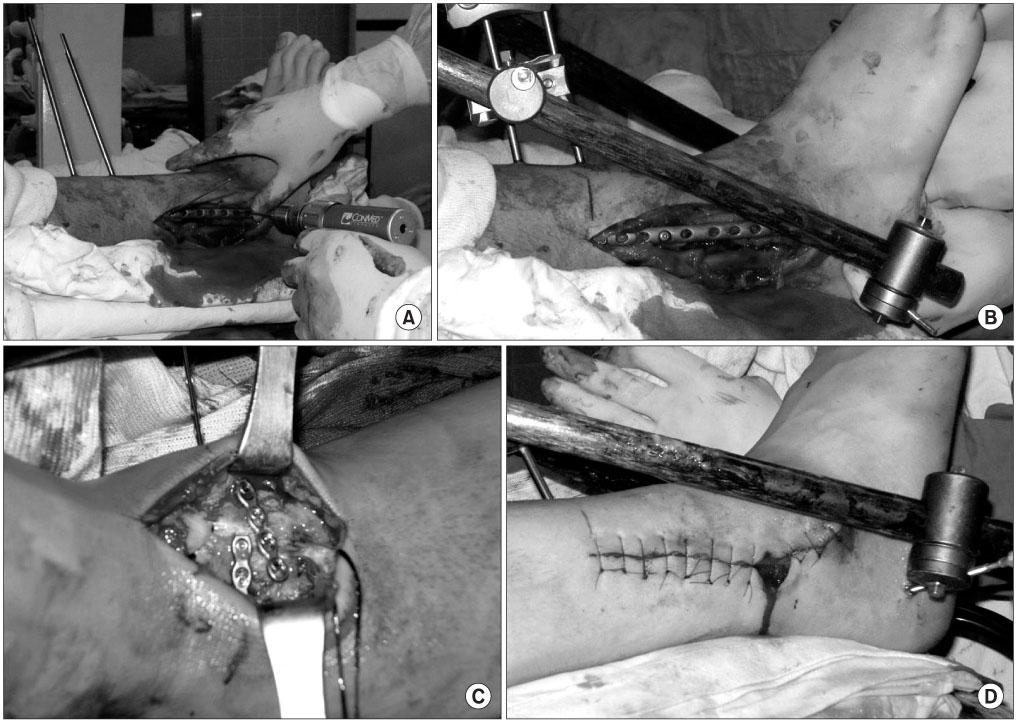
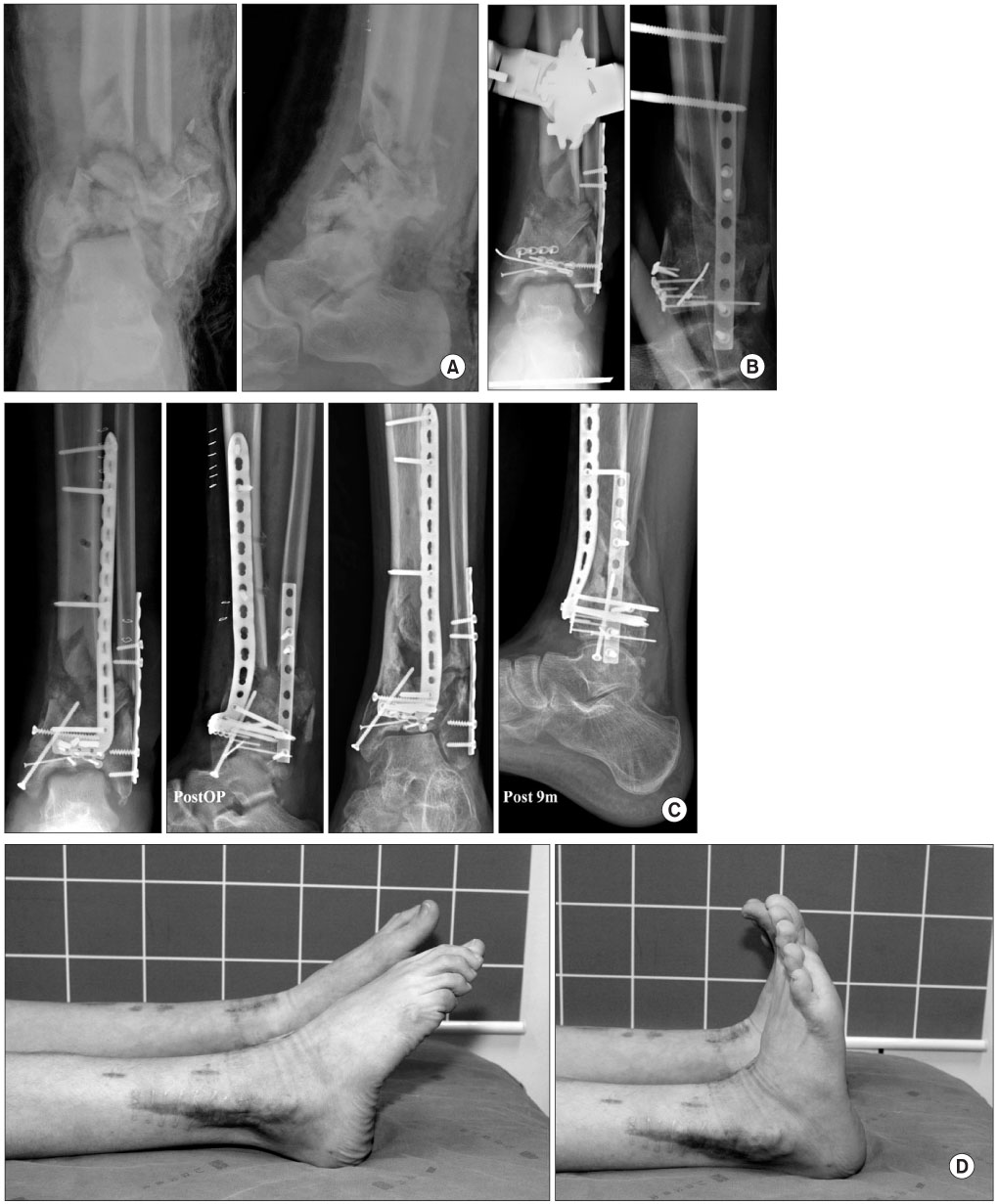
J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2010 Dec;45(6):473-481. 10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.6.473.
Management of Fractures of Distal Tibia by Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis through an Anterior Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gospel Hospital, Kosin University, Korea. jyujin2001@kosin.ac.kr
- 2Gi-Jang Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2185495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.6.473
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate functional results and complications after minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis through an anterior approach for distal tibial fractures, including pilon fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2007 and December 2008, thirteen patients with fractures of the distal tibia were treated with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis through an anterior approach, and were followed for a mean of 16.2 months (range, 12-30 months). Fractures according to the AO/OTA classification were six 43A, four 43B and three 43C. We analyzed functional results by bone union, postoperative complications, and the Olerud and Molander ankle scoring system.
RESULTS
All fractures were united after a mean of 15.7 weeks (range, 12 to 24 weeks) except one case. There were 2 cases of superficial wound infection, one case of fibular shortening and metal failure, and two cases of tibialis anterior tendon adhesion. The average functional score was 79 points (range, 35-95 points) and results were four excellent, six good and three fair.
CONCLUSION
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis through an anterior approach may be used for distal tibial fracture with medial soft tissue injury, and has an advantage in that the metaphyseal and distal articular fracture are fixed at the same time through a single incision However, it should be approached with caution because of the risk of complications due to the anterior approach, such as iatrogenic injury of the tibialis anterior tendon.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, Koval KJ, Zlowodzki M. Evidence-Based Orthopaedic Trauma Working Group. Treatment of distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006. 20:76–79.
Article2. Park KC, Park YS. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial metaphyseal fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:264–268.
Article3. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate stabilization of proximal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004. 17:224–229.
Article4. Oh CW. Treatment of complex distal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:485–490.
Article5. Hazarika S, Chakravarthy J, Cooper J. Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia--results in 20 patients. Injury. 2006. 37:877–887.
Article6. Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R. Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury. 2007. 38:365–370.
Article7. Helfet DL, Suk M. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis of fractures of the distal tibia. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:471–475.8. Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJ. Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2004. 35:615–620.
Article9. Krackhardt T, Dilger J, Flesch I, Höntzsch D, Eingartner C, Weise K. Fractures of the distal tibia treated with closed reduction and minimally invasive plating. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005. 125:87–94.10. Oh CW, Kyung HS, Park IH, Kim PT, Ihn JC. Distal tibia metaphyseal fractures treated by percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. 408:286–291.
Article11. Francois J, Vandeputte G, Verheyden F, Nelen G. Percutaneous plate fixation of fractures of the distal tibia. Acta Orthop Belg. 2004. 70:148–154.12. Borg T, Larsson S, Lindsjö U. Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Preliminary results in 21 patients. Injury. 2004. 35:608–614.13. Leonard M, Magill P, Khayyat G. Minimally-invasive treatment of high velocity intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. Int Orthop. 2009. 33(4):1149–1153.
Article14. Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D, Borrelli J Jr. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia. Injury. 1997. 28:Suppl 1. A42–A47.
Article15. Chang SA, Ahn HS, Byun YS, Kim JH, Bang HH, Kwon DY. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in unstable fractures of the distal tibia. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:155–159.
Article16. Tscherne H, Gotzen L. Fractures with soft tissue injuries. 1984. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.17. Bedi A, Le TT, Karunakar MA. Surgical treatment of nonarticular distal tibia fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006. 14:406–416.
Article18. Rüedi TP, Allgöwer M. The operative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the lower end of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:105–110.
Article19. Collinge CA, Sanders RW. Percutaneous plating in the lower extremity. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000. 8:211–216.
Article20. Ovadia DN, Beals RK. Fractures of the tibial plafond. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:543–551.
Article21. Lee KB. Distal tibia fracture: plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:306–303.
Article22. Giannoudis PV, Tzioupis C, Moed BR. Two-level reconstruction of comminuted posterior-wall fractures of the acetabulum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007. 89:503–509.
Article23. Collinge C, Kuper M, Larson K, Protzman R. Minimally invasive plating of high-energy metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:355–361.
Article24. Tarkin IS, Clare MP, Marcantonio A, Pape HC. An update on the management of high-energy pilon fractures. Injury. 2008. 39:142–154.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using Periarticular Plate for Distal Tibial Fractures
- Analysis of the Result Treated with Locking Compression Plate-Distal Tibia and Zimmer Periarticular Locking Plate in Distal Tibia Fracture
- Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis with Locking Compression Plate for Distal Tibia Fractures
- Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture
- Surgical Treatment of Distal Tibia Fractures