J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2014 Apr;49(2):140-146. 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.2.140.
Conformity of Proximal Humerus Internal Locking Plate System (PHILOS) and Anatomic Features of Proximal Locking Screws: Cadaveric Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jyujin2001@kosin.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2185219
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.2.140
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this cadaveric study was to evaluate the conformity of the anatomically preshaped proximal humerus internal locking plate system (PHILOS) to the humeri of the Korean and anatomical features of nine locking screws for the proximal humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
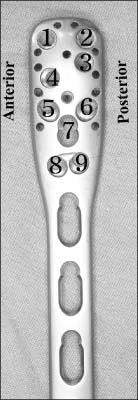
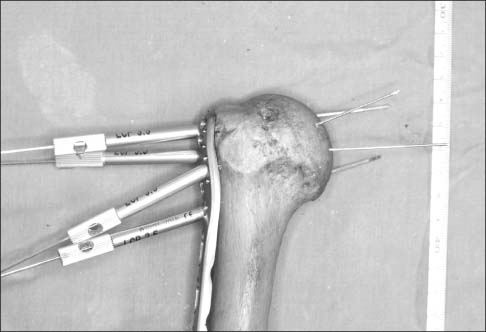
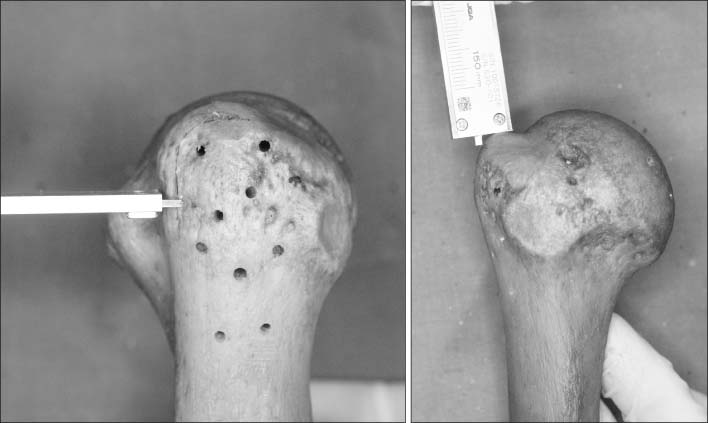
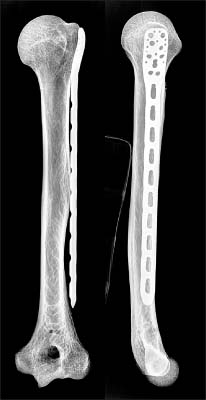
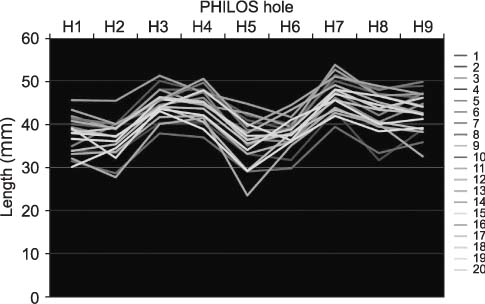
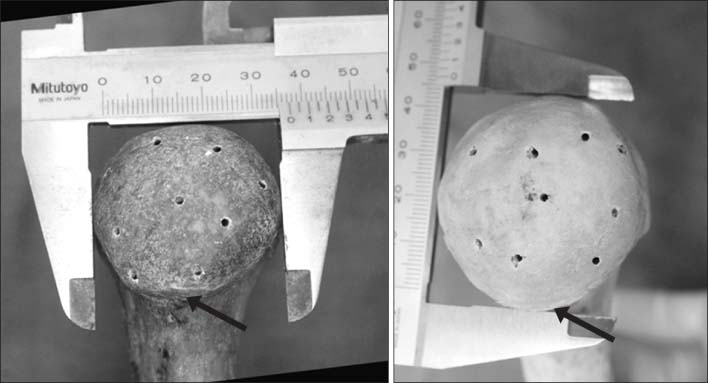
This study included 20 adult humeri (average length 30.2 mm) with no deformity or previous surgery. PHILOS was applied to the lateral surface of the proximal humerus according to the contour. Then, the distance from the outer surface of the plate to the greater tuberosity and bicipital groove was measured. After K-wires were passed through the proximal locking guide, the intra-osseous length of K-wire and the configuration of the K-wire exit were evaluated.
RESULTS
The overall conformity of PHILOS was excellent at the lateral aspect of the proximal humerus. The tip of the plate had an average distance of 3.6 mm (range, 1.4-6.6 mm; standard deviation [SD], 1.27) from the greater tuberosity and 2.5 mm (range, 0.0-4.6 mm; SD, 1.24) at the bicipital groove and the average intra-osseous length of K-wire through the locking guide was 41.1 mm (range, 23.5-53.7 mm). K-wires were evenly penetrated through the humeral head. On H8 and H9, the bottom hole of PHILOS is closely located at the most inferior area of the humeral articular surface. The bicipital groove was pierced by K-wires of H5, which was the middle hole of PHILOS in four cases (20%).
CONCLUSION
PHILOS had excellent conformity with the proximal humerus and K-wires through the locking guide were evenly penetrated through the humeral head. However, much care should be taken in piercing of the bicipital groove in H5.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hertel R. Fractures of the proximal humerus in osteoporotic bone. Osteoporos Int. 2005; 16:Suppl 2. S65–S72.
Article2. Hirschmann MT, Quarz V, Audigé L, et al. Internal fixation of unstable proximal humerus fractures with an anatomically preshaped interlocking plate: a clinical and radiologic evaluation. J Trauma. 2007; 63:1314–1323.
Article3. Agudelo J, Schürmann M, Stahel P, et al. Analysis of efficacy and failure in proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21:676–681.
Article4. Owsley KC, Gorczyca JT. Fracture displacement and screw cutout after open reduction and locked plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures [corrected]. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:233–240.5. Egol KA, Ong CC, Walsh M, Jazrawi LM, Tejwani NC, Zuckerman JD. Early complications in proximal humerus fractures (OTA Types 11) treated with locked plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22:159–164.
Article6. Solberg BD, Moon CN, Franco DP, Paiement GD. Locked plating of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures in older patients: the effect of initial fracture pattern on outcome. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23:113–119.
Article7. Anglen JO, Archdeacon MT, Cannada LK, Herscovici D Jr. Avoiding complications in the treatment of humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:1580–1589.8. Lee KW, Choi YJ, Ahn HS, et al. Internal fixation of proximal humerus fracture with polyaxial angular stable locking compression plate in patients older than 65 years. Clin Should Elbow. 2012; 15:25–31.
Article9. Charalambous CP, Siddique I, Valluripalli K, et al. Proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007; 127:205–210.
Article10. Erhardt JB, Stoffel K, Kampshoff J, Badur N, Yates P, Kuster MS. The position and number of screws influence screw perforation of the humeral head in modern locking plates: a cadaver study. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26:e188–e192.11. Südkamp N, Bayer J, Hepp P, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate. Results of a prospective, multicenter, observational study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:1320–1328.12. Spross C, Platz A, Rufibach K, Lattmann T, Forberger J, Dietrich M. The PHILOS plate for proximal humeral fractures-risk factors for complications at one year. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012; 72:783–792.
Article13. Gardner MJ, Weil Y, Barker JU, Kelly BT, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. The importance of medial support in locked plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21:185–191.
Article14. Osterhoff G, Hoch A, Wanner GA, Simmen HP, Werner CM. Calcar comminution as prognostic factor of clinical outcome after locking plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures. Injury. 2012; 43:1651–1656.
Article15. Osterhoff G, Ossendorf C, Wanner GA, Simmen HP, Werner CM. The calcar screw in angular stable plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures--a case study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011; 6:50.
Article16. Lescheid J, Zdero R, Shah S, Kuzyk PR, Schemitsch EH. The biomechanics of locked plating for repairing proximal humerus fractures with or without medial cortical support. J Trauma. 2010; 69:1235–1242.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anatomic Conformity of New Periarticular Locking Plates for Koreans: A Biomechanical Cadaveric Study
- The Treatment of Unstable Proximal Humerus Fracture Using Locking Plate
- Operative Treatment of Displaced Proximal Humerus Fractures with the Angular Stable Locking Compression Plate
- PHILOS plate fixation with polymethyl methacrylate cement augmentation of an osteoporotic proximal humerus fracture
- Internal Fixation of Proximal Humerus Fracture with Locking Compression Plate