J Korean Fract Soc.
2013 Oct;26(4):327-332. 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.327.
Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gachon University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. bklee@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2183835
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.327
Abstract
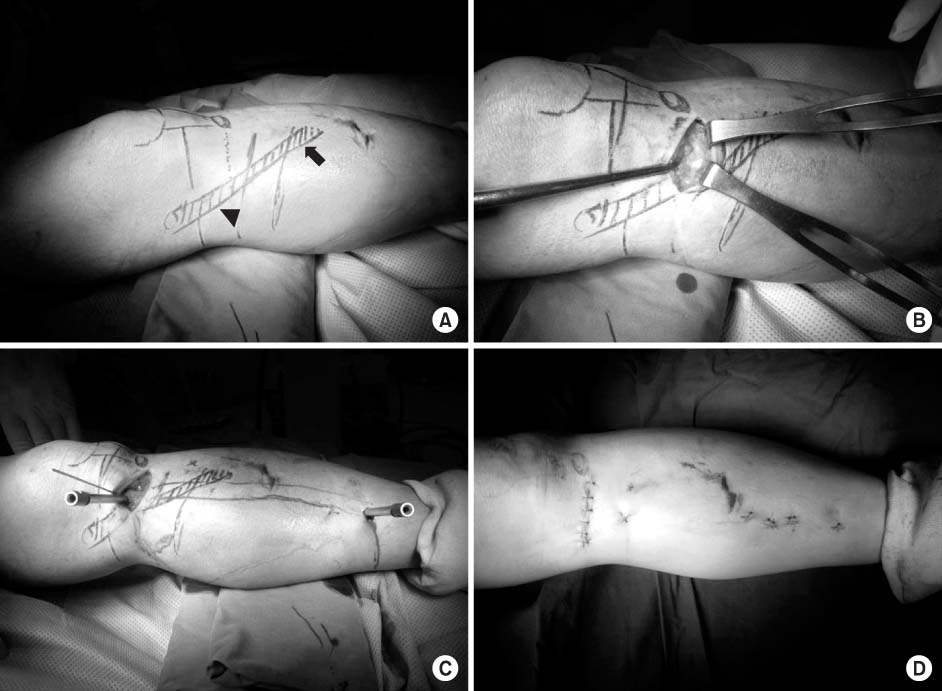
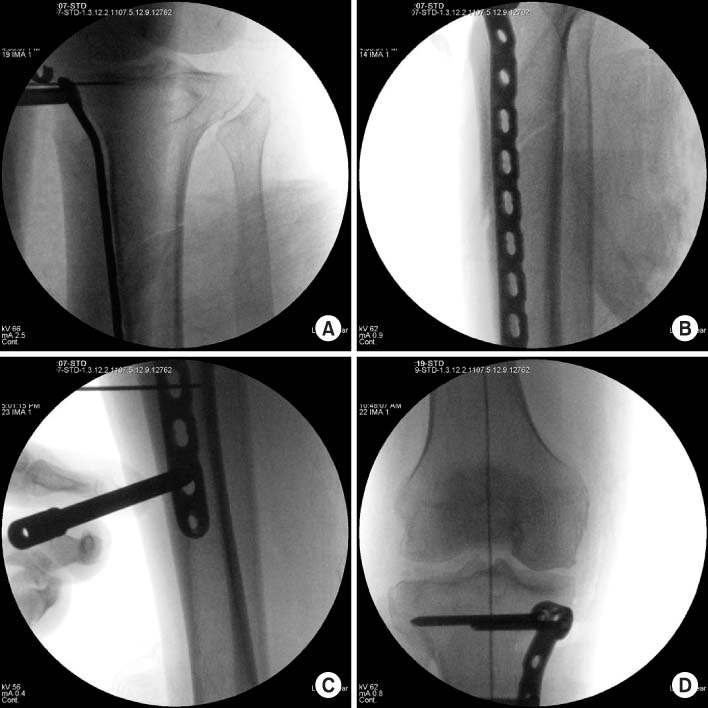
- Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) is beneficial for proximal tibial fractures since these injuries are mostly caused by high energy traumas. The advantages of MIPO are minimization of soft tissue dissection and preservation of periosteal vascularization. Lateral plating has mostly developed as MIPO for proximal tibial fractures. We introduce minimal invasive percutaneous plate stabilization using a medial locking plate as alternative treatment for proximal tibial fractures.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Byun YS, Park KC, Bong HJ, Lee CH. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for proximal tibial shaft fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2011; 24:23–27.
Article2. Cole JD. Intramedullary fixation of proximal tibia fractures. Tech Orthop. 1998; 13:27–37.
Article3. Dendrinos GK, Kontos S, Katsenis D, Dalas A. Treatment of high-energy tibial plateau fractures by the Ilizarov circular fixator. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:710–717.
Article4. Ha SH, Kim DH, Lee JY. Treatment of Proximal Tibia Fractures Using LCP by MIPO Technique. J Korean Fract Soc. 2010; 23:34–41.
Article5. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (315):64–74.6. Mullaji AB, Padmanabhan V, Jindal G. Total knee arthroplasty for profound varus deformity: technique and radiological results in 173 knees with varus of more than 20 degrees. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:550–561.7. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate stabilization of proximal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004; 17:224–229.
Article8. Park KC. Proximal tibia fracture: plating. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009; 22:206–213.
Article9. Spagnolo R, Pace F. Management of the Schatzker VI fractures with lateral locked screw plating. Musculoskelet Surg. 2012; 96:75–80.
Article10. Stannard JP, Wilson TC, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Fracture stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the proximal tibial LISS: early experience in Birmingham, Alabama (USA). Injury. 2003; 34:Suppl 1. A36–A42.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization of Proximal Tibial Fractures
- Comparison of Results of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis according to Types of Locking Plate in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Humeral Proximal or Distal Shaft Fractures Using a 3.5/5.0 Metaphyseal Locking Plate
- Anterolateral Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures Using an Anterolateral Locking Plate