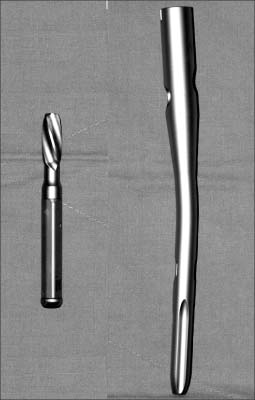
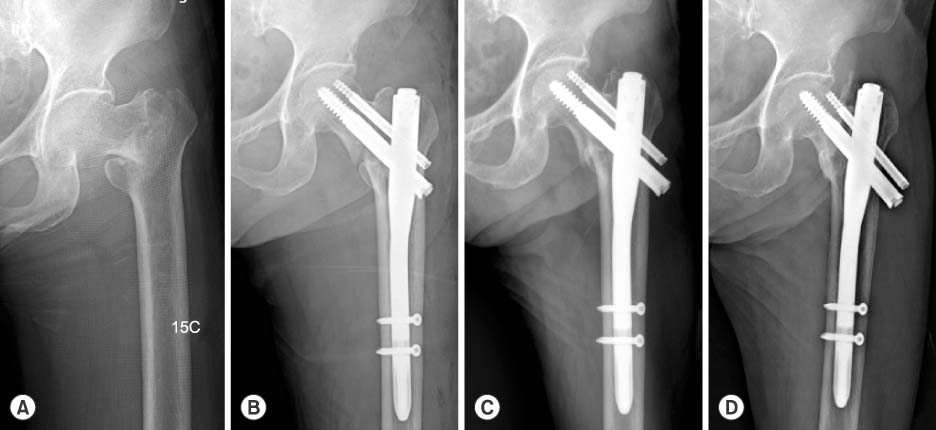
Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fracture: Comparison of Proximal Femoral Nail and Proximal Femoral Nail A
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ansan Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea University, Ansan, Korea. canal1@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2183904
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.2.103
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate the results of fracture fixation between using Proximal Femoral Nail and using Proximal Femoral Nail A and to analyze the effectiveness of proximal femoral nail A.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 32 patients who suffered from intertrochanteric fracture in our hospital, which were 19 cases of PFN and 13 cases of PFNA. Retrospectively we evaluated mean operation time, amount of bleeding, beginning of ambulation, average union period, changes of neck shaft angle and complication on set of telephone interview and OPD. We also evaluated postoperative capability of function and mobility using 'Social function score' and 'Mobility score'.
RESULTS
PFNA showed shorter mean operation time, less bleeding, shorter average union period, earlier ambulation and less change of neck shaft angle than PFN. Although they didn't show statistical difference, postoperative capability of function and mobility showed statistical and mathematical difference on each group.
CONCLUSION
PFNA showed better results of postoperative function and mobility and less complications than PFN. So treatment using PFNA is better method than that of PFN.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Treatment of the Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation: Comparison with Compression Hip Screw with Trochanteric Stabilizing Plate
Tae-Ho Kim, Jong-Oh Kim, Seung-Yup Lee, Geon-Ung Yun
J Korean Fract Soc. 2010;23(4):353-359. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.4.353.Comparison of the Compression Hip Screw (CHS) and the Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) for Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture
Jong Min Lim, Jeung Il Kim, Jong Seok Oh, Kuen Tak Suh, Jae Min Ahn, Dong Joon Kang
J Korean Fract Soc. 2010;23(4):360-366. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.4.360.Helical Blade versus Lag Screw for Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fracture
Kwang-Jun Oh, Sung-Tae Lee, Suk-Ha Lee, Jin-Ho Hwang, Min-Suk Kang
J Korean Fract Soc. 2010;23(1):6-12. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.6.Comparative Study of Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation and Zimmer Natural Nail for the Treatment of Stable Intertrochanteric Fractures
Jee-Hoon Kim, Oog-Jin Shon
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(4):305-313. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.305.Comparative Study of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with the Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation and the Third Generation of Gamma Nail
Jae-Cheon Sim, Tae-Ho Kim, Ki-Do Hong, Sung-Sik Ha, Jong-Seong Lee
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(1):37-43. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.37.Treatment of the Proximal Femoral Fracture Using the New Design Cephalomedullary Nail: Prospective Outcomes Study
Young Ho Roh, Joseph Rho, Kwang Woo Nam
J Korean Fract Soc. 2019;32(1):35-42. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.35.
