J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Jun;53(6):374-376. 10.3340/jkns.2013.53.6.374.
Cystic Abducens Schwannoma without Abducens Paresis : Possible Role of Cisternal Structures in Clinical Manifestation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital and Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. moonks@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital and Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2190828
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.6.374
Abstract
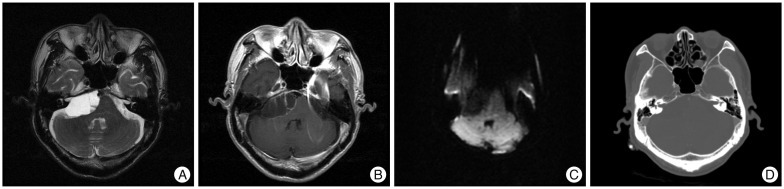
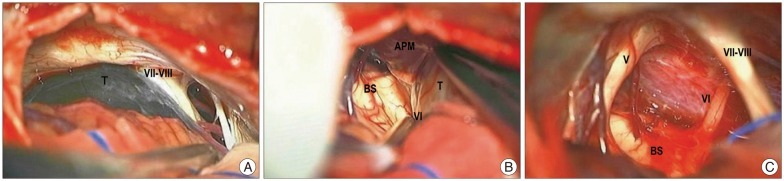
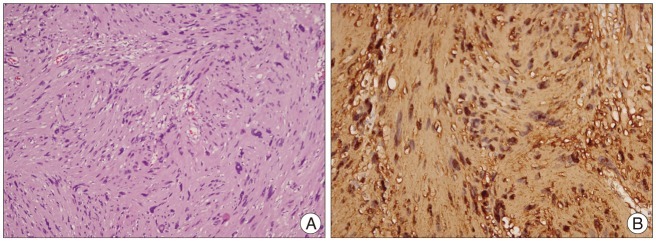
- The abducens nerve paresis generally can aid in the presumptive diagnosis of abducens schwannoma along with the typical radiological features of schwannomas. The authors present a case of a 76-year-old male patient with a abducens schwannoma without abducens nerve paresis. Peroperatively, abducens nerve located in the cerebellopontine cistern had normal in contour and diameter, despite the mass originated from this nerve. We hypothesize that anatomic location of abducens nerve may affect the vector of tumor growth to prevent destruction of its origin, the abducens nerve.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Celli P, Ferrante L, Acqui M, Mastronardi L, Fortuna A, Palma L. Neurinoma of the third, fourth, and sixth cranial nerves : a survey and report of a new fourth nerve case. Surg Neurol. 1992; 38:216–224. PMID: 1440207.
Article2. Erlich SA, Tymianski M, Kiehl TR. Cellular schwannoma of the abducens nerve : case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009; 111:467–471. PMID: 19200646.
Article3. Lantos PL, Vandenberg SR, Kleihues P. Tumours of the Peripheral Nerve. In : Graham DI, Lantos PL, editors. Greenfield's neuropathology. London, UK: Arnold;2001. p. 713–717.4. Matsuno H, Rhoton AL Jr, Peace D. Microsurgical anatomy of the posterior fossa cisterns. Neurosurgery. 1988; 23:58–80. PMID: 3173665.
Article5. Nakamura M, Carvalho GA, Samii M. Abducens nerve schwannoma : a case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2002; 57:183–188. discussion 188-189. PMID: 12009546.6. Park JH, Cho YH, Kim JH, Lee JK, Kim CJ. Abducens nerve schwannoma : case report and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev. 2009; 32:375–378. discussion 378. PMID: 19418078.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolated abducens nerve palsy in severe pre-eclampsia: A case report
- A Case of Isolated Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy Caused by Clival Metastasis from Rectal Cancer
- Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy Associated with Ruptured Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm
- A Patient Presented With Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy: A Variant Form of Guillain-Barre Syndrome With Anti-GT1a Antibody
- A Case of Traumatic Bilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy Associated with Skull Base Fracture