J Korean Med Assoc.
2010 Apr;53(4):299-305. 10.5124/jkma.2010.53.4.299.
Endoscopic Resection of Early Gastric Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Korea. hyjung@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2188294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2010.53.4.299
Abstract
- Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) has been accepted as one of the standard treatments of early gastric cancer (EGC) with a negligible risk of lymph node metastasis. EMR is similar to surgery in efficacy but less invasive and more cost-effective. And it allows accurate histological staging of the tumor, which is critical in deciding whether additional treatment is necessary. Standard indications for EMR of EGC include differentiated elevated cancer less than 2 cm in size and depressed cancer without ulceration less than 1 cm in size. Recently, expanded indication has been proposed in Japan to cover other lesions with a negligible risk of lymph node metastasis, which include larger lesions and lesions with ulceration. With the development of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), en bloc resection of larger and even ulcerative lesion is possible. However, the lack of long-term data makes it difficult to widely accept expanded indication. More long-term studies about therapeutic outcomes are needed to fully bolster the safety and establish correct therapeutic role of ESD in treatment of EGC.
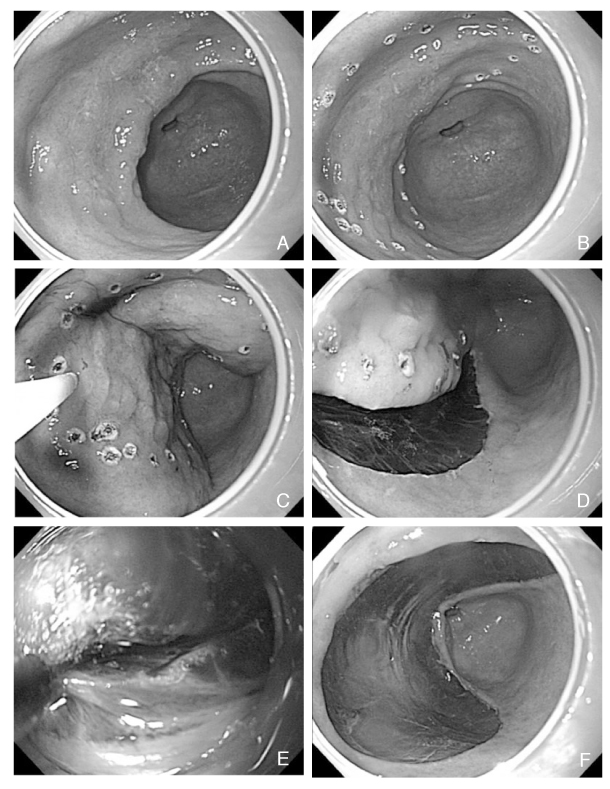
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Pneumothorax Following Gastric Endoscopic Mucosal Resect
Myeongseok Koh, Jin Seok Jang, Jae Hwang Cha
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;76(2):83-87. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.2.83.Pneumothorax Following Gastric Endoscopic Mucosal Resect
Myeongseok Koh, Jin Seok Jang, Jae Hwang Cha
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;76(2):83-87. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.2.83.Pathological differences between forceps biopsy specimens and endoscopic resection specimens in early gastric cancer patients
Joo Seok Kim, Sae Hee Kim, Min Gyu Kim, Ah Jeong Ryu, Il Hwan Ryu, Jae Jun Lee, Jae Woong Jeon, Ji Wook Choi, Anna Kim
Kosin Med J. 2014;29(2):117-124. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2014.29.2.117.
Reference
-
1. Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, Ono H, Nakanishi Y, Shimoda T, Kato Y. Incidence of lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: estimation with a large number of cases at two large centers. Gastric Cancer. 2000. 3:219–225.
Article2. Fukase K, Matsuda T, Suzuki M, Toda H, Okuyama Y, Sakai J, Saito H, Sato S, Mito S. Evaluation of the efficacy of endoscopic treatment for gastric cacner considered in terms of longterm prognosis. Dig Endosc. 1994. 6:241–247.
Article3. Uedo N, Iishi H, Tatsuta M, Ishihara R, Higashino K, Takeuchi Y, Imanaka K, Yamada T, Yamamoto S, Yamamoto S, Tsukuma H, Ishiguro S. Longterm outcomes after endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2006. 9:88–92.
Article4. Deyhle P, Largiadér F, Jenny S, Fumagalli I. A method for endoscopic electroresection of sessile colon polyps. Endoscopy. 1973. 5:38–40.
Article5. Tada M, Shimada M, Murakami F, Mizumachi M, Arima K, Yanai H. Development of strip-off biopsy (in Japanese with English abstract). Gastroenterol Endosc. 1984. 26:833–839.6. Hirao M, Masuda K, Asanuma T, Naka H, Noda K, Matsuura K, Yamaguchi O, Ueda N. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer and other tumors with local injection of hypertonic saline-epinephrine. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 34:264–269.
