J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2010 Apr;45(2):114-119. 10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.2.114.
Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Drjmlee@paran.com
- KMID: 2185578
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.2.114
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine results of treatment according to the guidelines of the Vancouver classification in periprosthetic femoral fractures after total hip arthroplasty.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
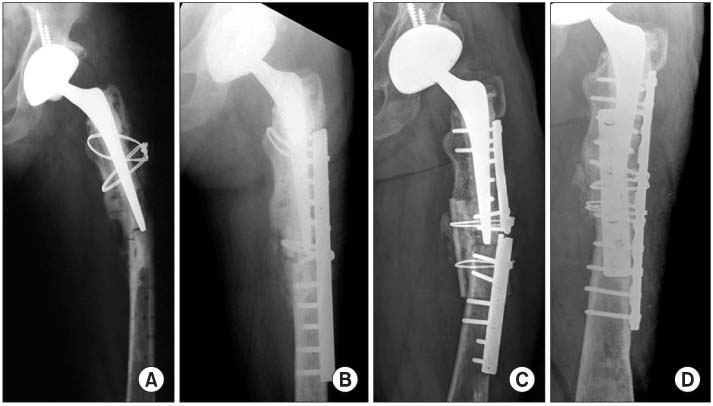
Among 44 cases of periproshtetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty treated between Aug. 1991 and Feb. 2008, thirty-two cases with minimum follow-up greater than one year were included. Outcomes were evaluated using the Beals and Tower's critieria.
RESULTS
Outcomes were excellent in 27 cases, and poor in 5 cases. Four of 5 cases with poor result were due to non-union. Three cases were treated with internal fixation and 1 case was treated with a conservative method. One case with a poor result was due to loosening of the cemented stem of a Vancouver type B1 fracture. Loosening of the stem after mid to long term follow up occurred in an additional 4 cases (3 cases with a cemented stem in a type B1 fracture, 1 case with a cemented stem of a type C fracture). Loosened stems were revised with a long revision stem.
CONCLUSION
For type B1 periprosthetic fractures around a cementless stem, and for type B2, type B3 periprosthetic fractures, treatment according to the guidelines of the Vancouver classification showed excellent results. However, type B1 periprosthetic fractures around a cemented stem showed poor results with non-union or stem loosening. Hence, more rigid fixation using a bone graft or revision of the stem is needed. In type C periprosthetic fractures in osteoporotic patients, closer attentions is needed to avoid complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Hip Arthroplasty
Joong-Myung Lee, Tae-sup Kim, Tae-ho Kim
Hip Pelvis. 2018;30(2):78-85. doi: 10.5371/hp.2018.30.2.78.
Reference
-
1. Duncan CP, Masri BA. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect. 1995. 44:293–304.2. Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur: principles of prevention and management. Instr Course Lect. 1998. 47:237–242.3. Lewallen DG, Berry DJ. Periprosthetic fracture of the femur after total hip arthroplasty: treatment and results to date. Instr Course Lect. 1998. 47:243–249.4. Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G. Periprosthetic femoral fractures classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthroplasty. 2005. 20:857–865.5. Ricci WM, Haidukewych GJ. Periprosthetic femoral fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2009. 58:105–115.6. Richards CJ, garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Vancouver type B3 periprosthetic fractures: evaluation and treatment. Instr Course Lect. 2009. 58:177–181.7. Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Marsri BA, Duncan CP. The reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification of femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15:59–62.8. Beals RK, Tower SS. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 327:238–246.9. Larsen E, Menck H, Rosenklint A. Fractures after hemialloplastic hip replacement. J Trauma. 1987. 27:72–74.
Article10. Lee SR, Bostrom MP. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after total hip arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:111–118.11. Haddad FS, Masri BA, Garbuz DS, Duncan CP. The prevention of periprosthetic fractures in total hip and knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999. 30:191–207.
Article12. Bethea JS III, Deandrade JR, Fleming LL, Lindenbaum SD, Welch RB. Proximal femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982. 170:95–106.
Article13. Johansson JE, McBroom R, Barrington TW, Hunter GA. Fracture of the ipsilateral femur in patients with total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981. 63:1435–1442.14. Crockarell JR Jr, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG. Nonunion after periprosthetic femoral fracture associated with total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81:1073–1079.
Article15. Giannoudis PV, Kanakaris NK, Tsiridis E. Principles of internal fixation and selection of implants for periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury. 2007. 38:669–687.
Article16. Wilson D, Frei H, Masri BA, Oxaland TR, Duncan CP. A biomechanical study comparing cortical onlay allograft struts and plates in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2005. 20:70–76.
Article17. chakravarthy J, Bansal R, Cooper J. Locking plate osteosynthesis for Vancouver type B1 and type C periprosthetic fractures of femur: a report on 12 patients. Injury. 2007. 38:725–733.
Article18. Lindahl H, Malchau H, Odén A, Garellick G. Risk factors for failure after treatment of a periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006. 88:26–30.
Article19. Macdonald SJ, Paprosky WG, Jablonsky WS, Magnus RG. Periprosthetic femoral fractures treated with a long-stem cementless component. J Arthroplasty. 2001. 16:379–383.
Article20. O'Shea K, Quinlan JF, Kutty S, Mulcahy D, Brady OH. The use of uncemented extensively porous-coated femoral components in the management of Vancouver B2 and B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:1617–1621.21. Lee JM, Roh JY, Suh JM. 5-12 year results of femoral revision total hip arthroplasty using the Wagner revision stem. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:785–792.
Article22. Ko PS, Lam JJ, Tio MK, Lee OB, Ip FK. Distal fixation with Wagner revision stem in treating Vancouver type B2 periprosthetic femur fractures in geriatric patients. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:446–452.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Periprosthetic Atypical Femoral Fracture-like Fracture after Hip Arthroplasty: A Report of Three Cases
- Decision-Making and Principle of Management in Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture after Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Management of Ipsilateral Femoral Fracture After Hip Arthroplasty