J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Feb;44(1):22-28. 10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.1.22.
Debridement Arthroplasty for Primary Elbow Osteoarthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gunsan Medical Center of Wonkwang University, Gunsan, Korea. oschae68@hanmail.net
- 3Ik San Hospital, Iksan, Korea.
- KMID: 2186374
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.1.22
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to analyze clinical and radiological results after debridement arthroplasty during primary elbow arthroplasty.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
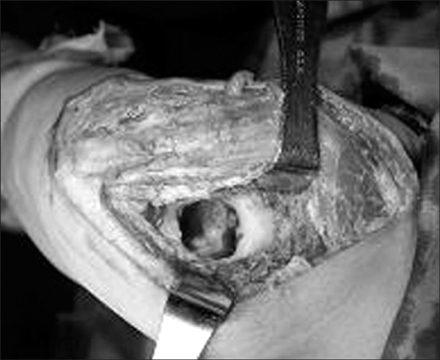
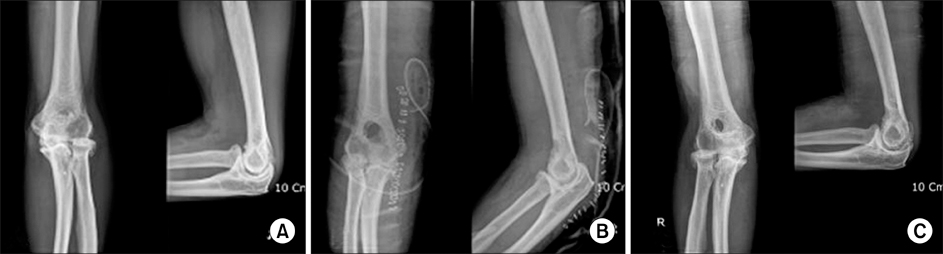
This study involved 25 primary elbow osteoarthritis cases that were treated by debridement arthroplasty from January 1996 to December 2004 with at least a 2 year follow up (mean: 41.3 months). Mean patient age was 45.5 years. Clinical outcomes were analyzed using preoperative and postoperative ranges of motion, Mayo Elbow Performance Scores (MEPS), and Visual Analogue Scale scores. Radiologic analysis was based on plain radiographs.
RESULTS
Average flexion-extension arc improved from 72degrees ROM preoperatively to 110.5degrees postoperatively (p<0.001). Mean MEPS was 89.5 points preoperatively and increased postoperatively (p<0.05). Humeral fenestration size decreased from 27% to 20.5%. Bony spurs of the olecranon and coronoid process recurred in 8 cases. Postoperative LOM was found to be associated with spur recurrence (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Debridement arthroplasty may be recommendable for primary elbow osteoarthritis as it reduces pain and improves functional outcomes, including range of motion. Spur recurrence was found to be associated with a reduced range of motion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Antuña SA, Morrey BF, Adams RA, O'Driscoll SW. Ulnohumeral arthroplasty for prim ary degenerative arthritis of the elbow: long-term outcome and complications. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:2168–2173.2. Collins DH. The pathology of articular and spinal disease. 1950. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.3. Doherty M, Preston B. Primary osteoarthritis of the elbow. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989. 48:743–747.
Article4. Foster MC, Clark DI, Lunn PG. Elbow osteoarthritis: prognostic indicators in ulnohumeral debridement the Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001. 10:557–560.5. Han CS, Rhee YG, Jeong BO, Kwon BK. Debridement arthroplasty for stiff elbow. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005. 40:723–728.
Article6. Huskisson EC, Dieppe PA, Tucker AK, Cannell LB. Another look at osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979. 38:423–428.
Article7. Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957. 16:494–502.
Article8. Kim SJ, Shin SJ. Arthroscopic treatment for limitation of motion of the elbow. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. 375:140–148.
Article9. McLaughlin RE 2nd, Savoie FH 3rd, Field LD, Ramsey JR. Arthroscopic treatment of the arthritic elbow due to primary radiocapitellar arthritis. Arthroscopy. 2006. 22:63–69.
Article10. Morrey BF, Askew LJ, Chao EY. A biomechanical study of normal functional elbow motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981. 63:872–877.
Article11. Morrey BF. Primary degenerative arthritis of the elbow. Treatment by ulnohumeral arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992. 74:409–413.
Article12. Morrey BF. Morrey BF, editor. Primary degenerative arthritis of the elbow: ulnohumeral arthroplasty. The elbow and its disorders. 2004. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunder;74–83.13. Morrey BF. Morrey BF, editor. Ulnohumeral arthroplasty. Master techniques in orthopaedic surgery. 1994. New York: Raven press Ltd;277–289.
Article14. O'Driscoll S. Arthroscopic treatment for osteoarthritis of the elbow. Orthop Clin North Am. 1995. 26:691–706.15. Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Gordon R, Mackay M. Arthroscopic treatment for posterior impingem ent in degenerative arthritis of the elbow. Arthroscopy. 1995. 11:437–443.16. Oka Y. Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow: 50 patients followed mean 5 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000. 71:185–190.17. Oka Y, Ohta K, Saitoh I. Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. 351:127–134.
Article18. Phillips NJ, Ali A, Stanley D. Treatment of primary degenerative arthritis of the elbow by ulnohumeral arthroplasty. A long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003. 85:347–350.19. Redden JF, Stanly D. Arthroscopic fenestration of the olecranon fossa in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the elbow. Arthroscopy. 1993. 9:14–16.
Article20. Rhee YG, Kim HS, Chun YS, Cho YL. Debridement arthroplasty for post-traumatic stiff elbow. J Korean Shoulder-Elbow Society. 1998. 1:242–249.21. Sarris I, Riano FA, Goebel F, Goitz RJ, Sotereanos DG. Ulnohumeral arthroplasty: results in primary degenerative arthritis of the elbow. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 420:190–193.22. Savoie FH, Nunley P, Field LD. Arthroscopic management of the arthritic elbow: indications, technique, and results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999. 8:214–219.23. Smith FM. Surgery of the elbow. 1972. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company.24. Tashjian RZ, Wolf JM, Ritter M, Weiss AP, Green A. Functional outcomes and general health status after ulnohumeral arthroplasty for primary degenerative arthritis of the elbow. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006. 15:357–366.
Article25. Tsuge K. Elbow arthroplasty. Comprehensive atlas of elbow surgery. 1989. St Louis: Mosby Year Book;579–588.26. Wada T, Isogai S, Ishii S, Yamashita T. Debridement arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:233–241.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Debridement Arthroplasty Through a Medial Approach for Primary Osteoarthritis of the Elbow
- Debridement Arthroplasty for Stiff Elbow
- Surgical Treatment of the Primary Osteoarthritis of the Elbow: Open vs. Arthroscopy
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Arthroscopic Anterior Compartment Debridement with Posterior Compartment Mini-Open Debridement and Arthroscopic Both Compartments Debridement of the Primary Elbow Osteoarthritis
- Total Elbow Arthroplasty for the Fracture of Elbow Arthrodesis Site: A Case Report