J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Jun;42(3):410-415. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.3.410.
Iliopsoas Bursitis following Total Hip Replacement Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. drchung@inje.ac.kr
- KMID: 2186569
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.3.410
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To report the clinical, radiological and surgical findings of iliopsoas bursitis, and to suggest an indication for diagnosis and treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We report two patients with iliopsoas bursitis who underwent THA in between June 1998 to June 2003. All presented with late onset hip joint discomfort, and their diagnosis were confirmed after interdepartmental consultations and with the help of investigations such as interventional angiography and MRI. Their signs, symptoms, investigations and surgical findings were reviewed retrospectively.
RESULTS
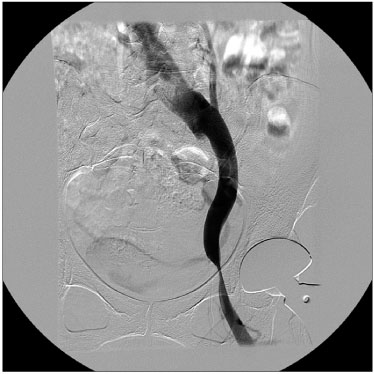
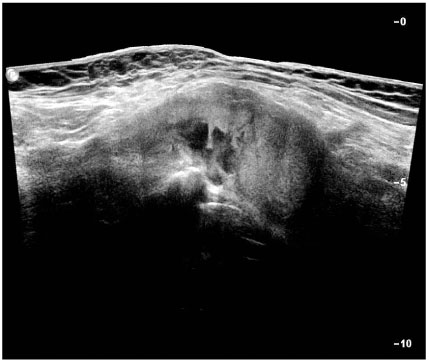
Iliopsoas bursitis presented with hip pain, leg edema, palpable inguinal mass and ecchymosis, femoral nerve irritation and flexion contracture of hip. The radiographs provided no diagnostic clues but the MRI revealed a well marginated cystic lesion filled with fluid signals. Ultrasonography revealed the anatomic location that enabled guided aspiration and even ruled out vascular compromise. Two patients were treated with USG guided aspiration. One aspirate was serosanguinous and the other was old blood tinged fluid. One patient underwent surgical debridement of the cyst. Surgery revealed an intrapelvic hemorrhagic bursa with an ill-defined cystic wall and intramuscular extension into the iliacus.
CONCLUSION
It is important for surgeons to rule out iliopsoas bursitis when a patient presents with vague hip pain after total hip arthroplasty without any evidence of infection or loosening. A diagnosis of iliopsoas bursitis can be made from the clinical features and ultrasonography.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Al-Khodairy AT, Gobelet C, Nancoz R, De Preux J. Iliopsoas bursitis and pseudogout of the knee mimicking L2-L3 radiculopathy: case report and review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 1997. 6:336–341.
Article2. Armstrong P, Saxton H. Ilio-psoas bursa. Br J Radiol. 1972. 45:493–495.
Article3. Bianchi S, Martinoli C, Keller A, Bianchi-Zamorani MP. Giant iliopsoas bursitis: sonographic findings with magnetic resonance correlations. J Clin Ultrasound. 2002. 30:437–441.
Article4. Binek R, Levinshon EM. Enlarged iliopsoas bursa. An unusual cause of thigh and hip pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987. 224:158–163.5. Chandler SB. The iliopsoas bursa in man. Anat Rec. 1934. 58:235–240.
Article6. Cheung YM, Gupte CM, Beverly MJ. Iliopsoas bursitis following total hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004. 124:720–723.
Article7. Coventry MB, Polley HF, Weiner AD. Rheumatoid synovial cyst of the hip. Report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959. 41:721–730.8. Eisenberg KS, Johnston JO. Synovial chondromatosis of the hip joint presenting as an intrapelvic mass: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972. 54:176–178.9. Kerry R, King DG, Gibson MF. Iliopsoas bursitis: Physical diagnosis and management with ultrasonography and corticosteroid infiltration in a 33 year-old man. Physiotheraphy. 2000. 86:306–311.
Article10. Kolmert L, Persson BM, Herrlin K, Ekelund L. Ileopectineal bursitis following total hip replacement. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984. 55:63–65.
Article11. Lee HS, Heo JN, Park KC, Han HY. Meralgia paresthetica by iliopsoas bursa associated with osteonecrosis femoral head: a case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2003. 38:444–446.12. Matsumoto K, Hukuda S, Nishioka J, Fusita T. Iliopsoas bursal distension caused by acetabular loosening after total hip arthroplasty. A rare complication of total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992. 279:144–148.
Article13. Melamed A, Bauer CA, Johnson JH. Iliopsoas bursal extension of arthritic disease of the hip. Radiology. 1967. 89:54–58.
Article14. Steinbach LS, Schneider R, Goldman AB, Kazam E, Ranawat CS, Ghelman B. Bursae and abscess cavities communicating with the hip. Diagnosis using arthrography and CT. Radiology. 1985. 156:303–307.
Article15. Sumanovac Z. Traumatic cyst in the hip joint; a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959. 41:175–178.16. Toohey AK, LaSalle TL, Martinez S, Polisson RP. Iliopsoas busitis: clinical features, radiographic findings, and disease associations. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990. 20:41–47.17. Underwood PL, McLeod RA, Ginsburg WW. The varied clinical manifestations of iliopsoas bursitis. J Rheumatol. 1988. 15:1683–1685.18. Weisser JR, Robinson DW. Pigmented villonodular synovitis of iliopectineal bursa; a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1951. 33:988–992.19. Wunderbaldinger P, Bremer C, Schellenberger E, Cejna M, Turetschek K, Kainberger F. Imaging features of iliopsoas bursitis. Eur Radiol. 2002. 12:409–415.
Article20. Yamamoto T, Marui T, Akisue T, Yoshiya S, Hitora T, Kurosaka M. Dumbbell-shaped iliopsoas bursitis penetrating the pelvic wall: a rare complication of hip arthrodesis. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85:343–345.21. Yang SS, Bronson MJ. Cystic enlargement of the iliopsoas bursa causing venous obstruction as a complication of total hip arthroplasty. A case report. J Arthroplasty. 1993. 8:657–661.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Femoral Nerve Palsy due to Noninfectious Iliopsoas Bursitis and Hematoma after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Femoral Nerve Palsy caused by Iliopsoas Bursitis Associated with Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head : A Case Report
- Femoral Neuropathy caused by Iliopsoas Hematoma: A Case Report
- Abductor Reconstruction with Gluteus Maximus Transfer in Primary Abductor Deficiency during Total Hip Arthroplasty
- An Enlarged Iliopsoas Bursa Associated with Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Case Report