Article7. Inoue H, Takeshita K, Hori H, Muraoka Y, Yoneshima H, Endo M. Endoscopic mucosal resection with a cap-fitted panendoscope for esophagus, stomach, and colon mucosal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993. 39:58–62.
Article8. Akiyama M, Ota M, Nakajima H, Yamagata K, Munakata A. Endoscopic mucosal resection of gastric neoplasms using a ligating device. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997. 45:182–186.
Article9. Gotoda T, Kondo H, Ono H, Saito Y, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Yokota T. A new endoscopic mucosal resection procedure using an insulation-tipped electrosurgical knife for rectal flat lesions: report of two cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999. 50:560–563.
Article10. Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Boku N, Ohtu A, Tajiri H, Yoshida S. New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy. 2001. 33:221–226.
Article11. Oyama T, Kikuchi Y. Aggressive endoscopic mucosal resection in the upper GI tract: hook knife EMR method. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2002. 11:291–295.
Article12. Yahagi N, Fujishiro M, Kakushima N, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Oka M, Iguchi M, Enomoto S, Ichinose M, Niwa H, Omata M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer using the tip of an electrosurgical snare (thin type). Dig Endosc. 2004. 16:34–38.
Article13. Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, Mouri R, Hirata M, Kanao H, Kawamura T, Yoshida S, Yoshihara M, Chayama K. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for residual/local recurrence of early gastric cancer after endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy. 2006. 38:996–1000.
Article14. Kim WS, Kim BS, Chung BS, Km HC, Yook JH, Oh ST, Park KC. Clinical analysis for lymph node metastasis as a guide to modified surgery for early gastric cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 1998. 54:47–55.15. Kwak CS, Lee HK, Cho SJ, Yang HK, Lee KU, Choe KJ, Kim JP. Analysis of clinicopathological factors associated with lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer-review of 2,137 cases. J Korean Cancer Assoc. 2000. 32:674–681.16. An JY, Baik YH, Choi MG, Noh JH, Sohn TS, Kim S. Predictive factors for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer with submucosal invasion: analysis of a single institutional experience. Ann Surg. 2007. 246:749–753.
Article17. Kurokawa Y, Hasuike N, Ono H, Boku N, Fukuda H. Gastrointestinal Oncology Study Group of Japan Clinical Oncology Group. A phase II trial of endoscopic submucosal dissection for mucosal gastric cancer: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG0607. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2009. 39:464–466.
Article18. Hirasawa T, Gotoda T, Miyata S, Kato Y, Shimoda T, Taniguchi H, Fujisaki J, Sano T, Yamaguchi T. Incidence of lymph node metastasis and the feasibility of endoscopic resection for undifferentiated-type early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2009. 12:148–152.
Article19. Kojima T, Parra-Blanco A, Takahashi H, Fujita R. Outcome of endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer: review of the Japanese literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 48:550–554.
Article20. Hiki Y, Shimao H, Mieno H, Sakakibara Y, Kobayashi N, Saigenji K. Modified treatment of early gastric cancer: evaluation of endoscopic treatment of early gastric cancer with respect to treatment indication groups. World J Surg. 1995. 19:517–522.
Article21. Kim JJ, Lee JH, Jung HY, Lee GH, Cho JY, Ryu CB, Chun HJ, Park JJ, Lee WS, Kim HS, Chung MG, Moon JS, Choi SR, Song GA, Jeong HY, Jee SR, Seol SY, Yoon YB. EMR for early gastric cancer in Korea: a multicenter retrospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007. 66:693–700.22. Jung HY, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee GH, Kim JH. Risk management in endoscopic submucosal dissection using needle knife in Korea. Dig Endosc. 2007. 19:S. S5–S8.
Article23. Ono H, Kondo H, Gotoda T, Shirao K, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Hosokawa K, Shimoda T, Yoshida S. Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer. Gut. 2001. 48:225–229.
Article24. Ono H. Early gastric cancer: diagnosis, pathology, treatment techniques and treatment outcomes. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 18:863–866.
Article25. Oda I, Gotoda T, Hamanaka H, Eguchi T, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Bhandari P, Emura F, Saito D, Ono H. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: technical feasibility, operation time and complications from a large consecutive series. Dig Endosc. 2005. 17:54–58.
Article26. Chung IK, Lee JH, Lee SH, Kim SJ, Cho JY, Cho WY, Hwangbo Y, Keum BR, Park JJ, Chun HJ, Kim HJ, Kim JJ, Ji SR, Seol SY. Therapeutic outcomes in 1000 cases of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: Korean ESD Study Group multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009. 69:1228–1235.
Article27. Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, Mouri R, Hirata M, Kawamura T, Yoshihara M, Chayama K. Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006. 64:877–883.
Article28. Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Shiozawa J, Kohno S. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: a large-scale feasibility study. Gut. 2009. 58:331–336.
Article29. Goto O, Fujishiro M, Kodashima S, Ono S, Omata M. Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer with special reference to validation for curability criteria. Endoscopy. 2009. 41:118–122.
Article