J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Jul;54(1):30-33. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.1.30.
Usefulness of Three Dimensional Proset MR Images for Diagnosis of Symptomatic L5-S1 Foraminal and Extraforaminal Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. sw902@ynu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Saint Mary's Hospital, Pohang, Korea.
- 3Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2190854
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.1.30
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
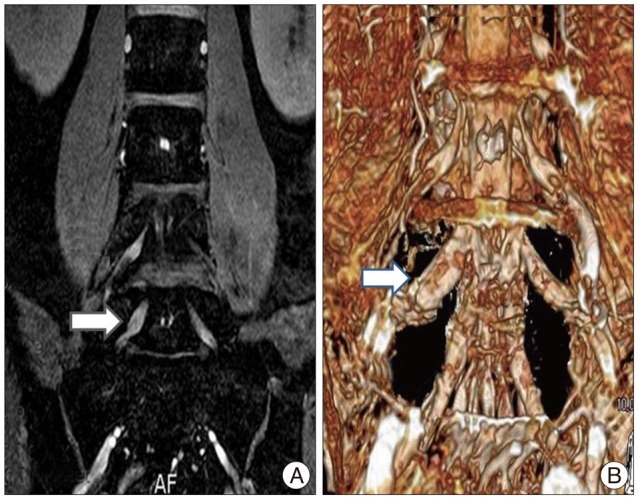
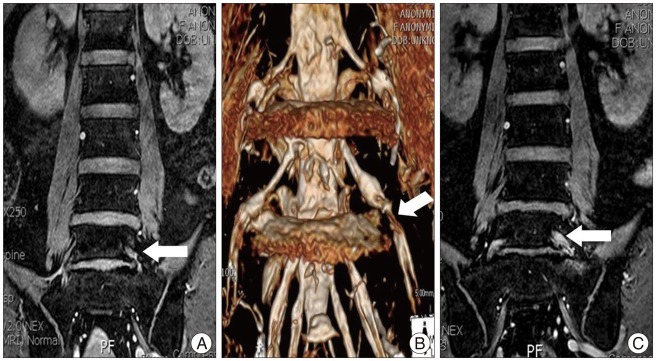
To suggest a new useful diagnostic technique, principles of the selective excitation technique-magnetic resonance images (Proset-MRI), and to know the precise radiologic findings that can prove symptomatic foraminal and extraforaminal stenosis at L5-S1.
METHODS
Nineteen patients with symptomatic L5-S1 stenosis were checked by Proset-MRI. Four patients were performed decompressive surgery and 15 patients were performed selective nerve root block (SNRB) at L5. The pain scale of patients was checked by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) scores at the pre- and post-treatment state.
RESULTS
Proset-MRI findings of patients with symptomatic stenosis are root swelling (RS) and indentation. The comparisons with VAS scores had a meaningful statistical result at each RS (p<0.01) and indentation (p<0.01). However, the findings of RS combined with indentation lacked statistical significance (p=0.0249). In addition, according to a comparison with the treatment modalities, reducing of VAS scores had statistical meaningful significance in decompressive surgery cases (p<0.01), and also in SNRB cases (p<0.01) after a 3-month follow-up period.
CONCLUSION
The three dimensional Proset-MRI is very useful and sensitive technique to diagnose the symptomatic foraminal and extraforaminal stenosis at L5-S1.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Borthne AS, Dormagen JB, Gjesdal KI, Storaas T, Lygren I, Geitung JT. Bowel MR imaging with oral Gastrografin : an experimental study with healthy volunteers. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:100–106. PMID: 12541116.
Article2. Byun WM, Ahn SH, Ahn MW. Significance of perianular enhancement associated with anular tears on magnetic resonance imagings in diagnosis of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:2440–2443. PMID: 18923321.
Article3. Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Huntoon M, Yeasting RA. Location of the extraforaminal lumbar nerve roots. An anatomic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; 230–235. PMID: 9224261.
Article4. Elster AD. Bertolotti's syndrome revisited. Transitional vertebrae of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14:1373–1377. PMID: 2533403.5. Heo DH, Lee MS, Sheen SH, Cho SM, Cho YJ, Oh SM. Simple oblique lumbar magnetic resonance imaging technique and its diagnostic value for extraforaminal disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:2419–2423. PMID: 19829256.
Article6. Kang SH, Choi SH, Seong NJ, Ko JM, Cho ES, Ko KP. Comparative study of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging and myelography in young soldiers with herniated lumbar disc. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 48:501–505. PMID: 21430976.
Article7. Kim SB, Jang JS, Lee SH. Morphologic changes of L5 root at coronal source images of MR myelography in cases of foraminal or extraforaminal compression. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:11–15. PMID: 19707488.
Article8. Lee IS, Kim HJ, Lee JS, Moon TY, Jeon UB. Extraforaminal with or without foraminal disk herniation : reliable MRI findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:1392–1396. PMID: 19380567.
Article9. Moon KP, Suh KT, Lee JS. Reliability of MRI findings for Symptomatic Extraforaminal Disc Herniation in Lumbar Spine. Asian Spine J. 2009; 3:16–20. PMID: 20404941.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three-Dimension Magnetic Resonance Lumbosacral Radiculography by Principles of the Selective Excitation Technique Imaging in the Diagnosis of Symptomatic Foraminal Stenosis
- Differentiation between Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Extraforaminal Stenosis in Lumbosacral Transitional Vertebra: Role of Three-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Lumbosacral Radiculography
- Full Endoscopic Interlaminar Contralateral Lumbar Foraminotomy for Recurrent L5-S1 Foraminal-extraforaminal Stenosis: A Case Report with a Technical Note
- Morphologic Changes of L5 Root at Coronal Source Images of MR Myelography in Cases of Foraminal or Extraforaminal Compression
- Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Spinal Surgery Using a 30° Arthroscope for L5–S1 Foraminal Decompression