Reference
-
1. Ahn SJ, Park JH. Proximal femoral nail (PFN) for the treatment of the femoral trochanteric fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004; 17:7–12.
Article2. Al-yassari G, Langstaff RJ, Jones JW, Al-Lami M. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN) for the treatment of unstable trochanteric femoral fracture. Injury. 2002; 33:395–399.
Article3. Bess RJ, Jolly SA. Comparison of compression hip screw and gamma nail for treatment of peritrochanteric fractures. J South Orthop Assoc. 1997; 6:173–179.4. Boriani S, Bettelli G. The Gamma nail. A preliminary note. Chir Organi Mov. 1990; 75:67–70.5. Bridle SH, Patel AD, Bircher M, Calvert PT. Fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. A randomised prospective comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:330–334.
Article6. Domingo LJ, Cecilia D, Herrera A, Resines C. Trochanteric fractures treated with a proximal femoral nail. Int Orthop. 2001; 25:298–301.
Article7. Halder SC. The gamma nail for peritrochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992; 74:340–344.
Article8. Herrera A, Domingo LJ, Calvo A, Martinez A, Cuenca J. A comparative study of trochanteric fractures treated with the Gamma nail or the proximal femoral nail. Int Orthop. 2002; 26:365–369.
Article9. Ito K, Hungerbühler R, Wahl D, Grass R. Improved intramedullary nail interlocking in osteoporotic bone. J Orthop Trauma. 2001; 15:192–196.
Article10. Jensen JS. Determining factors for the mortality following hip fractures. Injury. 1984; 15:411–414.
Article11. Kim BS, Lew SG, Ko SH, Cho SD, Yang JH, Park MS. Treatment of femoral intertrochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004; 17:1–6.
Article12. Lenich A, Mayr E, Ruter A, Mockl C, Füchtmeier B. First results with the trochanter fixation nail (TFN): a report on 120 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006; 126:706–712.
Article13. Lindsey RW, Teal P, Probe RA, Rhoads D, Davenport S, Schauder K. Early experience with the gamma interlocking nail for peritrochanteric fractures of the proximal femur. J Trauma. 1991; 31:1649–1658.
Article14. Moon YW, Seo HS, Eun SS, Lim SJ, Park YS. Comparison of the Gamma nail and the proximal femoral nail in the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007; 19:97–104.
Article15. Moon YW, Suh DH, Kang ST, Kwon DJ, Ji YN, Lee KB. The proximal femoral nail for intertrochanteric fracture of the femur. J Korean Soc Fract. 2003; 16:29–36.
Article16. Parker MJ, Palmer CR. A new mobility score for predicting mortality after hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993; 75:797–798.
Article17. Schipper IB, Steyerberg EW, Castelein RM, et al. Treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Randomised comparison of the gamma nail and the proximal femoral nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:86–94.18. Simmermacher RK, Bosch AM, Van der Werken C. The AO/ASIF-proximal femoral nail (PFN): a new device for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 1999; 30:327–332.
Article19. Singh M, Nagrath AR, Maini PS. Changes in trabecular pattern of the upper end of the femur as an index of osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970; 52:457–467.
Article20. Strauss E, Frank J, Lee J, Kummer FJ, Tejwani N. Helical blade versus sliding hip screw for treatment of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures: a biomechanical evaluation. Injury. 2006; 37:984–989.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail
- Excessive Sliding of the Helical Blade and the Femoral Neck Fracture after Insertion of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation for Type A2 Intertrochanteric Fractures - A Case Report -
- Comparative Study of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with the Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation and the Third Generation of Gamma Nail
- Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail
- Fixation Failure of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation in Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture