9. Vanik RK, Weber RC, Matloub HS, Sanger JR, Gingrass RP. The comparative strengths of internal fixation techniques. J Hand Surg Am. 1984; 9:216–21.
Article10. Mann RJ, Black D, Constine R, Daniels AU. A quantitative comparison of metacarpal fracture stability with five different methods of internal fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:1024–8.
Article11. Firoozbakhsh KK, Moneim MS, Doherty W, Naraghi FF. Internal fixation of oblique metacarpal fractures. A biomechanical evaluation by impact loading. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (325):296–301.
Article12. Dabezies EJ, Schutte JP. Fixation of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures with miniature plates and screws. J Hand Surg Am. 1986; 11:283–8.
Article13. Kozin SH, Thoder JJ, Lieberman G. Operative treatment of metacarpal and phalangeal shaft fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000; 8:111–21.
Article14. Melone CP Jr. Rigid fixation of phalangeal and metacarpal fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1986; 17:421–35.
Article15. Page SM, Stern PJ. Complications and range of motion following plate fixation of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1998; 23:827–32.
Article16. Stern PJ, Wieser MJ, Reilly DG. Complications of plate fixation in the hand skeleton. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (214):59–65.
Article17. Fambrough RA, Green DP. Tendon rupture as a complication of screw fixation in fractures in the hand. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61:781–2.
Article18. Rhee SH, Lee SK, Lee SL, Kim J, Baek GH, Lee YH. Prospective multicenter trial of modified retrograde percutaneous intramedullary Kirschner wire fixation for displaced metacarpal neck and shaft fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012; 129:694–703.
Article19. Fusetti C, Meyer H, Borisch N, Stern R, Santa DD, Papaloizos M. Complications of plate fixation in metacarpal fractures. J Trauma. 2002; 52:535–9.
Article20. Shimizu T, Omokawa S, Akahane M, et al. Predictors of the postoperative range of finger motion for comminuted periarticular metacarpal and phalangeal fractures treated with a titanium plate. Injury. 2012; 43:940–5.
Article21. O'Sullivan ST, Limantzakis G, Kay SP. The role of low-profile titanium miniplates in emergency and elective hand surgery. J Hand Surg Br. 1999; 24:347–9.22. Ouellette EA, Freeland AE. Use of the minicondylar plate in metacarpal and phalangeal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (327):38–46.
Article23. Omokawa S, Fujitani R, Dohi Y, Okawa T, Yajima H. Prospective outcomes of comminuted periarticular metacarpal and phalangeal fractures treated using a titanium plate system. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33:857–63.
Article24. Chen SH, Wei FC, Chen HC, Chuang CC, Noordhoff S. Miniature plates and screws in acute complex hand injury. J Trauma. 1994; 37:237–42.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Plate fixation with a single incisional approach in adjoining two metacarpal shaft fractures
- Treatment of Metacarpal Shaft Fractures with Plates and Screws
- Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
- The prognosis of fixation of mandibular fractures with biodegradable plates and screws
- Usefulness of Miniplate Fixation for the Fractures of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Bones of the Hand